Ann Lab Med.
2019 Sep;39(5):438-446. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.5.438.
Clonal Cell Proliferation in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Evaluation of PIGA Mutations and T-cell Receptor Clonality
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yonggoo@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Catholic Genetic Laboratory Center, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Catholic Blood and Marrow Transplantation Center, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jwlee@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2450966
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.5.438
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is an acquired pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell disorder associated with an increase in the number of glycosyl-phosphatidyl inositol (GPI)-deficient blood cells. We investigated PNH clonal proliferation in the three cell lineages"”granulocytes, T lymphocytes, and red blood cells (RBCs)"”by analyzing PIGA gene mutations and T-cell receptor (TCR) clonality.
METHODS
Flow cytometry was used on peripheral blood samples from 24 PNH patients to measure the GPI-anchored protein (GPI-AP) deficient fraction in each blood cell lineage. PIGA gene mutations were analyzed in granulocytes and T lymphocytes by Sanger sequencing. A TCR clonality assay was performed in isolated GPI-AP deficient T lymphocytes.
RESULTS
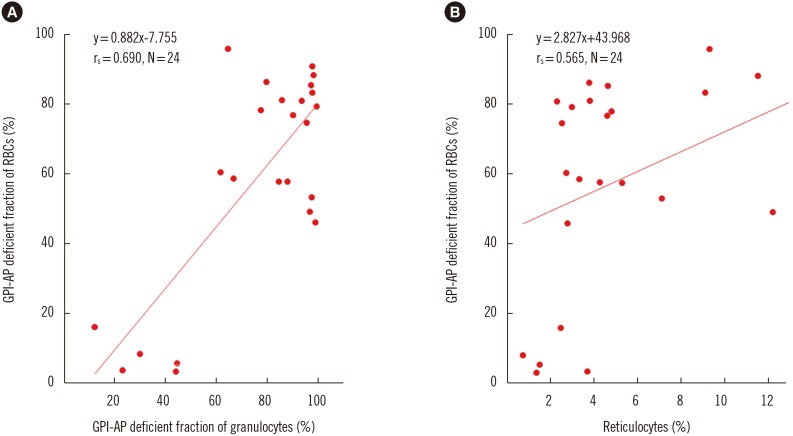
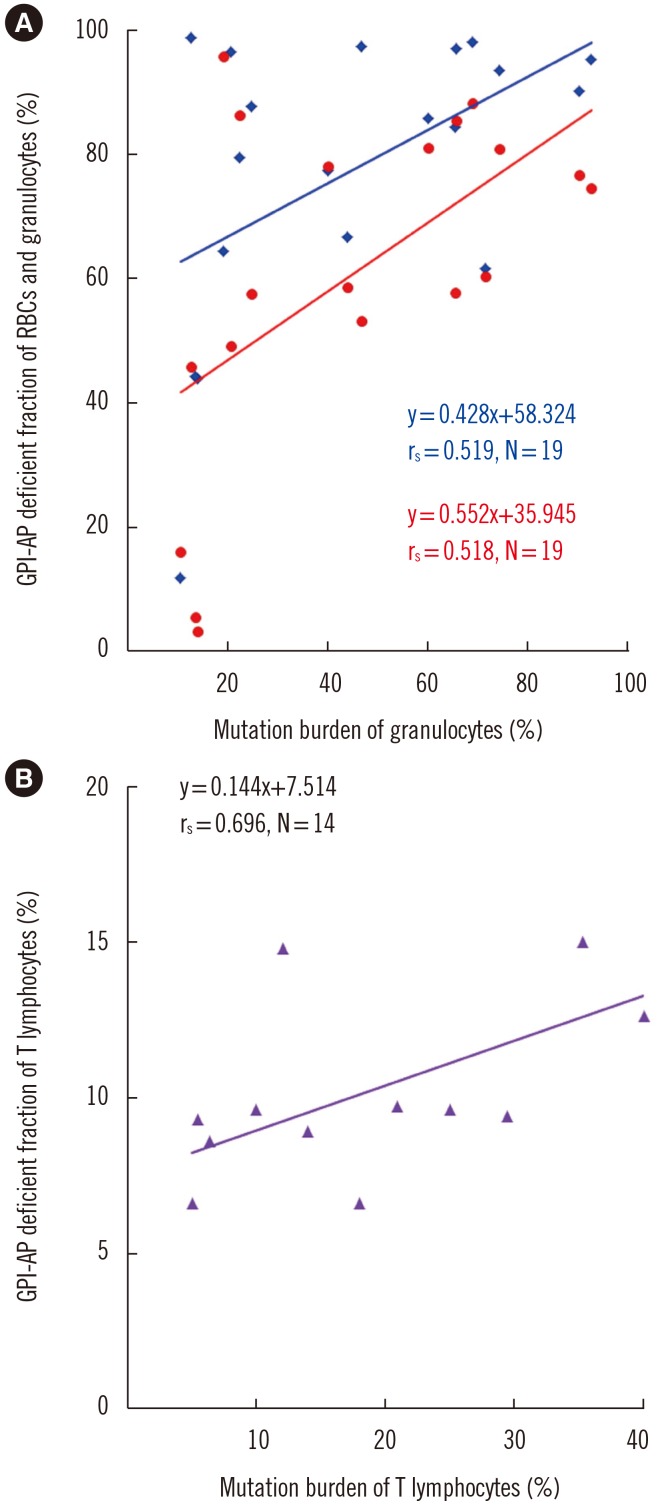
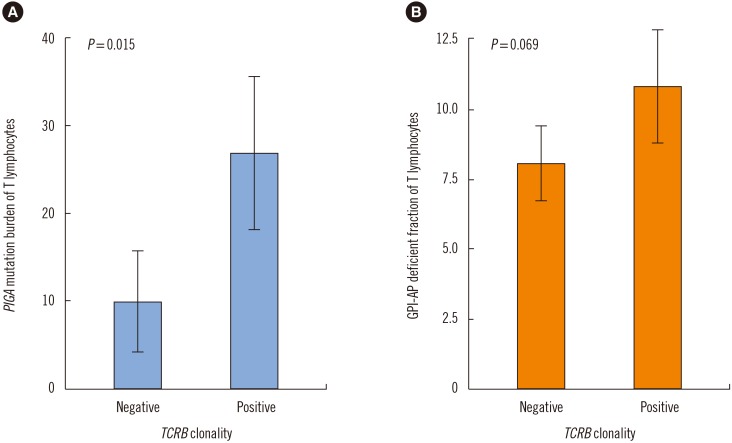
The GPI-AP deficient fraction among the three lineages was the highest in granulocytes, followed by RBCs and T lymphocytes. PIGA mutations were detected in both granulocytes and T lymphocytes of 19 patients (79.2%), with a higher mutation burden in granulocytes. The GPI-AP deficient fractions of granulocytes and T lymphocytes correlated moderately (rs=0.519, P=0.049) and strongly (rs=0.696, P=0.006) with PIGA mutation burden, respectively. PIGA mutations were more frequently observed in patients with clonal rearrangements in TCR genes (P=0.015). The PIGA mutation burden of T lymphocytes was higher in patients with clonal TCRB rearrangement.
CONCLUSIONS
PIGA mutations were present in approximately 80% of PNH patients. PNH clone size varies according to blood cell lineage, and clonal cells may obtain proliferation potential or gain a survival advantage over normal cells.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bessler M, Mason PJ, Hillmen P, Miyata T, Yamada N, Takeda J, et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH) is caused by somatic mutations in the PIG-A gene. EMBO J. 1994; 13:110–117. PMID: 8306954.2. Ware RE, Rosse WF, Howard TA. Mutations within the Piga gene in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1994; 83:2418–2422. PMID: 8167330.3. Brodsky RA, Mukhina GL, Nelson KL, Lawrence TS, Jones RJ, Buckley JT. Resistance of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells to the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-binding toxin aerolysin. Blood. 1999; 93:1749–1756. PMID: 10029605.4. Fujita M, Kinoshita T. GPI-anchor remodeling: potential functions of GPI-anchors in intracellular trafficking and membrane dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012; 1821:1050–1058. PMID: 22265715.5. Kinoshita T, Fujita M, Maeda Y. Biosynthesis, remodelling and functions of mammalian GPI-anchored proteins: recent progress. J Biochem. 2008; 144:287–294. PMID: 18635593.6. Brodsky RA. How I treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2009; 113:6522–6527. PMID: 19372253.7. Brodsky RA. How do PIG-A mutant paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria stem cells achieve clonal dominance. Expert Rev Hematol. 2009; 2:353–356. PMID: 21082939.8. Hill A, DeZern AE, Kinoshita T, Brodsky RA. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017; 3:17028. PMID: 28516949.9. Parker C, Omine M, Richards S, Nishimura J, Bessler M, Ware R, et al. Diagnosis and management of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2005; 106:3699–3709. PMID: 16051736.10. Kim JS, Jang JH, Yoon SS, Lee JH, Kim YK, Jo DY, et al. Distinct subgroups of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) with cytopenia: results from South Korean National PNH Registry. Ann Hematol. 2016; 95:125–133. PMID: 26416513.11. Donohue RE, Marcogliese AN, Sasa GS, Elghetany MT, Redkar AA, Bertuch AA, et al. Standardized high-sensitivity flow cytometry testing for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in children with acquired bone marrow failure disorders: A single center US study. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2018; 94:699–704. PMID: 28574201.12. Rahman K, Gupta R, Yadav G, Husein N, Singh MK, Nityanand S. Fluorescent aerolysin (FLAER)-based paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) screening: a single center experience from India. Int J Lab Hematol. 2017; 39:261–271. PMID: 28432724.13. Battiwalla M, Hepgur M, Pan D, McCarthy PL, Ahluwalia MS, Camacho SH, et al. Multiparameter flow cytometry for the diagnosis and monitoring of small GPI-deficient cellular populations. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2010; 78:348–356. PMID: 20533383.14. Oh H, Siano B, Diamond S. Neutrophil isolation protocol. J Vis Exp. 2008; 17.15. Mortazavi Y, Merk B, McIntosh J, Marsh JC, Schrezenmeier H, Rutherford TR, et al. The spectrum of PIG-A gene mutations in aplastic anemia/paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (AA/PNH): a high incidence of multiple mutations and evidence of a mutational hot spot. Blood. 2003; 101:2833–2841. PMID: 12424196.16. Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods. 2010; 7:248–249. PMID: 20354512.17. Choi Y, Sims GE, Murphy S, Miller JR, Chan AP. Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e46688. PMID: 23056405.18. Roy S, Schreiber E. Detecting and quantifying low level gene variants in sanger sequencing traces using the ab1 peak reporter tool. J Biomol Tech. 2014; 25:S13–S14.19. Choi CW, Jang JH, Kim JS, Jo DY, Lee JH, Kim SH, et al. Efficacy of eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patients with or without aplastic anemia: prospective study of a Korean PNH cohort. Blood Res. 2017; 52:207–211. PMID: 29043236.20. Nafa K, Mason P, Hillmen P, Luzzatto L, Bessler M. Mutations in the PIG-A gene causing paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria are mainly of the frameshift type. Blood. 1995; 86:4650–4655. PMID: 8541557.21. Brodsky RA. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2014; 124:2804–2811. PMID: 25237200.22. Ratajczak J, Kucia M, Mierzejewska K, Liu R, Kim CH, Natarajan N, et al. A novel view of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria pathogenesis: more motile PNH hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells displace normal HSPC’s from their niches in bone marrow due to defective adhesion, enhanced migration and mobilization in response to erythrocyte-released sphingosine-1 phosphate gradient. Leukemia. 2012; 26:1722–1725. PMID: 22343521.23. Kinoshita T. Biosynthesis and deficiencies of glycosylphosphatidylinositol. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2014; 90:130–143.24. Krawitz PM, Höchsmann B, Murakami Y, Teubner B, Krüger U, Klopocki E, et al. A case of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria caused by a germline mutation and a somatic mutation in PIGT. Blood. 2013; 122:1312–1315. PMID: 23733340.25. Nafa K, Bessler M, Castro-Malaspina H, Jhanwar S, Luzzatto L. The spectrum of somatic mutations in the PIG-A gene in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria includes large deletions and small duplications. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 1998; 24:370–384. PMID: 10087994.26. Yoon JH, Cho H, Park SS, Chang YH, Kim BK. Mutation analysis of the PIG-A gene in Korean patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. J Clin Pathol. 2002; 55:410–413. PMID: 12037021.27. Wang H, Chuhjo T, Yamazaki H, Shiobara S, Teramura M, Mizoguchi H, et al. Relative increase of granulocytes with a paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria phenotype in aplastic anaemia patients: the high prevalence at diagnosis. Eur J Haematol. 2001; 66:200–205. PMID: 11350489.28. Mukhina GL, Buckley JT, Barber JP, Jones RJ, Brodsky RA. Multilineage glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor-deficient haematopoiesis in untreated aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2001; 115:476–482. PMID: 11703352.29. Pu JJ, Hu R, Mukhina GL, Carraway HE, McDevitt MA, Brodsky RA. The small population of PIG-A mutant cells in myelodysplastic syndromes do not arise from multipotent hematopoietic stem cells. Haematologica. 2012; 97:1225–1233. PMID: 22315493.30. Wiedmer T, Hall SE, Ortel TL, Kane WH, Rosse WF, Sims PJ. Complement-induced vesiculation and exposure of membrane prothrombinase sites in platelets of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1993; 82:1192–1196. PMID: 7688991.31. Christmas SE, de la Mata Espinosa CT, Halliday D, Buxton CA, Cummerson JA, Johnson PM. Levels of expression of complement regulatory proteins CD46, CD55 and CD59 on resting and activated human peripheral blood leucocytes. Immunology. 2006; 119:522–528. PMID: 16999828.32. Michie CA, McLean A, Alcock C, Beverley PC. Lifespan of human lymphocyte subsets defined by CD45 isoforms. Nature. 1992; 360:264–265. PMID: 1436108.33. Tseng JE, Hall SE, Howard TA, Ware RE. Phenotypic and functional analysis of lymphocytes in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hematol. 1995; 50:244–253. PMID: 7485098.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delivery in a Patient with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Successfully Managed with Low Molecular Weight Heparin Therapy
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Presenting as Recurrent Jejunitis
- Anesthetic and Perioperative Management of Patient with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
- Progressive Moyamoya Syndrome Associated with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria