J Adv Prosthodont.
2019 Jun;11(3):155-161. 10.4047/jap.2019.11.3.155.
A simple and effective method for addition silicone impression disinfection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Faculty of Dental Medicine, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal. aportela@fmd.up.pt
- 2National Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal.
- 3Institute of Research and Innovation in Health, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal.
- KMID: 2450991
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2019.11.3.155
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although dental impression disinfection is determinant to reduce the cross-infection risk, some studies have shown that, in real practice, the disinfection procedures vary considerably. Thus, the aim of this study was to evaluate the antimicrobial effectiveness and the impact on the dimensional stability of addition silicone' impressions of water wash and the most clinically used disinfection solutions: 3% hydrogen peroxide, commercial disinfectant MD520 (Durr) and 1% and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
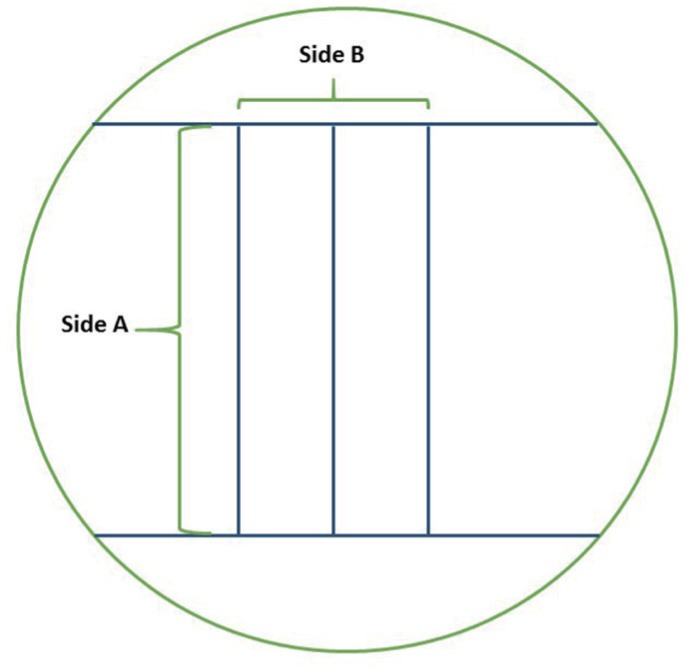
For this investigation, dental impressions were taken on 16 volunteer dental students. The antimicrobial effectiveness of each procedure was evaluated by pour plate method. The dimensional stability was evaluated using a standardized stainless-steel model, according to ANSI/ADA nº19 specification.
RESULTS
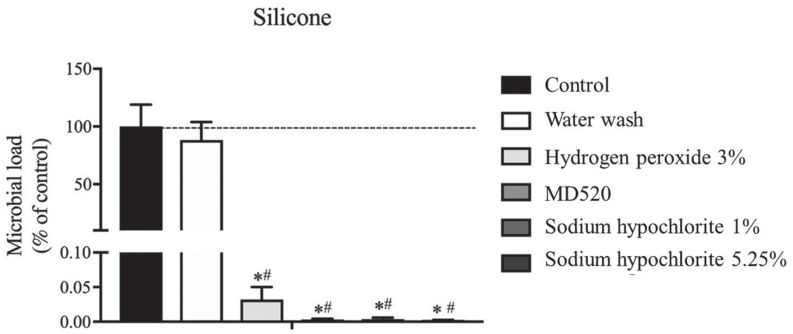
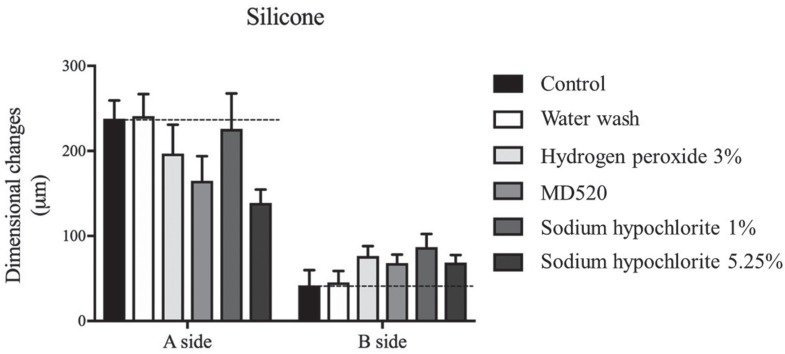
The study results showed that water wash does not alter the dimensional stability of addition silicone impressions but doesn't reduce the microbial load of the material (P>.05). On the other hand, addition silicone disinfection by immersion with 3% hydrogen peroxide, MD520 (Durr), or sodium hypochlorite at 1% and 5.25% does not alter the dimensional stability significantly but reduces > 99.9% of the microbial load of the impressions (P<.001).
CONCLUSION
Addition silicone impressions should always be disinfected after water wash in order to reduce effectively the cross-infection risk. All disinfectants tested showed high antimicrobial efficiency without significant changes in three-dimensional shape of impressions. Hydrogen peroxide and sodium hypochlorite are of particular importance because are easily accessible in dental setting. The less explored hydrogen peroxide could be a valuable alternative for silicone impressions disinfection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rentzia A, Coleman DC, O'Donnell MJ, Dowling AH, O'Sullivan M. Disinfection procedures: their efficacy and effect on dimensional accuracy and surface quality of an irreversible hydrocolloid impression material. J Dent. 2011; 39:133–140. PMID: 21093528.
Article2. Choi YR, Kim KN, Kim KM. The disinfection of impression materials by using microwave irradiation and hydrogen peroxide. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 112:981–987. PMID: 24819529.
Article3. Amin WM, Al-Ali MH, Al Tarawneh SK, Taha ST, Saleh MW, Ereifij N. The effects of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy and surface quality of impression materials and gypsum casts. J Clin Med Res. 2009; 1:81–89. PMID: 22505972.
Article4. Flanagan DA, Palenik CJ, Setcos JC, Miller CH. Antimicrobial activities of dental impression materials. Dent Mater. 1998; 14:399–404. PMID: 10483401.5. Badrian H, Ghasemi E, Khalighinejad N, Hosseini N. The effect of three different disinfection materials on alginate impression by spray method. ISRN Dent. 2012; 2012:695151. PMID: 22900196.
Article6. Chidambaranathan AS, Balasubramanium M. Comprehensive review and comparison of the disinfection techniques currently available in the literature. J Prosthodont. 2019; 28:e849–e856. PMID: 28422353.
Article7. Ganavadiya R, Chandra Shekar BR, Saxena V, Tomar P, Gupta R, Khandelwal G. Disinfecting efficacy of three chemical disinfectants on contaminated diagnostic instruments: A randomized trial. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2014; 5:98–104. PMID: 25316989.
Article8. Aeran H, Sharma S, Kumar V, Gupta N. Use of clinical UV chamber to disinfect dental impressions: A comparative study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015; 9:ZC67–ZC70.
Article9. Correia-Sousa J, Tabaio AM, Silva A, Pereira T, Sampaio-Maia B, Vasconcelos M. The effect of water and sodium hypochlorite disinfection on alginate impressions. Rev Port Estomatol Med Dent Cir Maxilofac. 2013; 54:8–12.
Article10. Australian Dental Association (ADA)'s Guidelines for Infection Control. Third Edition. Australian Dental Association;2015.11. Guidelines for Infection Control in Dental Health-Care Settings. MMWR 2003;52(No RR-17). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2003.12. Almortadi N, Chadwick RG. Disinfection of dental impressions - compliance to accepted standards. Br Dent J. 2010; 209:607–611. PMID: 21169966.
Article13. Tullner JB, Commette JA, Moon PC. Linear dimensional changes in dental impressions after immersion in disinfectant solutions. J Prosthet Dent. 1988; 60:725–728. PMID: 3060605.
Article14. Marinheiro Marques MC, Rebelo Amorim SC, Soares Framegas de Araújo FM, Figueiral MH, Maia Correia AR. Behaviors of dentists and dental technicians in Viseu regarding dental impressions disinfection. Rev Port Estomatol Med Dent Cir Maxilofac. 2014; 55:232–237.15. McDonnell G, Russell AD. Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action, and resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999; 12:147–179. PMID: 9880479.
Article16. Giammanco GM, Melilli D, Rallo A, Pecorella S, Mammina C, Pizzo G. Resistance to disinfection of a polymicrobial association contaminating the surface of elastomeric dental impressions. New Microbiol. 2009; 32:167–172. PMID: 19579694.17. Melilli D, Rallo A, Cassaro A, Pizzo G. The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials. J Oral Sci. 2008; 50:441–446. PMID: 19106472.
Article18. Pal PK, Kamble SS, Chaurasia RR, Chaurasia VR, Tiwari S, Bansal D. Evaluation of different disinfactants on dimensional accuracy and surface quality of type IV gypsum casts retrieved from elastomeric impression materials. J Int Oral Health. 2014; 6:77–81.19. Suarez F, Monje A, Galindo-Moreno P, Wang HL. Implant surface detoxification: a comprehensive review. Implant Dent. 2013; 22:465–473. PMID: 24013398.20. Presterl E, Suchomel M, Eder M, Reichmann S, Lassnigg A, Graninger W, Rotter M. Effects of alcohols, povidone-iodine and hydrogen peroxide on biofilms of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:417–420. PMID: 17586808.
Article21. Faria AC, Rodrigues RC, Macedo AP, Mattos Mda G, Ribeiro RF. Accuracy of stone casts obtained by different impression materials. Braz Oral Res. 2008; 22:293–298. PMID: 19148382.
Article22. Pande NA, Parkhedkar RD. An evaluation of dimensional accuracy of one-step and two-step impression technique using addition silicone impression material: an in vitro study. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2013; 13:254–259. PMID: 24431743.
Article23. Goel K, Gupta R, Solanki J, Nayak M. A comparative study between microwave irradiation and sodium hypochlorite chemical disinfection: a prosthodontic view. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:ZC42–ZC46.24. Ismail HA, Mahross HZ, Shikho S. Evaluation of dimensional accuracy for different complete edentulous impressions immersed in different disinfectant solutions. Eur J Dent. 2017; 11:242–249. PMID: 28729801.
Article25. ISO 4823. Dentistry - Elastomeric impression materials. Geneva; Switzerland: International Standards Organization (ISO);2015. Available at: https://www.iso.org/standard/60586.html.26. American National Standards Institute/American Dental Association. Specification No. 19: Dental elastometric impression materials. American Dental Association;2004. p. 5.27. Demajo JK, Cassar V, Farrugia C, Millan-Sango D, Sammut C, Valdramidis V, Camilleri J. Effectiveness of disinfectants on antimicrobial and physical properties of dental impression materials. Int J Prosthodont. 2016; 29:63–67. PMID: 26757331.
Article28. Samra RK, Bhide SV. Comparative evaluation of dimensional stability of impression materials from developing countries and developed countries after disinfection with different immersion disinfectant systems and ultraviolet chamber. Saudi Dent J. 2018; 30:125–141. PMID: 29628736.
Article29. Gounder R, Vikas BV. Comparison of disinfectants by immersion and spray atomization techniques on the linear dimensional stability of different interocclusal recording materials: An in vitro study. Eur J Dent. 2016; 10:7–15. PMID: 27011733.
Article30. Kronström MH, Johnson GH, Hompesch RW. Accuracy of a new ring-opening metathesis elastomeric dental impression material with spray and immersion disinfection. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103:23–30. PMID: 20105678.
Article31. Taylor RL, Wright PS, Maryan C. Disinfection procedures: their effect on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of irreversible hydrocolloid impression materials and gypsum casts. Dent Mater. 2002; 18:103–110. PMID: 11755588.
Article32. Rowe AH, Forrest JO. Dental impressions. The probability of contamination and a method of disinfection. Br Dent J. 1978; 145:184–186. PMID: 359005.
Article33. Dasgupta D, Sen SK, Ghosh S, Bhattacharyya J, Goel P. Effectiveness of mouthrinses and oral prophylaxis on reduction of microorganisms count in irreversible hydrocolloid impression: an in vivo study. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2012; 13:578–586. PMID: 24431795.
Article34. Bustos J, Herrera R, González U, Martínez A, Catalán A. Effect of inmersion desinfection with 0.5% sodium hypochlorite and 2% glutaraldehyde on alginate and silicone:Microbiology and SEM study. Int J Odontostomat. 2010; 4:169–177.35. Jeyapalan V, Krishnan CS, Ramasubramanian H, Sampathkumar J, Azhagarasan NS, Krishnan M. Comparative evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of three immersion chemical disinfectants on clinically derived poly(vinyl siloxane) impressions. J Prosthodont. 2018; 27:469–475. PMID: 27385390.
Article36. Queiroz DA, Peçanha MM, Neves AC, Frizzera F, Tonetto MR, Silva-Concílio LR. Influence of disinfection with peracetic acid and hypochlorite in dimensional alterations of casts obtained from addition silicone and polyether impressions. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013; 14:1100–1105. PMID: 24858758.37. Thouati A, Deveaux E, Iost A, Behin P. Dimensional stability of seven elastomeric impression materials immersed in disinfectants. J Prosthet Dent. 1996; 76:8–14. PMID: 8814627.
Article38. Celebi H, Büyükerkmen EB, Torlak E. Disinfection of polyvinyl siloxane impression material by gaseous ozone. J Prosthet Dent. 2018; 120:138–143. PMID: 29310874.
Article39. Aeran H, Sharma S, Kumar V, Gupta N. Use of clinical UV chamber to disinfect dental impressions: A comparative study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015; 9:ZC67–ZC70.
Article40. Surendra GP, Anjum A, Satish Babu CL, Shetty S. Evaluation of dimensional stability of autoclavable elastomeric impression material. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2011; 11:63–66. PMID: 22379308.
Article41. Thota KK, Jasthi S, Ravuri R, Tella S. A comparative evaluation of the dimensional stability of three different elastomeric impression materials after autoclaving - an in vitro study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:ZC48–ZC50.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of interproximal undercut on the dimensional accuracy of impression
- The effect of prolonged storage and disinfection on the dimensional stability of 5 vinyl polyether silicone impression materials
- A STUDY OF IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE USING PUTTY MATERIAL OF PVS IMPRESSION MATERIAL
- WETTABILITY OF POLYVINYLSILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIALS AND IMPROVED STONE MATERIALS
- THE EFFECT OF IMMERSION DISINFECTION ON THE DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF RUBBER IMPRESSION MATERIALS