Yonsei Med J.
2015 May;56(3):825-831. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.825.
Hypoxia Increases Epithelial Permeability in Human Nasal Epithelia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ENTMAN@yuhs.ac
- 2The Airway Mucus Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Research Center for Human Natural Defense System, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2450360
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.825
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The nasal mucosa is the first site to encounter pathogens, and it forms continuous barriers to various stimuli. This barrier function is very important in the innate defense mechanism. Additionally, inflammation of the nasal sinus is known to be a hypoxic condition. Here, we studied the effect of hypoxia on barrier function in normal human nasal epithelial (NHNE) cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
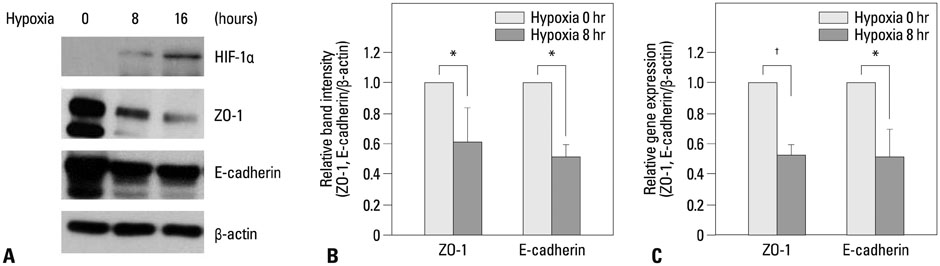
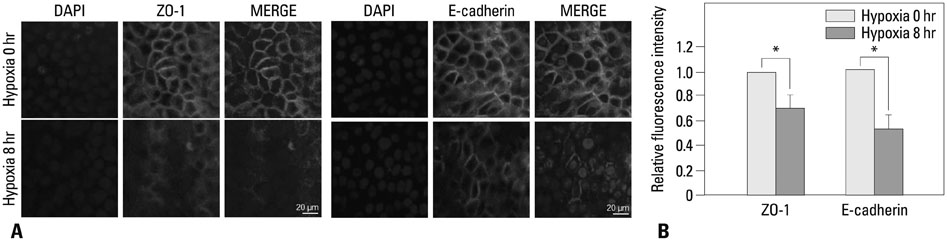
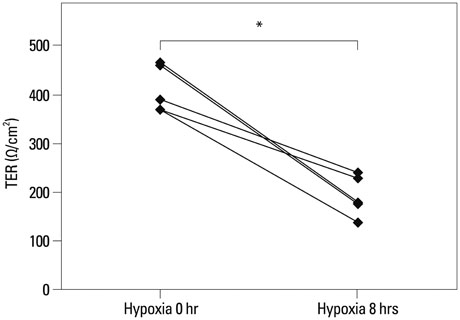
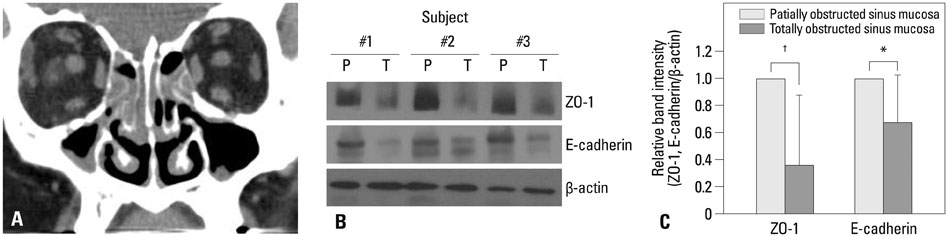
The expression levels of various junction complex proteins were assessed in hypoxia-stimulated NHNE cells and human nasal mucosal tissues. We performed real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis, western blotting, and immunofluorescence assays to examine differences in the mRNA and protein expression of ZO-1, a tight junction protein, and E-cadherin in NHNE cells. Moreover, we evaluated the trans-epithelial resistance (TER) of NHNE cells under hypoxic conditions to check for changes in permeability. The expression of ZO-1 and E-cadherin was measured in human nasal mucosa samples by western blotting.
RESULTS
Hypoxia time-dependently decreased the expression of ZO-1 and E-cadherin at the gene and protein levels. In addition, hypoxia decreased the TER of NHNE cells, which indicates increased permeability. Human nasal mucosa samples, which are supposed to be hypoxic, showed significantly decreased levels of ZO-1 and E-cadherin expression compared with control.
CONCLUSION
Our results demonstrate that hypoxia altered the expression of junction complex molecules and increased epithelial permeability in human nasal epithelia. This suggests that hypoxia causes barrier dysfunction. Furthermore, it may be associated with innate immune dysfunction after encountering pathogens.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anoxia/etiology/*metabolism
Blotting, Western
Cadherins/*analysis/genetics
Epithelium/chemistry/pathology
Humans
Membrane Proteins/*analysis
Nasal Mucosa/*chemistry/pathology/*secretion
Permeability/*radiation effects
RNA, Messenger/genetics/metabolism
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Tight Junctions/*metabolism
Zonula Occludens-1 Protein
Cadherins
Membrane Proteins
RNA, Messenger
Zonula Occludens-1 Protein
Figure
Reference
-
1. Herard AL, Zahm JM, Pierrot D, Hinnrasky J, Fuchey C, Puchelle E. Epithelial barrier integrity during in vitro wound repair of the airway epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1996; 15:624–632.
Article2. van Kempen MJ, Rijkers GT, Van Cauwenberge PB. The immune response in adenoids and tonsils. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000; 122:8–19.
Article3. Koizumi J, Kojima T, Kamekura R, Kurose M, Harimaya A, Murata M, et al. Changes of gap and tight junctions during differentiation of human nasal epithelial cells using primary human nasal epithelial cells and primary human nasal fibroblast cells in a noncontact coculture system. J Membr Biol. 2007; 218:1–7.
Article4. Schneeberger EE, Lynch RD. Structure, function, and regulation of cellular tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1992; 262(6 Pt 1):L647–L661.
Article5. Gumbiner BM. Breaking through the tight junction barrier. J Cell Biol. 1993; 123(6 Pt 2):1631–1633.
Article6. Takano K, Kojima T, Go M, Murata M, Ichimiya S, Himi T, et al. HLA-DR- and CD11c-positive dendritic cells penetrate beyond well-developed epithelial tight junctions in human nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005; 53:611–619.
Article7. Nelson WJ. Adaptation of core mechanisms to generate cell polarity. Nature. 2003; 422:766–774.
Article8. Niessen CM. Tight junctions/adherens junctions: basic structure and function. J Invest Dermatol. 2007; 127:2525–2532.
Article9. Capaldo CT, Macara IG. Depletion of E-cadherin disrupts establishment but not maintenance of cell junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2007; 18:189–200.
Article10. Yeo NK, Jang YJ. Rhinovirus infection-induced alteration of tight junction and adherens junction components in human nasal epithelial cells. Laryngoscope. 2010; 120:346–352.
Article11. Steinke JW. The relationship between rhinosinusitis and asthma sinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2006; 6:495–501.
Article12. Early SB, Hise K, Han JK, Borish L, Steinke JW. Hypoxia stimulates inflammatory and fibrotic responses from nasal-polyp derived fibroblasts. Laryngoscope. 2007; 117:511–515.
Article13. Matsune S, Kono M, Sun D, Ushikai M, Kurono Y. Hypoxia in paranasal sinuses of patients with chronic sinusitis with or without the complication of nasal allergy. Acta Otolaryngol. 2003; 123:519–523.
Article14. Sumbayev VV, Nicholas SA. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 as one of the "signaling drivers" of Toll-like receptor-dependent and allergic inflammation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2010; 58:287–294.
Article15. Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M, Dvorak AM. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1995; 146:1029–1039.16. Zhou H, Chen X, Zhang WM, Zhu LP, Cheng L. HIF-1α inhibition reduces nasal inflammation in a murine allergic rhinitis model. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e48618.
Article17. Huerta-Yepez S, Baay-Guzman GJ, Bebenek IG, Hernandez-Pando R, Vega MI, Chi L, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor promotes murine allergic airway inflammation and is increased in asthma and rhinitis. Allergy. 2011; 66:909–918.
Article18. Kim SR, Lee KS, Park HS, Park SJ, Min KH, Moon H, et al. HIF-1α inhibition ameliorates an allergic airway disease via VEGF suppression in bronchial epithelium. Eur J Immunol. 2010; 40:2858–2869.
Article19. Kim HJ, Kim CH, Ryu JH, Kim MJ, Park CY, Lee JM, et al. Reactive oxygen species induce antiviral innate immune response through IFN-λ regulation in human nasal epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013; 49:855–865.
Article20. Yoon JH, Gray T, Guzman K, Koo JS, Nettesheim P. Regulation of the secretory phenotype of human airway epithelium by retinoic acid, triiodothyronine, and extracellular matrix. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997; 16:724–731.
Article21. Fokkens W, Lund V, Bachert C, Clement P, Helllings P, Holmstrom M, et al. EAACI position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps executive summary. Allergy. 2005; 60:583–601.
Article22. Pruteanu M, Shanahan F. Digestion of epithelial tight junction proteins by the commensal Clostridium perfringens. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013; 305:G740–G748.23. Chen ST, Liu RS, Wu MF, Lin YL, Chen SY, Tan DT, et al. CLEC5A regulates Japanese encephalitis virus-induced neuroinflammation and lethality. PLoS Pathog. 2012; 8:e1002655.
Article24. Sajjan U, Wang Q, Zhao Y, Gruenert DC, Hershenson MB. Rhinovirus disrupts the barrier function of polarized airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 178:1271–1281.
Article25. Kimura K, Teranishi S, Kawamoto K, Nishida T. Protective effect of dexamethasone against hypoxia-induced disruption of barrier function in human corneal epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 2011; 92:388–393.
Article26. Takeuchi K, Kishioka C, Ishinaga H, Sakakura Y, Majima Y. Histamine alters gene expression in cultured human nasal epithelial cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:310–314.
Article27. Jang YJ, Kim HG, Koo TW, Chung PS. Localization of ZO-1 and E-cadherin in the nasal polyp epithelium. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2002; 259:465–469.
Article28. Mankertz J, Schulzke JD. Altered permeability in inflammatory bowel disease: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007; 23:379–383.
Article29. Pahl A, Szelenyi S, Brune K. Hypoxia induced chemokine expression in nasal epithelial cells: development of an in vitro model for chronic rhinosinusitis. ALTEX. 2006; 23:59–63.30. Kojima T, Go M, Takano K, Kurose M, Ohkuni T, Koizumi J, et al. Regulation of tight junctions in upper airway epithelium. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:947072.
Article31. Jin J, Chang DY, Kim SH, Rha KS, Mo JH, Shin EC, et al. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in regulatory T cells on nasal polypogenesis. Laryngoscope. 2014; 124:E151–E159.
Article32. Bai S, Yang T, Abbruscato TJ, Ahsan F. Evaluation of human nasal RPMI 2650 cells grown at an air-liquid interface as a model for nasal drug transport studies. J Pharm Sci. 2008; 97:1165–1178.
Article33. Kobayashi N, Dezawa M, Nagata H, Yuasa S, Konno A. Immunohistochemical study of E-cadherin and ZO-1 in allergic nasal epithelium of the guinea pig. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1998; 116:196–205.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultra-Structures And 14C-mannitol Transport Study of Human Nasal Epithelial Cells using ALI Culture Technique
- Expression of Placenta Growth Factor mRNA Transcripts and Protein in Nasal Mucosa and Nasal Polyps
- Increased vascular permeability and reduced neutral endopeptidase activity in rat nasal mucosa after ozone exposure
- Expression and Distribution of the Na+ : HCO3- Cotransporter(NBC) and K+ : Cl- Cotransporter(KCC) mRNA in Human Nasal Mucosa and Nasal Polyp
- Effects of Hantaan Virus and IFN-gammaon Induction of Surface ICAM-1 in Primary Cultured Buman Nasal Epithelial Cells and Human Lung Fibroblasts