Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Apr;48(2):687-697. 10.4143/crt.2014.320.
The Effect of Chemoradiotherapy with SRC Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, PP2 and Temozolomide on Malignant Glioma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University, Graduate School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. inah228@snu.ac.kr
- 2Medical Science Research Institute, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2454347
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.320
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the effect of chemoradiotherapy with PP2 and temozolomide (TMZ) on malignant glioma cells using clonogenic assays and in vivo brain tumor model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
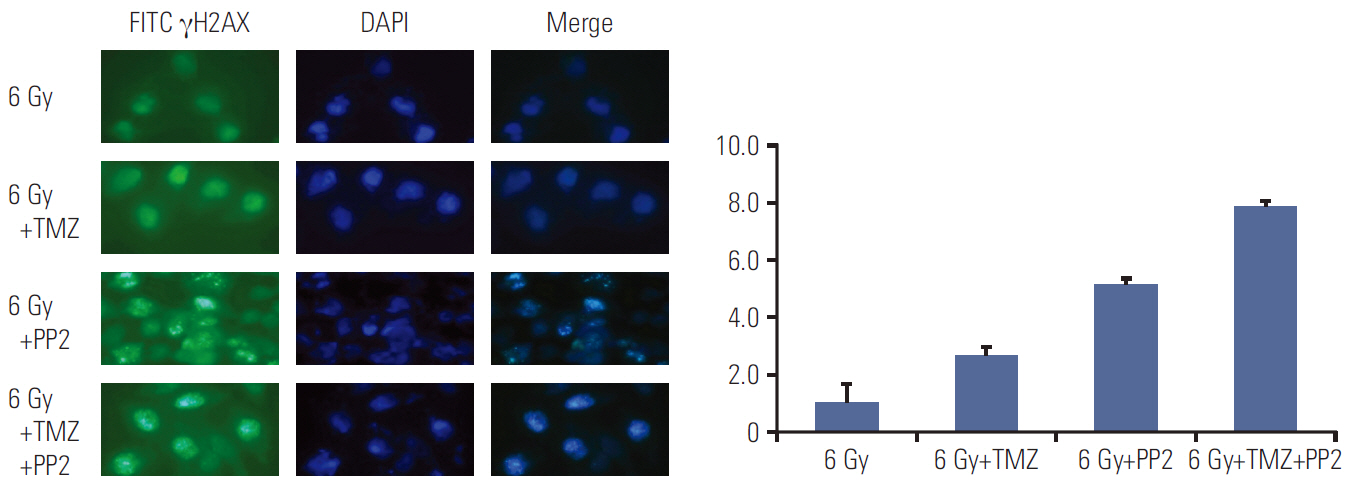
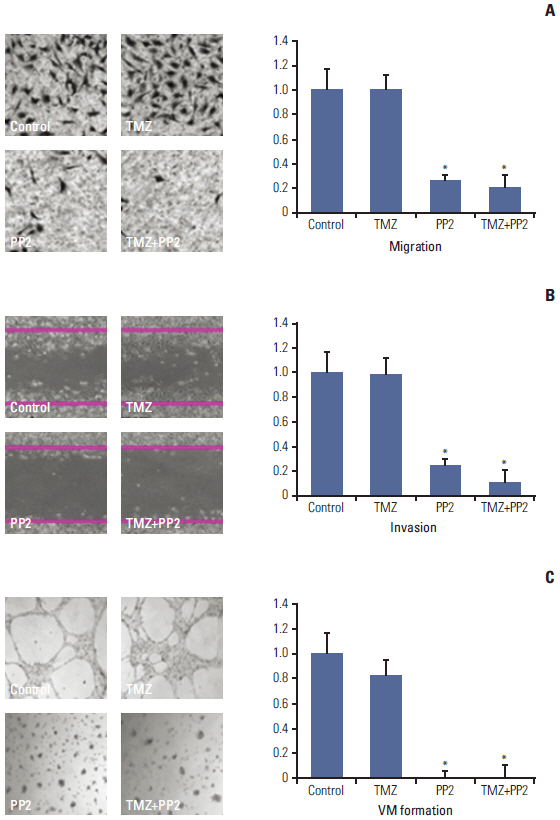
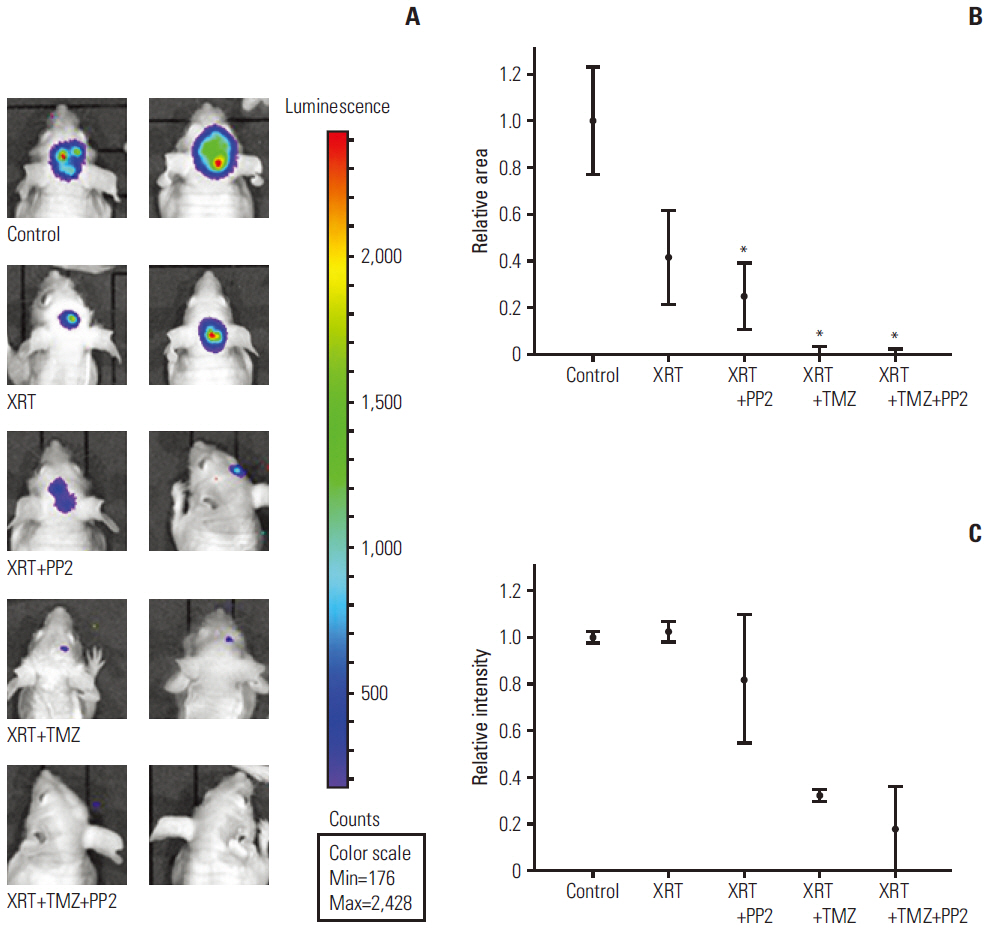
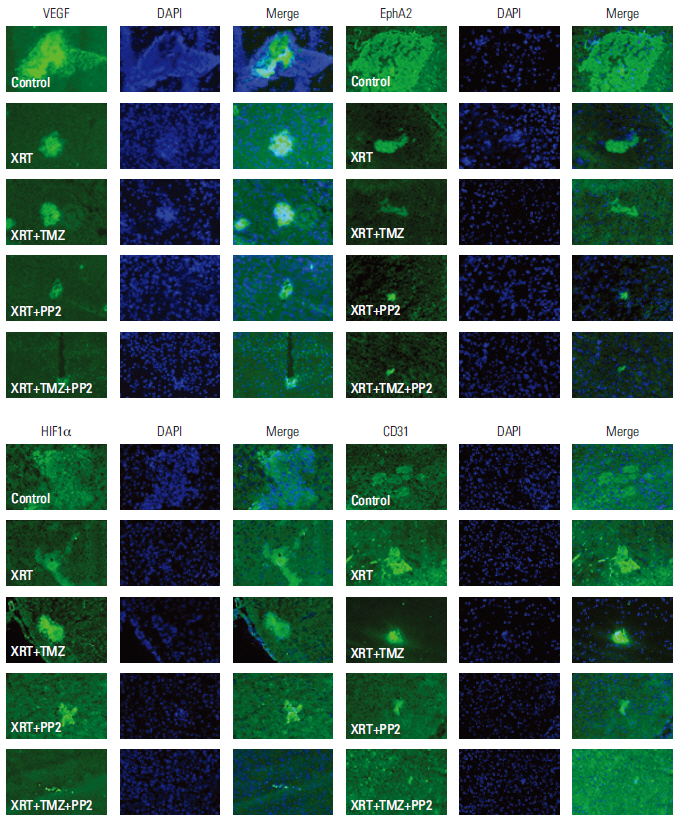
The effect of PP2 on radiosensitivity of U251 and T98G cells was investigated using clonogenic assays. The expression of E-cadherin, matrix metalloproteinases 2 (MMP2), Ephrin type-A receptor 2 (EphA2), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was measured by Western blotting and an accumulation of γH2AX foci 6 hours after radiotherapy was measured after PP2 treatment. The effect of PP2 on migration, invasion, and vasculogenic mimicry formation (VMF) of U251 cells was evaluated. In an orthotopical brain tumor model with U251 cells, PP2 was injected intraperitoneally with or without oral TMZ before, during and after whole brain radiotherapy. Bioluminescence images were taken to visualize in vivo tumors and immunohistochemical staining of VEGF, CD31, EphA2, and hypoxia-inducible factor 1a was performed.
RESULTS
PP2 increased radiosensitivity of U251 and T98G cells without decreasing survival of normal human astrocytes. Chemoradiotherapy with PP2 and TMZ resulted in increased accumulation of γH2AX foci. PP2 induced overexpression of E-cadherin and suppression of MMP2, VEGF, and EphA2. PP2 also compromised invasion, migration, and VMF of U251 cells. In brain tumors, chemoradiotherapy with PP2 and TMZ decreased tumor volume best, but not statistically significantly compared with chemoradiotherapy with TMZ. The expression of VEGF and CD31 was suppressed in PP2-treated tumors.
CONCLUSION
PP2 enhances radiosensitivity of malignant glioma cells and suppresses invasion and migration of U251 cells. Chemoradiotherapy with PP2 and TMZ resulted in non-significant tumor volume decrease.
MeSH Terms
-
Astrocytes
Blotting, Western
Brain
Brain Neoplasms
Cadherins
Chemoradiotherapy*
Glioblastoma
Glioma*
Humans
In Vitro Techniques*
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases*
Radiation Tolerance
Radiotherapy
Tumor Burden
Tyrosine*
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Cadherins
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Tyrosine
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:987–96.
Article2. Masui K, Cloughesy TF, Mischel PS. Review: molecular pathology in adult high-grade gliomas: from molecular diagnostics to target therapies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2012; 38:271–91.3. Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Weller M, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:997–1003.4. Angers-Loustau A, Hering R, Werbowetski TE, Kaplan DR, Del Maestro RF. SRC regulates actin dynamics and invasion of malignant glial cells in three dimensions. Mol Cancer Res. 2004; 2:595–605.5. Stehelin D, Fujita DJ, Padgett T, Varmus HE, Bishop JM. Detection and enumeration of transformation-defective strains of avian sarcoma virus with molecular hybridization. Virology. 1977; 76:675–84.
Article6. Stettner MR, Wang W, Nabors LB, Bharara S, Flynn DC, Grammer JR, et al. Lyn kinase activity is the predominant cellular SRC kinase activity in glioblastoma tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:5535–43.
Article7. Du J, Bernasconi P, Clauser KR, Mani DR, Finn SP, Beroukhim R, et al. Bead-based profiling of tyrosine kinase phosphorylation identifies SRC as a potential target for glioblastoma therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2009; 27:77–83.
Article8. Ding Q, Stewart J Jr, Olman MA, Klobe MR, Gladson CL. The pattern of enhancement of Src kinase activity on platelet-derived growth factor stimulation of glioblastoma cells is affected by the integrin engaged. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:39882–91.
Article9. Jallal H, Valentino ML, Chen G, Boschelli F, Ali S, Rabbani SA. A Src/Abl kinase inhibitor, SKI-606, blocks breast cancer invasion, growth, and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:1580–8.10. Park CM, Park MJ, Kwak HJ, Lee HC, Kim MS, Lee SH, et al. Ionizing radiation enhances matrix metalloproteinase-2 secretion and invasion of glioma cells through Src/epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated p38/Akt and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:8511–9.
Article11. Rothschild SI, Gautschi O, Haura EB, Johnson FM. Src inhibitors in lung cancer: current status and future directions. Clin Lung Cancer. 2010; 11:238–42.
Article12. Cuneo KC, Geng L, Tan J, Brousal J, Shinohara ET, Osusky K, et al. SRC family kinase inhibitor SU6656 enhances antiangiogenic effect of irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 64:1197–203.
Article13. Kim IA, No M, Lee JM, Shin JH, Oh JS, Choi EJ, et al. Epigenetic modulation of radiation response in human cancer cells with activated EGFR or HER-2 signaling: potential role of histone deacetylase 6. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 92:125–32.
Article14. Lee KM, Choi EJ, Kim IA. microRNA-7 increases radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with activated EGFR-associated signaling. Radiother Oncol. 2011; 101:171–6.
Article15. Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J, Zeller R. Cryosectioning tissues. CSH Protoc. 2008; 2008:pdb.prot4991.
Article16. Chahal M, Abdulkarim B, Xu Y, Guiot MC, Easaw JC, Stifani N, et al. O6-Methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase is a novel negative effector of invasion in glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012; 11:2440–50.
Article17. Hanson JA, Hsu FP, Jacob AT, Bota DA, Alexandru D. Antivascular endothelial growth factor antibody for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Perm J. 2013; 17:68–74.
Article18. Wong ET, Gautam S, Malchow C, Lun M, Pan E, Brem S. Bevacizumab for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a meta-analysis. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2011; 9:403–7.
Article19. Huveldt D, Lewis-Tuffin LJ, Carlson BL, Schroeder MA, Rodriguez F, Giannini C, et al. Targeting Src family kinases inhibits bevacizumab-induced glioma cell invasion. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e56505.
Article20. Le DM, Besson A, Fogg DK, Choi KS, Waisman DM, Goodyer CG, et al. Exploitation of astrocytes by glioma cells to facilitate invasiveness: a mechanism involving matrix metalloproteinase- 2 and the urokinase-type plasminogen activator-plasmin cascade. J Neurosci. 2003; 23:4034–43.21. Wilkinson DG. Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001; 2:155–64.
Article22. Wykosky J, Gibo DM, Stanton C, Debinski W. EphA2 as a novel molecular marker and target in glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Cancer Res. 2005; 3:541–51.
Article23. Zhou N, Zhao WD, Liu DX, Liang Y, Fang WG, Li B, et al. Inactivation of EphA2 promotes tight junction formation and impairs angiogenesis in brain endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 2011; 82:113–21.
Article24. Zhuang G, Brantley-Sieders DM, Vaught D, Yu J, Xie L, Wells S, et al. Elevation of receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 mediates resistance to trastuzumab therapy. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:299–308.
Article25. Holen HL, Shadidi M, Narvhus K, Kjosnes O, Tierens A, Aasheim HC. Signaling through ephrin-A ligand leads to activation of Src-family kinases, Akt phosphorylation, and inhibition of antigen receptor-induced apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 84:1183–91.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Involvement of Src Family Tyrosine Kinase in Apoptosis of Human Neutrophils Induced by Protozoan Parasite Entamoeba histolytica
- Fyn Tyrosine Kinase-mediated Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Roundabout (Robo), the Slit Receptor
- The Difference in Biological Properties between Parental and v-Ha-ras Transformed NIH3T3 Cells
- Mutant IDH1 Enhances Temozolomide Sensitivity via Regulation of the ATM/CHK2 Pathway in Glioma
- Src Family Kinase Inhibitor PP2 Has Different Effects on All-Trans-Retinoic Acid or Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Differentiation of an Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Line