J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2015 Oct;53(4):330-336. 10.4047/jkap.2015.53.4.330.
Effect of interproximal undercut on the dimensional accuracy of impression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Samsung Medical Center, College of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. seokgyu_k@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2118805
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2015.53.4.330
Abstract
- PURPOSE
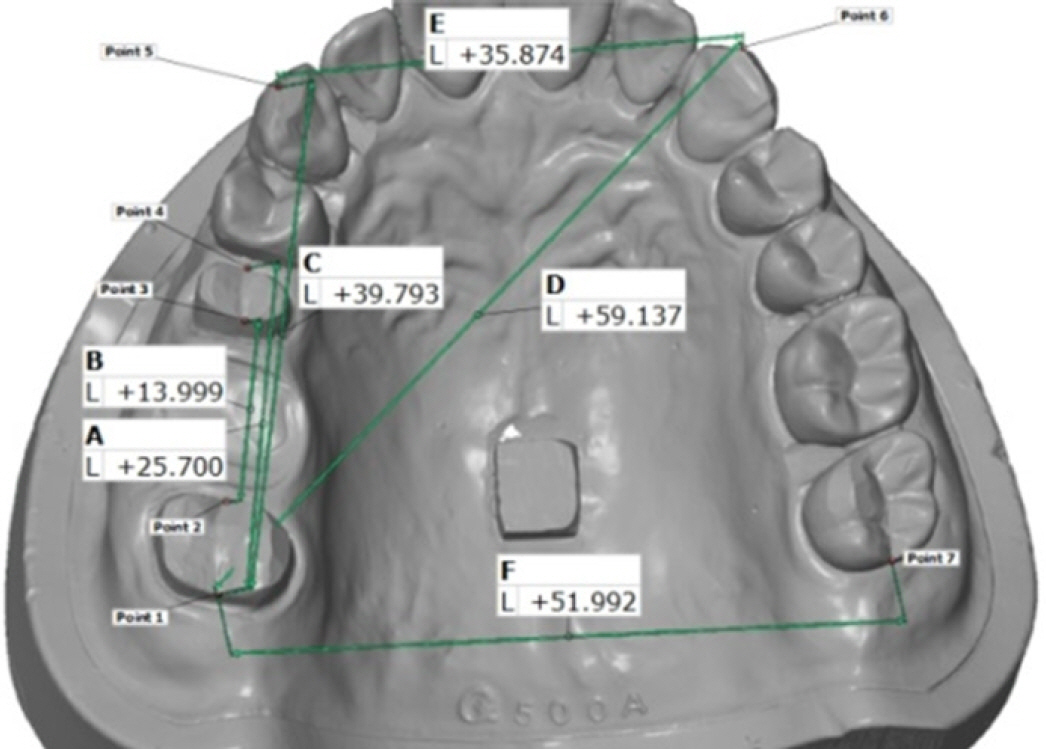
This study evaluated the effect of loss of interproximal papilla, creating an undercut, on the accuracy of impression materials.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Two addition type silicone impression materials (Extrude(R) Wash, Imprint(TM) II Quick Step Light Body) and one alginate impression material (Cavex Impressional) were used to make impressions of a maxillary master model simulating clinical conditions with or without interproximal papilla. Stone was poured in the impressions and working casts were fabricated. A total of 6 groups with 6 working casts in each group were scanned using 3-dimensional optical scanner. The accuracy of the impressions was assessed by measuring the dimensional changes (DeltaI (%)) of 6 distances on working casts compared to a master model with a 3-dimensional digitizing and inspection software. The data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA (P<.05).
RESULTS
Three of 6 distances showed statistically significant differences among the impression materials. Only 1 of 6 distances in alginate impression showed a statistically significant difference between casts with and without interproximal papilla (P=.047).
CONCLUSION
The presence of undercut due to loss of interproximal papilla did not significantly influence the dimensional accuracy of addition type silicone and alginate impression materials.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Finger WJ, Kurokawa R, Takahashi H, Komatsu M. Sulcus reproduction with elastomeric impression materials: a new in vitro testing method. Dent Mater. 2008; 24:1655–60.
Article2. Shah S, Sundaram G, Bartlett D, Sherriff M. The use of a 3D laser scanner using superimpositional software to assess the accuracy of impression techniques. J Dent. 2004; 32:653–8.
Article3. Peutzfeldt A, Asmussen E. Accuracy of alginate and elastomeric impression materials. Scand J Dent Res. 1989; 97:375–9.
Article4. Lawson NC, Burgess JO, Litaker MS. Tensile elastic recovery of elastomeric impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2008; 100:29–33.
Article5. Rubel BS. Impression materials: a comparative review of impression materials most commonly used in restorative dentistry. Dent Clin North Am. 2007; 51:629–42. vi.
Article6. Eriksson A, Ockert-Eriksson G, Lockowandt P. Accuracy of irreversible hydrocolloids (alginates) for fixed prosthodontics. A comparison between irreversible hydrocolloid, reversible hydrocolloid, and addition silicone for use in the syringe-tray technique. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998; 106:651–60.
Article7. Kaiser DA, Nicholls JI. A study of distortion and surface hard-ness of improved artificial stone casts. J Prosthet Dent. 1976; 36:373–81.
Article8. Nandini VV, Venkatesh KV, Nair KC. Alginate impressions: A practical perspective. J Conserv Dent. 2008; 11:37–41.
Article9. Eames WB, Sieweke JC, Wallace SW, Rogers LB. Elastomeric impression materials: effect of bulk on accuracy. J Prosthet Dent. 1979; 41:304–7.
Article10. Eames WB, Wallace SW, Suway NB, Rogers LB. Accuracy and dimensional stability of elastomeric impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1979; 42:159–62.
Article11. de Araujo PA, Jorgensen KD. Effect of material bulk and undercuts on the accuracy of impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1985; 54:791–4.
Article12. Stober T, Johnson GH, Schmitter M. Accuracy of the newly for-mulated vinyl siloxanether elastomeric impression material. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103:228–39.
Article13. Brosky ME, Pesun IJ, Lowder PD, Delong R, Hodges JS. Laser digitization of casts to determine the effect of tray selection and cast formation technique on accuracy. J Prosthet Dent. 2002; 87:204–9.
Article14. Goldfogel M, Harvey WL, Winter D. Dimensional change of acrylic resin tray materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1985; 54:284–6.
Article15. Pagniano RP, Scheid RC, Clowson RL, Dagefoerde RO, Zardiackas LD. Linear dimensional change of acrylic resins used in the fabrication of custom trays. J Prosthet Dent. 1982; 47:279–83.
Article16. Davis GB, Moser JB, Brinsden GI. The bonding properties of elas-tomer tray adhesives. J Prosthet Dent. 1976; 36:278–85.
Article17. [No authors listed] Revised american dental association speci-fication no. 19 for non-aqueous, elastomeric dental impression materials. J Am Dent Assoc. 1977; 94:733–41.18. Goldberg AJ. Viscoelastic properties of silicone, polysulfide, and polyether impression materials. J Dent Res. 1974; 53:1033–9.
Article19. Inoue K, Wilson HJ. Viscoelastic properties of elastomeric impression materials. III. The elastic recovery after removal of strains applied at the setting time. J Oral Rehabil. 1978; 5:323–7.20. de Araujo PA, Jorgensen KD, Finger W. Viscoelastic properties of setting elastomeric impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1985; 54:633–6.
Article21. Donovan TE, Chee WW. A review of contemporary impression materials and techniques. Dent Clin North Am. 2004; 48:vi–vii. 445–70.
Article22. Klooster J, Logan GI, Tjan AH. Effects of strain rate on the behavior of elastomeric impression. J Prosthet Dent. 1991; 66:292–8.
Article23. Chai J, Takahashi Y, Lautenschlager EP. Clinically relevant mechanical properties of elastomeric impression materials. Int J Prosthodont. 1998; 11:219–23.24. Balkenhol M, Haunschild S, Erbe C, Wö stmann B. Influence of prolonged setting time on permanent deformation of elastomeric impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103:288–94.
Article25. Burke FJ, Crisp RJ. A practice-based assessment of the handling of a fast-setting polyvinyl siloxane impression material used with the dual-arch tray technique. Quintessence Int. 2001; 32:805–10.26. Vinyl polysiloxane impression materials: a status report. Council on Dental Materials, Instruments, and Equipment. J Am Dent Assoc. 1990; 120:595–6. 598, 600.27. Quick DC, Holtan JR, Ross GK. Use of a scanning laser three-dimensional digitizer to evaluate dimensional accuracy of dental impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1992; 68:229–35.
Article28. DeLong R, Pintado MR, Ko CC, Hodges JS, Douglas WH. Factors influencing optical 3D scanning of vinyl polysiloxane impression materials. J Prosthodont. 2001; 10:78–85.
Article29. Rosenstiel SF, Land MF, Fujimoto J. Contemporary fixed prosthodontics. 3rd ed.St. Louis: USA, Elsevier;2001. p. 354–79.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of individual tooth tray on the teeth with undercut in impression taking
- ACCURACY OF IMPROVED STONE CASTS FROM ELASTOMERIC IMPRESSION MATERIALS
- COMPARISON OF THE ACCURACY OF STONE CASTS MADE FROM ALGINATE IMPRESSION MATERIAL BY MIXING METHODS AND APPLICATION OF TRAY ADHESIVE
- Effect of impression technique on the accuracy of master cast for implant prosthesis
- A STUDY OF IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE USING PUTTY MATERIAL OF PVS IMPRESSION MATERIAL