J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2014 Dec;21(4):174-178. 10.4184/jkss.2014.21.4.174.
Failure of Long Spinal Construct and Pseudarthrosis in a Patient with Parkinson Disease for the Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disorder: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kangnam Sacred heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea. chungkjmd@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2097868
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2014.21.4.174
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Case report.
OBJECTIVES
We report a case of treated failure spinal construct and pseudarthrosis in a patient with Parkinson's disease. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: There have been no reports about revision surgery due to failure and pseuarthrosis of degenerative lumbar spine disease in patients with Parkinson's disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
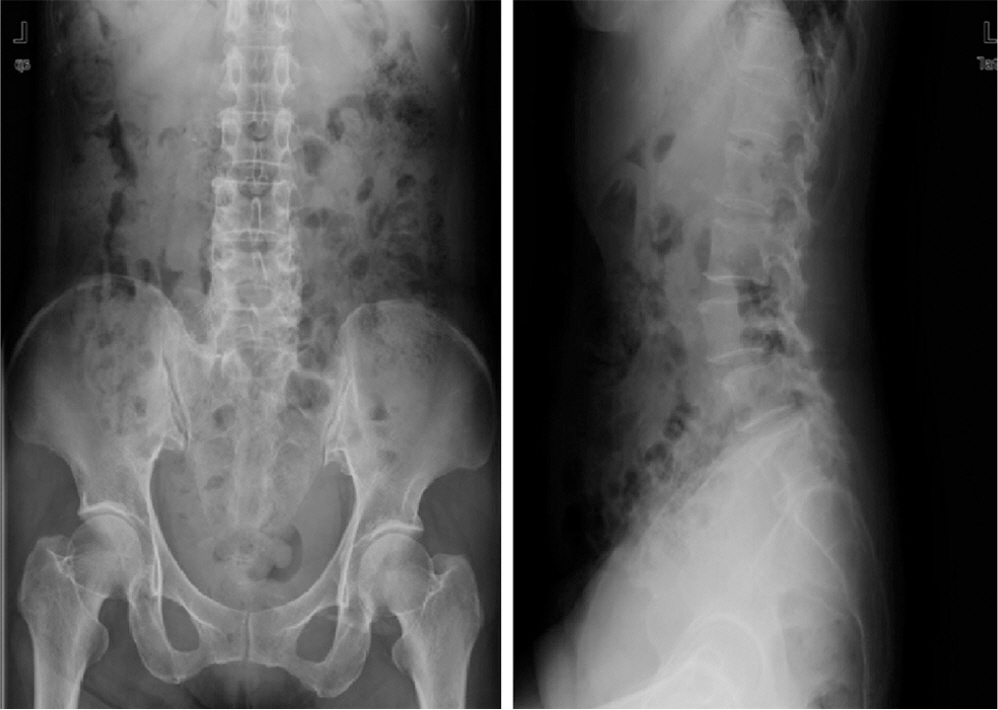
A 55-year-old female who had been diagnosed with Parkinson's disease 4 years ago presented with back pain and radiating pain on both legs. Radiographic assessment showed spinal stenosis from L2 to L5 combined with degenerative spondylolisthesis at L3-4. Posterior decompression, instrumentation, and posterolateral fusion were performed and her symptoms improved.
RESULTS
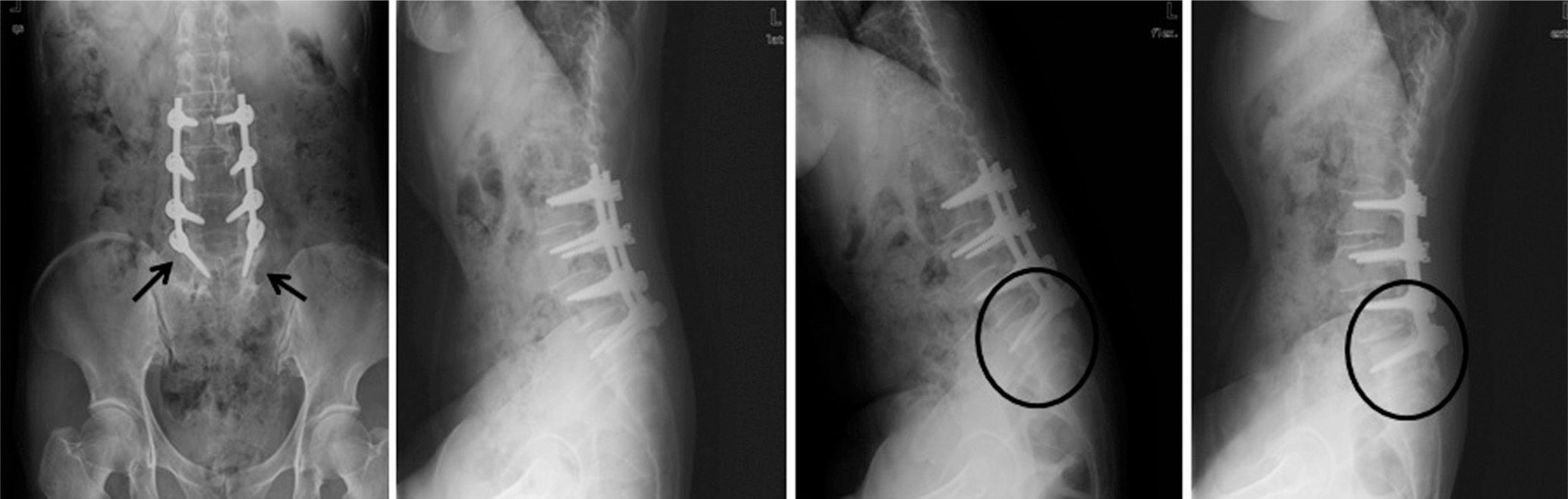
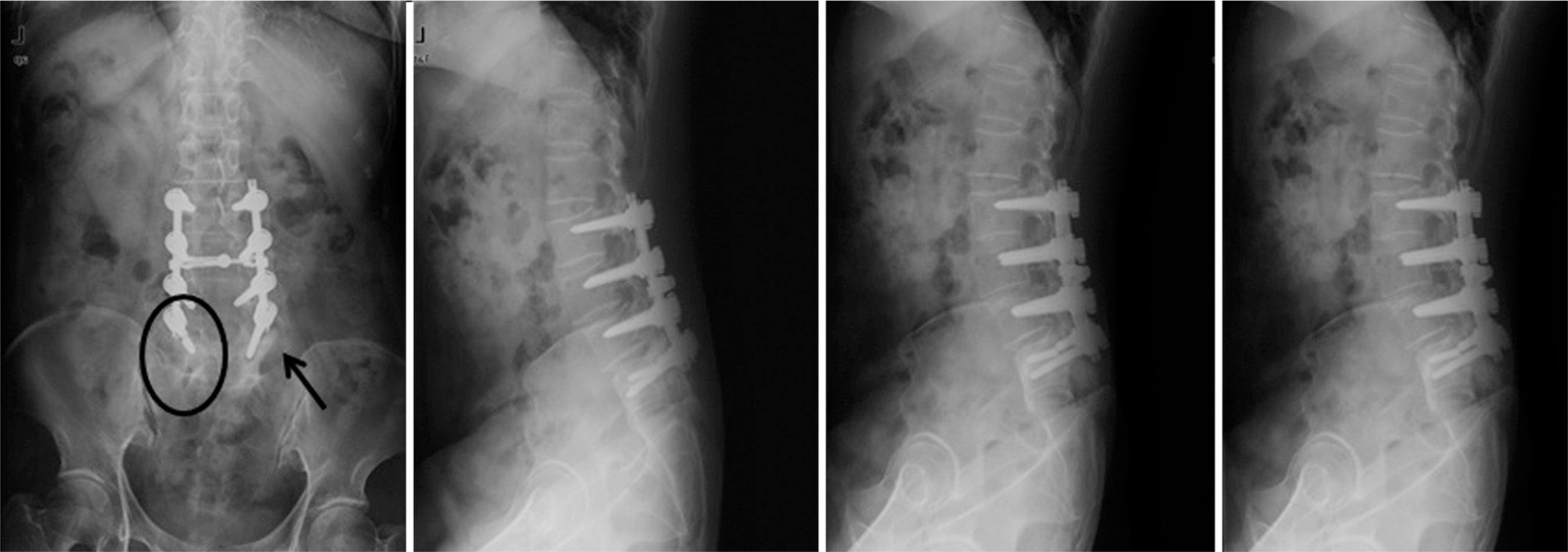
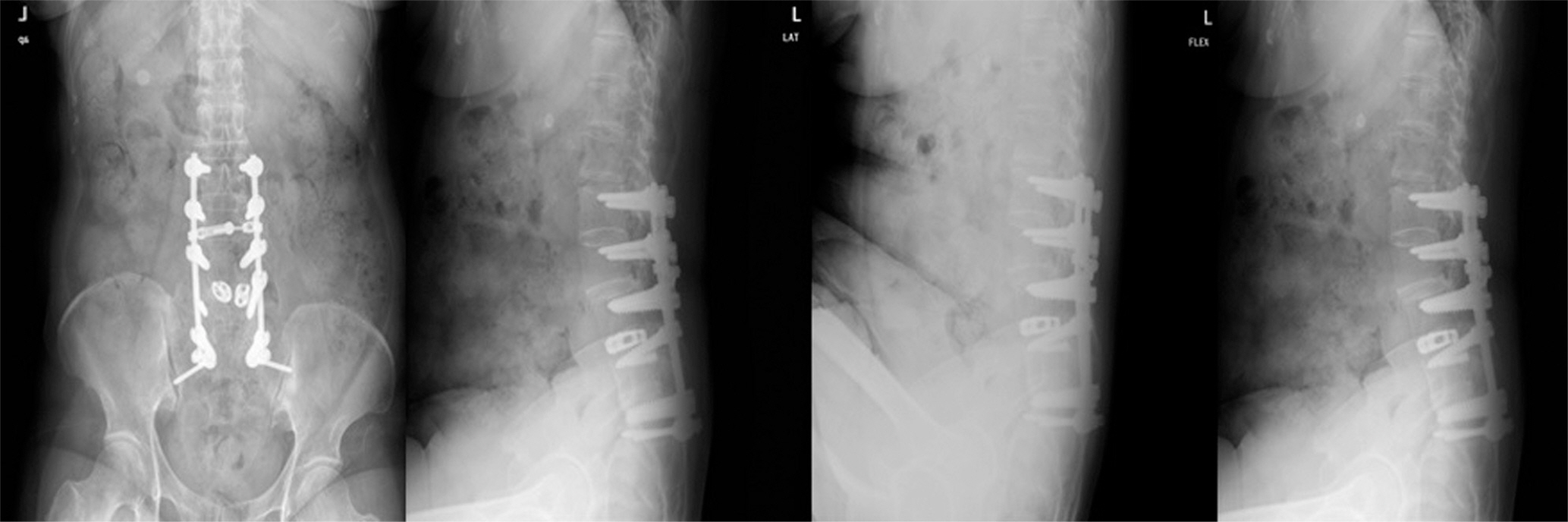
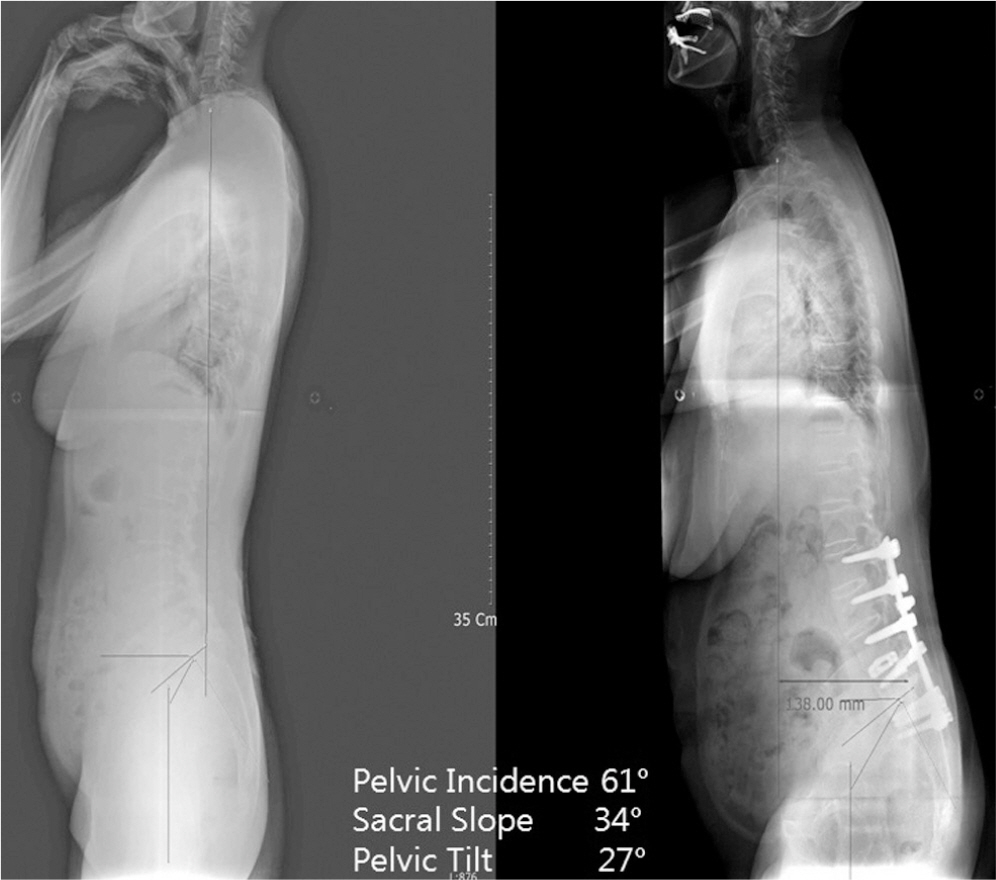
Two years after the operation, she complained of severe back pain without injury. A simple X-ray showed the pull out of bilateral L5 screws, and revision surgery was performed. Three years after the revision, she underwent re-reoperation due to metal failure. The breakage of a unilateral pedicle screw at L5 was found, and her fusion level was extended to S1 with a posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cages and alar screws. Finally, she has not shown any further failure but, a sagittal imbalance and aggravation of pelvic incidence due to Parkinson's disease have been detected.
CONCLUSIONS
Spine surgeons always should consider metal failure, pseudarthrosis, and aggravated spinal imbalance caused by natural history in patients with Parkinson's disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adams RD, Victor M Principles of Neruology 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1981. 807.2. Seo WK, Koh SB, Kim BJ, Yu SW, Park MH, Park KW, Lee DH. Prevalence of Parkinson's disease in Korea. J Clin Neurosci. 2007; 14:1155–7.
Article3. Yoon HK, Kim BK, Shin DE, Song SJ, Park HK, Chang JH. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty of displaced femoral neck fracu-tres ion Parkinsonism patients. J of Korean Fracture Society. 2005; 18:126–30.4. Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonim: onset, progression, and mortality. Neurology. 1967; 17:427–42.5. Babat LB, McLain RF, Bingaman W, Kalfas I, Young P, Rufo-Smith C. Spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson’s disease: contruct failure and progressive deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:2006–12.6. Laroche M, Delisle M, Aziza R, Laqarrique J, Mazieres B. Is camptrocormia a primary muscular disease? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:1011–6.7. Gau YL, Lonstein JE, Winter RB, Koop S, Denis F. Luque-Galveston procedure for correction and stabilization of neuromuscular scoliosis and pelvic obliquity: a review of 68 patients. J Spinal Disord. 1991; 4:399–410.8. Bell DF, Moseley CF, Koresca J. Unit rod segmental spinal instrumentation in the management of patients with progressive mneuromuscular spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14:1301–7.9. Banta JV, Drummond DS, Ferguson RL. The treatment of neuromuscular scoliosis. Instruct Course Lect. 1999; 64:551–62.10. Swank SM, Cohen DS, Brown JC. Spine fusion in cerebral palsy with L-rod segmental spinal instrumentation. A comparison of single and two-stage combined approach with Zilke instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14:750–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Clinical Analysis of Long Segment Fusion with Pedicle Screw in Degenerative Lumbar Spine
- A Clinical Analysis of Surgical Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis
- Pathophysiology of degenerative spinal disease causing lumbar and cervical spinal pain
- A Case of Coexisting Cervical and Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Degenerative Instability of the Lumbar Spine