Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2014 Dec;13(4):129-138. 10.12779/dnd.2014.13.4.129.
Efficacy of the Phosphorylated tau 181 in Differential Diagnosis of the Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Evidence-based Health Care Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Chung Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. neudoc@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2443078
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2014.13.4.129
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the value of phosphorylated tau with epitopes threonine 181(p-tau181) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease typed dementia from other type of dementia.
METHODS
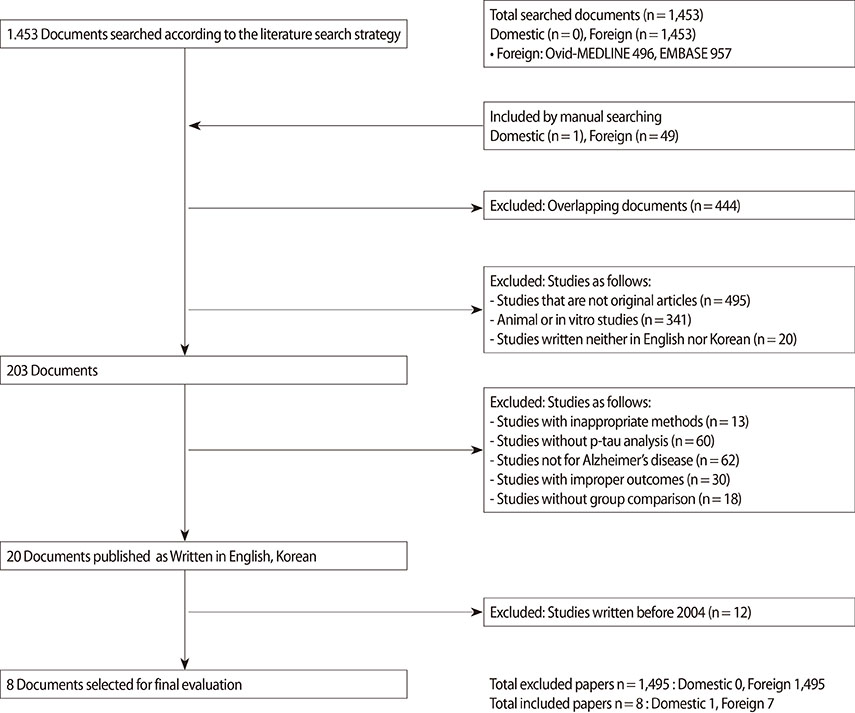
A systematic literature search was performed to identify studies on p-tau181. Two evaluators independently evaluated the quality of the ten studies using the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) tool. The literature review covered from October 27, 1946 to October 22, 2013, and eight domestic databases including KoreaMed and international databases including Ovid-MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library were used. Tau concentrations were compared to healthy controls and to subjects with Alzheimer's disease (AD) using random effect meta-analysis. Outcome measures were Cohen's delta, sensitivity and specificity.
RESULTS
Finally, 8 studies (8 diagnostic evaluation studies) were identified to evaluate CSF p-tau181. The effectiveness of this test was evaluated based on diagnostic accuracy. The diagnostic accuracy for identifying AD by ELISA was high which revealed pooled sensitivity as 0.843 (95% CI 0.818-0.867), pooled specificity as 0.799(95% CI 0.768-0.828) and summary receiver operating characteristic area under the curve 0.9082+/-0.0236.
CONCLUSIONS
CSF p-tau181 concentrations in other type of dementia are intermediate between controls and AD patients. Overlap between both controls and AD patients results in insufficient diagnostic accuracy, and the development of more specific biomarkers for these disorders is needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM. Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2007; 3:186–191.
Article2. Jack CR Jr, Albert MS, Knopman DS, McKhann GM, Sperling RA, Carrillo MC, et al. Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011; 7:257–262.
Article3. Aisen PS, Andrieu S, Sampaio C, Carrillo M, Khachaturian ZS, Dubois B, et al. Report of the task force on designing clinical trials in early (predementia) AD. Neurology. 2011; 76:280–286.
Article4. Golde TE, Schneider LS, Koo EH. Anti-abeta therapeutics in Alzheimer's disease: the need for a paradigm shift. Neuron. 2011; 69:203–213.
Article5. Cummings JL. Biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease drug development. Alzheimers Dement. 2011; 7:e13–e44.
Article6. Jack CR Jr, Lowe VJ, Senjem ML, Weigand SD, Kemp BJ, Shiung MM, et al. 11C PiB and structural MRI provide complementary information in imaging of Alzheimer's disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Brain. 2008; 131:665–680.
Article7. Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathologica. 1991; 82:239–259.
Article8. Petersen RC, Parisi JE, Dickson DW, Johnson KA, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, et al. Neuropathologic features of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2006; 63:665–672.
Article9. Ferreira D, Perestelo-Perez L, Westman E, Wahlund LO, Sarria A, Serrano-Aguilar P. Meta-Review of CSF Core Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease: The State-of-the-Art after the New Revised Diagnostic Criteria. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014; 6:47.
Article10. Dumurgier J, Vercruysse O, Paquet C, Bombois S, Chaulet C, Laplanche JL, et al. Intersite variability of CSF Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in clinical setting. Alzheimers Dement. 2013; 9:406–413.
Article11. Ravaglia S, Bini P, Sinforiani E, Franciotta D, Zardini E, Tosca P, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 in patients with Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Neurol Sci. 2008; 29:417–423.
Article12. Reijn TS, Rikkert MO, van Geel WJ, de Jong D, Verbeek MM. Diagnostic accuracy of ELISA and xMAP technology for analysis of amyloid beta(42) and tau proteins. Clin Chem. 2007; 53:859–865.
Article13. Schoonenboom NS, Pijnenburg YA, Mulder C, Rosso SM, Van Elk EJ, Van Kamp GJ, et al. Amyloid beta(1-42) and phosphorylated tau in CSF as markers for early-onset Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2004; 62:1580–1584.
Article14. Le Bastard N, Coart E, Vanderstichele H, Vanmechelen E, Martin JJ, Engelborghs S. Comparison of two analytical platforms for the clinical qualification of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in pathologically-confirmed dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013; 33:117–131.
Article15. Herukka SK, Pennanen C, Soininen H, Pirttila T. CSF Abeta42, tau and phosphorylated tau correlate with medial temporal lobe atrophy. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008; 14:51–57.
Article16. Kapaki EN, Paraskevas GP, Tzerakis NG, Sfagos C, Seretis A, Kararizou E, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid tau, phospho-tau181 and beta-amyloid1-42 in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a discrimination from Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2007; 14:168–173.
Article17. Lewczuk P, Kornhuber J, Vanderstichele H, Vanmechelen E, Esselmann H, Bibl M, et al. Multiplexed quantification of dementia biomarkers in the CSF of patients with early dementias and MCI: a multicenter study. Neurobiol Aging. 2008; 29:812–818.
Article18. Park SA, Kim HJ, Kim TE, Kim YJ, Lee DH, Park JH, et al. Preliminary Study for a Multicenter Study of Alzheimer's Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker. Dementia and Neurocognitive Disorders. 2013; 12:1–8.
Article19. Verwey NA, van der Flier WM, Blennow K, Clark C, Sokolow S, De Deyn PP, et al. A worldwide multicentre comparison of assays for cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Clin Biochem. 2009; 46:235–240.
Article20. Mitchell AJ. CSF phosphorylated tau in the diagnosis and prognosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis of 51 studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 80:966–975.
Article21. Frank RA, Galasko D, Hampel H, Hardy J, de Leon MJ, Mehta PD, et al. Biological markers for therapeutic trials in Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the biological markers working group; NIA initiative on neuroimaging in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003; 24:521–536.22. Olsson A, Vanderstichele H, Andreasen N, De Meyer G, Wallin A, Holmberg B, et al. Simultaneous measurement of beta-amyloid(1-42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau (Thr181) in cerebrospinal fluid by the xMAP technology. Clin Chem. 2005; 51:336–345.
Article23. Hansson O, Zetterberg H, Buchhave P, Londos E, Blennow K, Minthon L. Association between CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer's disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a follow-up study. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:228–234.
Article24. Molinuevo JL, Gispert JD, Dubois B, Heneka MT, Lleo A, Engelborghs S, et al. The AD-CSF-index discriminates Alzheimer's disease patients from healthy controls: a validation study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013; 36:67–77.
Article25. Sperling R, Johnson K. Biomarkers of Alzheimer disease: current and future applications to diagnostic criteria. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2013; 19:325–338.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pathobiolgy and Management of Alzheimer’s Disease
- The Effect of Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitor on Cerebrospinal Fluid beta-Amyloid 1-42 and Phosphorylated Tau Protein in Korean Alzheimer's Disease Patients: Preliminary Study
- An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Recent Updates on PET Imaging in Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Development of tau PET Imaging Ligands and their Utility in Preclinical and Clinical Studies