Hanyang Med Rev.
2015 Feb;35(1):9-17. 10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.9.
An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swj0208@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2149099
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.9
Abstract
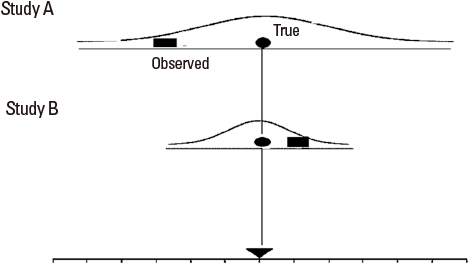
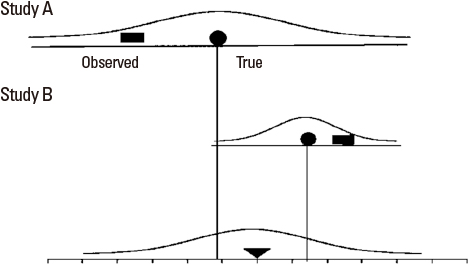
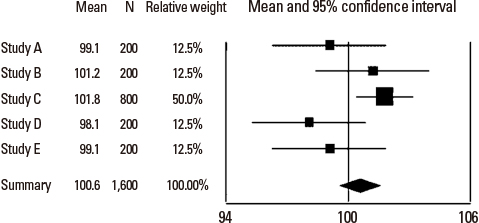
- Systematic reviews and meta-analysis represent a specific type of medical research in which an original article is a unit of analysis. These methods of research are essential tools in integrating scientific information, increasing the internal and external validity of the conclusions of original articles, and suggesting areas for future research. Meta-analysis is becoming popular because it can combine results from similar studies to calculate an overall estimate of a treatment effect. They are also necessary for the practice of evidence-based medicine and the medical decision making. However, conducting good quality systematic reviews is not easy and difficult to interpret. Since analysis of a data with meta-analysis is a relatively new field of research, many clinicians have not had the opportunity to learn about systematic review and meta-analysis systematically. An introduction of the rationale for carrying out meta-analysis will be helpful to the clinician in interpreting the results of meta-analysis.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Why Perform Meta-Analysis?
Woo Jong Shin
Hanyang Med Rev. 2015;35(1):1-2. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Berman NG, Parker RA. Meta-analysis: neither quick nor easy. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2002; 2:10.
Article2. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009; 62:e1–e34.
Article3. Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000; 283:2008–2012.
Article4. Petrie A, Bulman JS, Osborn JF. Further statistics in dentistry Part 8: systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Br Dent J. 2003; 194:73–78.
Article5. Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses. Lancet. 1999; 354:1896–1900.
Article6. Horwitz RI. "Large-scale randomized evidence: large, simple trials and overviews of trials": discussion. A clinician's perspective on meta-analyses. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995; 48:41–44.
Article7. Eysenck HJ. Meta-analysis and its problems. BMJ. 1994; 309:789–792.8. Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ. Publication and related biases. Health Technol Assess. 2000; 4:1–115.
Article9. Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet. 1991; 337:867–872.
Article10. Stern JM, Simes RJ. Publication bias: evidence of delayed publication in a cohort study of clinical research projects. BMJ. 1997; 315:640–645.
Article11. Egger M, Smith GD. Bias in location and selection of studies. BMJ. 1998; 316:61–66.12. Egger M, Zellweger-Zahner T, Schneider M, Junker C, Lengeler C, Antes G. Language bias in randomised controlled trials published in English and German. Lancet. 1997; 350:326–329.
Article13. McAuley L, Pham B, Tugwell P, Moher D. Does the inclusion of grey literature influence estimates of intervention effectiveness reported in meta-analyses? Lancet. 2000; 356:1228–1231.
Article14. Sutton AJ, Duval SJ, Tweedie RL, Abrams KR, Jones DR. Empirical assessment of effect of publication bias on meta-analyses. BMJ. 2000; 320:1574–1577.
Article15. Slavin RE. Best evidence synthesis: an intelligent alternative to meta-analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995; 48:9–18.
Article16. Oxman AD, Guyatt GH. The science of reviewing research. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993; 703:125–133. discussion 33-4.
Article17. Edwards P, Clarke M, DiGuiseppi C, Pratap S, Roberts I, Wentz R. Identification of randomized controlled trials in systematic reviews: accuracy and reliability of screening records. Stat Med. 2002; 21:1635–1640.
Article18. Kraemer HC. Correlation coefficients in medical research: from product moment correlation to the odds ratio. Stat Methods Med Res. 2006; 15:525–545.
Article19. Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR. An illustrated guide to the methods of meta-analysis. J Eval Clin Pract. 2001; 7:135–148.
Article20. Moher D, Jadad AR, Nichol G, Penman M, Tugwell P, Walsh S. Assessing the quality of randomized controlled trials: an annotated bibliography of scales and checklists. Control Clin Trials. 1995; 16:62–73.
Article21. Juni P, Witschi A, Bloch R, Egger M. The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta-analysis. JAMA. 1999; 282:1054–1060.
Article22. Moher D, Tetzlaff J, Tricco AC, Sampson M, Altman DG. Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2007; 4:e78.
Article23. Delaney A, Bagshaw SM, Ferland A, Manns B, Laupland KB, Doig CJ. A systematic evaluation of the quality of meta-analyses in the critical care literature. Crit Care. 2005; 9:R575–R582.24. Jadad AR, Cook DJ, Jones A, Klassen TP, Tugwell P, Moher M, et al. Methodology and reports of systematic reviews and meta-analyses: a comparison of Cochrane reviews with articles published in paper-based journals. JAMA. 1998; 280:278–280.
Article25. Mulrow CD. The medical review article: state of the science. Ann Intern Med. 1987; 106:485–488.
Article26. McAlister FA, Clark HD, van Walraven C, Straus SE, Lawson FM, Moher D, et al. The medical review article revisited: has the science improved? Ann Intern Med. 1999; 131:947–951.
Article27. Shea BJ, Hamel C, Wells GA, Bouter LM, Kristjansson E, Grimshaw J, et al. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009; 62:1013–1020.
Article28. Egger M, Schneider M, Davey Smith G. Spurious precision? Meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ. 1998; 316:140–144.
Article29. Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN. Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ. 1997; 315:1533–1537.
Article30. Thompson SG. Controversies in meta-analysis: the case of the trials of serum cholesterol reduction. Stat Methods Med Res. 1993; 2:173–192.
Article31. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002; 21:1539–1558.
Article32. Thompson SG. Why sources of heterogeneity in meta-analysis should be investigated. BMJ. 1994; 309:1351–1355.
Article33. Greenland S, Salvan A. Bias in the one-step method for pooling study results. Stat Med. 1990; 9:247–252.
Article34. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article35. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article36. Davey Smith G, Egger M. Meta-analysis. Unresolved issues and future developments. BMJ. 1998; 316:221–225.
Article37. LeLorier J, Gregoire G, Benhaddad A, Lapierre J, Derderian F. Discrepancies between meta-analyses and subsequent large randomized, controlled trials. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:536–542.
Article