J Korean Acad Nurs.
2019 Apr;49(2):191-202. 10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.191.
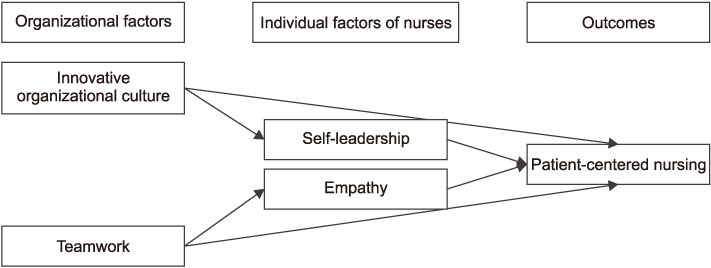
A Predictive Model on Patient-Centered Care of Hospital Nurses in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Deajeon Health Institute of Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. mhpark@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2444834
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.191
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Patient-centered care is a widely utilized concept in nursing and health care. However, the key components of patient-centered nursing have not yet been reported. Moreover, previous studies on patient-centered care have mostly focused on components of nursing rather than organizational factors. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of influential factors of patient-centered care is required.
METHODS
The purpose of this study was to develop a theoretical model based on person-centered care theory, and the relevant literature and to test the developed model with covariance structure analysis in order to determine the causal paths among the variables.
RESULTS
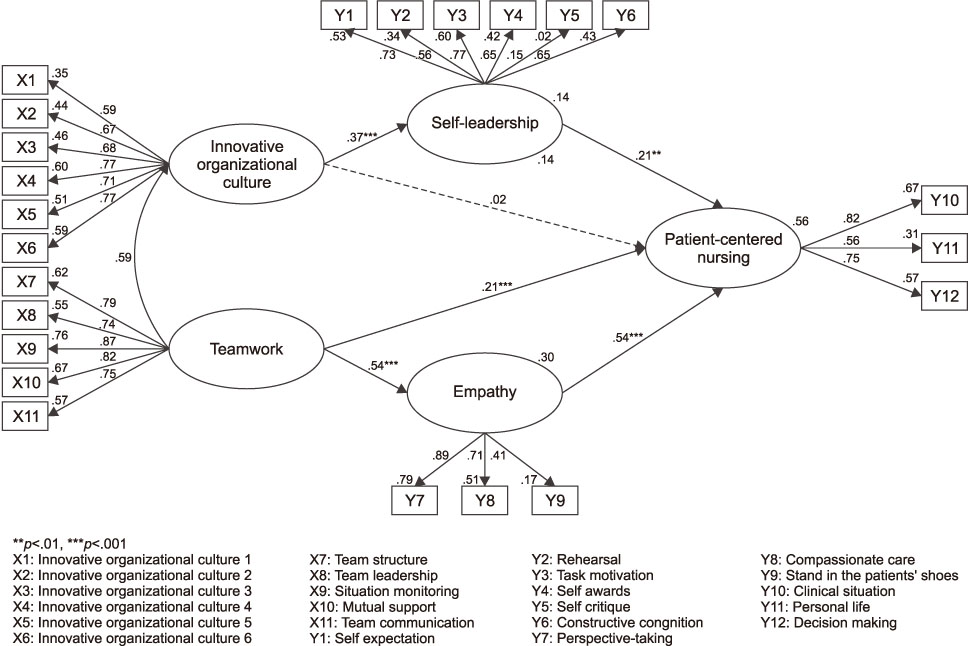
The model fit indices for the hypothetical model were suitable for the recommended level (goodness of fit index=.87, standardized root mean residual=.01, root mean square error of approximation=.06, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.92, parsimonious normed fit index=.75). In this study, five of the six paths established in the initial hypothetical model were supported. The variables of teamwork, self-leadership, and empathy accounted for 56.4% of hospital nurses' patient-centered care. Among these, empathy was the strongest predictor of patient-centered care.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that it is necessary to use strategies to improve self-leadership and empathy. In addition to enhancing the personal factors of nurses, nursing organizations should strive for effective multidisciplinary cooperation with active support for patient-centered care and openness to change.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim EK, Kim SY, Lee E. Analysis of mission statements and organizational performance of hospitals in South Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2015; 45(4):565–575. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.565.
Article2. Korea Institute for Healthcare Accreditation (KOIHA). Criteria for 2-cycle health care accreditation in acute hospitals (ver 2.1) [Internet]. Seoul: KOIHA;c2016. cited 2018 Sep 09. Available from: http://www.koiha.kr/.3. Papastavrou E, Acaroglu R, Sendir M, Berg A, Efstathiou G, Idvall E, et al. The relationship between individualized care and the practice environment: An international study. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2015; 52(1):121–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.05.008.
Article4. Lusk JM, Fater K. A concept analysis of patient-centered care. Nursing Forum. 2013; 48(2):89–98. DOI: 10.1111/nuf.12019.
Article5. Morgan S, Yoder LH. A concept analysis of person-centered care. Journal of Holistic Nursing. 2012; 30(1):6–15. DOI: 10.1177/0898010111412189.
Article6. Suhonen R, Gustafsson ML, Katajisto J, Välimäki M, Leino-Kilpi H. Individualized care scale - nurse version: A Finnish validation study. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice. 2010; 16(1):145–154. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2009.01168.x.
Article7. Yang IS. Individualized care, satisfaction with nursing care and health-related quality of life-focusing on heart disease. Korean Journal of Women's Health. 2008; 9(1):37–56.8. Lee JE. Patients' and nurses' perceptions of patient centered nursing care [master's thesis]. Daejeon: Chungnam University;2015. 1–62.9. Charalambous A, Katajisto J, Välimäki M, Leino-Kilpi H, Suhonen R. Individualised care and the professional practice environment: Nurses' perceptions. International Nursing Review. 2010; 57(4):500–507. DOI: 10.1111/j.1466-7657.2010.00831.x.
Article10. Suhonen R, Stolt M, Gustafsson ML, Katajisto J, Charalambous A. The associations among the ethical climate, the professional practice environment and individualized care in care settings for older people. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2014; 70(6):1356–1368. DOI: 10.1111/jan.12297.
Article11. Bolster D, Manias E. Person-centred interactions between nurses and patients during medication activities in an acute hospital setting: Qualitative observation and interview study. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2010; 47(2):154–165. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.05.021.
Article12. McCormack B, McCance T. Person-centred nursing: Theory, models and methods. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell;2010. p. 1–269.13. Mead N, Bower P. Patient-centredness: A conceptual framework and review of the empirical literature. Social Science & Medicine. 2000; 51(7):1087–1110. DOI: 10.1016/S0277-9536(00)00098-8.
Article14. Brown D, McWilliam C, Ward-Griffin C. Client-centred empowering partnering in nursing. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2006; 53(2):160–168. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03711.x.
Article15. Slater P, McCance T, McCormack B. Exploring person-centred practice within acute hospital settings. International Practice Development Journal. 2015; 5:Suppl 9. 1–8. DOI: 10.19043/ipdj.5SP.011.
Article16. Pelzang R. Time to learn: Understanding patient-centred care. British Journal of Nursing. 2010; 19(14):912–917. DOI: 10.12968/bjon.2010.19.14.49050.
Article17. Sagong H, Lee GE. Person-centered care and nursing service quality of nurses in long-term care hospitals. Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2016; 27(4):309–318. DOI: 10.12799/jkachn.2016.27.4.309.
Article18. Kitson A, Marshall A, Bassett K, Zeitz K. What are the core elements of patient-centred care? A narrative review and synthesis of the literature from health policy, medicine and nursing. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69(1):4–15. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2012.06064.x.
Article19. Cohen-Mansfield J, Parpura-Gill A. Practice style in the nursing home: Dimensions for assessment and quality improvement. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2008; 23(4):376–386. DOI: 10.1002/gps.1888.
Article20. Kirkley C, Bamford C, Poole M, Arksey H, Hughes J, Bond J. The impact of organisational culture on the delivery of person-centred care in services providing respite care and short breaks for people with dementia. Health & Social Care in the Community. 2011; 19(4):438–448. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2524.2011.00998.x.
Article21. Luxford K, Safran DG, Delbanco T. Promoting patient-centered care: A qualitative study of facilitators and barriers in healthcare organizations with a reputation for improving the patient experience. International Journal for Quality in Health Care. 2011; 23(5):510–515. DOI: 10.1093/intqhc/mzr024.
Article22. Rogers EM. YS Kim NW Kang HK Park . Diffusion of innovations. Seoul: Communication Books, Inc.;c2005. p. 1–576.23. Haley B, Heo S, Wright P, Barone C, Rettiganti MR, Anders M. Relationships among active listening, self-awareness, empathy, and patient-centered care in associate and baccalaureate degree nursing students. NursingPlus Open. 2017; 3:11–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.npls.2017.05.001.
Article24. Manz CC, Sims HP Jr. SuperLeadership: Beyond the myth of heroic leadership. Organizational Dynamics. 1991; 19(4):18–35. DOI: 10.1016/0090-2616(91)90051-A.
Article25. Won HJ, Cho SH. A review of research on self-leadership in nurses'. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2013; 19(3):382–393. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2013.19.3.382.
Article26. Kim MS, Han SJ, Kim JH. The development of the nursing organization culture measurement tool. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2004; 10(2):175–184.27. Kim MS. Role of self-leadership in the relationship between organizational culture and informatics competency. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009; 39(5):731–740. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2009.39.5.731.
Article28. Hojat M, Bianco JA, Mann D, Massello D, Calabrese LH. Overlap between empathy, teamwork and integrative approach to patient care. Medical Teacher. 2015; 37(8):755–758. DOI: 10.3109/0142159X.2014.971722.
Article29. Xyrichis A, Ream E. Teamwork: A concept analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2008; 61(2):232–241. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04496.x.
Article30. Bae BR. Structural equation modeling with Amos 19. Seoul: Chenngram Books;2011. p. 1–668.31. Yu JP. The concept and understanding of structural equation modeling. Seoul: Hannarae Publishing Co.;2012. p. 1–567.32. Battles J, King HB. TeamSTEPPS® team work perceptions questionnaire (T-TPQ) manual [Internet]. Washington, DC: American Institutes for Research;c2010. cited 2018 Sep 9. Available from: https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/teamstepps/instructor/reference/teamperceptionsmanual.pdf.
Article33. Ahn SA, Lee NJ. The effect of operating room nursing and medical staff teamwork and perception of patient safety culture on the performance of surgical patient safety protocol. Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing. 2016; 9(1):27–39.34. Hojat M, Mangione S, Nasca TJ, Cohen MJM, Gonnella JS, Erdmann JB, et al. The Jefferson scale of physician empathy: Development and preliminary psychometric data. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 2001; 61(2):349–365. DOI: 10.1177/00131640121971158.
Article35. Ryu HR, Bang KS. A validation study of the Korean version of the Jefferson empathy scale for health professionals for Korean nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2016; 46(2):207–214. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.207.
Article36. Manz CC. The art of self-leadership: Strategies for personal effectiveness in your life and work. Englewood Cliffs (NJ): Prentice-Hall;1983. p. 1–115.37. Kim HS. The relationship between self-leadership and job satisfaction of middle school teacher [master's thesis]. Seoul: Soongsil University;2003. 1–83.38. Wong N, Rindfleisch A, Burroughs JE. Do reverse-worded items confound measures in cross-cultural consumer research? The case of the material values scale. Journal of Consumer Research. 2003; 30(1):72–91. DOI: 10.1086/374697.
Article39. Hayes AF. Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. New York: Guilford Publications;2013. p. 1–507.40. Lynch BM, McCormack B, McCance T. Development of a model of situational leadership in residential care for older people. Journal of Nursing Management. 2011; 19(8):1058–1069. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2834.2011.01275.x.
Article41. Neumann M, Edelhäuser F, Tauschel D, Fischer MR, Wirtz M, Woopen C, et al. Empathy decline and its reasons: A systematic review of studies with medical students and residents. Academic Medicine. 2011; 86(8):996–1009. DOI: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e318221e615.
Article42. Lee IK. To seek ‘Homo empathicus’: A study on the empathy discourse-based character education. Korean Journal of General Education. 2014; 8(1):311–342.43. Lamb BW, Taylor C, Lamb JN, Strickland SL, Vincent C, Green JSA, et al. Facilitators and barriers to teamworking and patient centeredness in multidisciplinary cancer teams: Findings of a national study. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2013; 20(5):1408–1416. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-012-2676-9.
Article44. Røsvik J, Brooker D, Mjorud M, Kirkevold Ø. What is person-centred care in dementia? Clinical reviews into practice: The development of the VIPS practice model. Reviews in Clinical Gerontology. 2013; 23(2):155–163. DOI: 10.1017/S0959259813000014.
Article45. Henrikson M. Great leaders are made, not born. AWHONN Lifelines. 2006; 10(6):510–515. DOI: 10.1111/j.1552-6356.2006.00101.x.
Article46. Lee MJ, Han JS, Jang YM. Convergence study of the effects of nurses' perceived nursing organization culture and on their customer orientation. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2015; 13(11):303–311. DOI: 10.14400/JDC.2015.13.11.303.
Article47. Kwon HJ, Suk BH, Chee SJ, Ahn YM, Kim YJ, Park SA, et al. The relationships between the types of nursing organizational culture, nurses' satisfaction with life, and job satisfaction. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2011; 17(1):57–69.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance and Needs of Person-Centered Care of Intensive Care Unit Nurses
- The perceptions and performance of family-centered care among pediatric nurses at a children's hospital in South Korea: a descriptive study
- The Factors Affecting Person-centered Care Nursing in Intensive Care Unit Nurses
- Influence of Positive Psychological Capital and Nursing Professional Pride on Person-Centered Care Among General Hospital Clinical Nurses
- The influence of health literacy competencies on patient-centered care among clinical nurses