Clin Exp Vaccine Res.
2019 Jan;8(1):64-69. 10.7774/cevr.2019.8.1.64.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting anti-pertussis toxin antibody in mouse
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center, GC Pharma, Yongin, Korea.
- 2The Vaccine Bio Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. kjhan@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2438967
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2019.8.1.64
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although the DTaP and Tdap vaccines used to prevent pertussis have been used for a long time, there is no standard method for measuring pertussis antigens. Therefore, this preliminary study was conducted to develop an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method using an animal model for measuring antibodies against pertussis toxin, the most important pertussis pathogenic antigen, in the sera of vaccinated mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
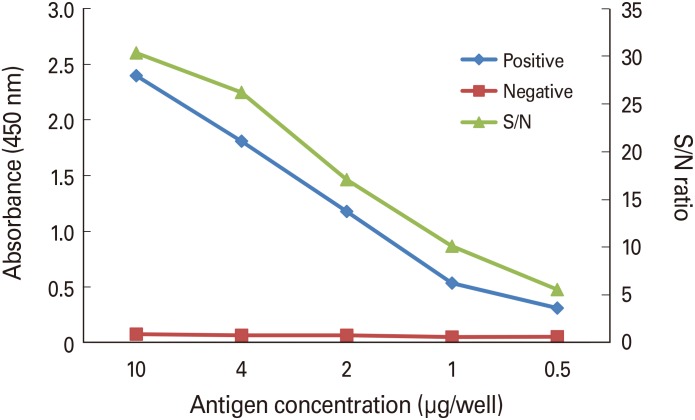
Bordetella pertussis Tohama phase I was cultured for 24-30 hours, and then pertussis toxin was purified from the culture medium by chromatography. Purified pertussis toxin was diluted in phosphate-buffered saline-coating buffer, and 100 µL of diluted pertussis toxin was added to each well and reacted at room temperature for 4 hours. Positive serum was diluted to 1/1,250-1/80,000 and negative serum was diluted to 1/50 to determine the coating concentration with the optimal signal/noise ratio. Optimal test conditions were confirmed from the dilution factors of the secondary antibody and streptavidin horseradish peroxidase (SA-HRP).
RESULTS
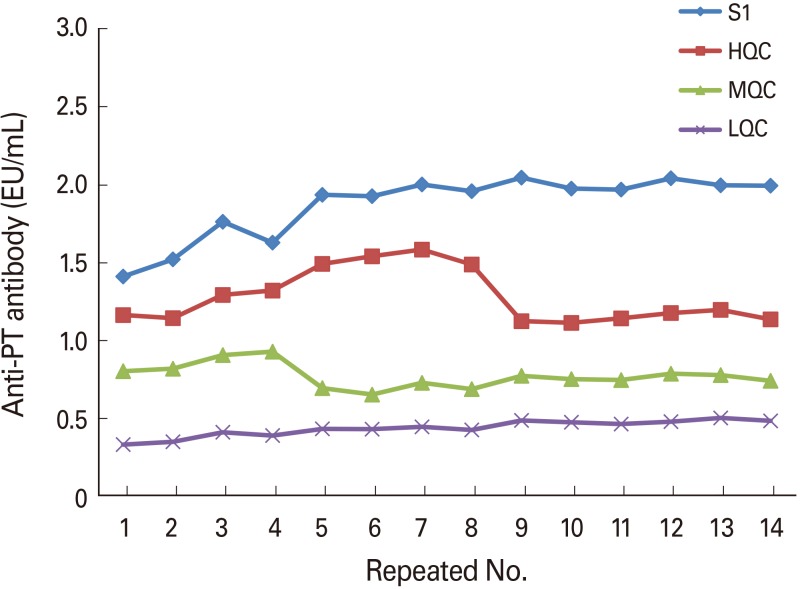
Optimal conditions were as follows: 4 µg/mL for coating antigen; 1/40,000 for secondary antibody; and 1/1,000 for the SA-HRP dilution factor. Comparison of the sera obtained from mice treated with a developing vaccine and commercial vaccine with National Institute for Biological Standard and Control standard serum under the established conditions showed the following results: 1,300.62, 534.94, and 34.85, respectively.
CONCLUSION
The method developed in this study is suitable for measuring anti-pertussis toxin antibodies and may be applicable for clinical sample analysis or indirect diagnosis of pertussis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee JH, Ha YH, Han JW, Lee WB, Lee KS. Pertussis antibodies in the sera of children after acellular pertussis vaccination. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1997; 40:167–172.2. Kwon HJ, Han SB, Kim BR, et al. Assessment of safety and efficacy against Bordetella pertussis of a new tetanus-reduced dose diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine in a murine model. BMC Infect Dis. 2017; 17:247. PMID: 28376777.
Article3. Choi UY, Lee SY, Kwak GY, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of primary and secondary DTaP booster vaccination. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011; 54:979–987.
Article4. Gaines Das R, Xing D, Rigsby P, Newland P, Corbel M. International collaborative study: evaluation of proposed International Reference Reagent of pertussis antiserum (mouse) 97/642. Biologicals. 2001; 29:137–148. PMID: 11580218.
Article5. Dalby T, Petersen JW, Harboe ZB, Krogfelt KA. Antibody responses to pertussis toxin display different kinetics after clinical Bordetella pertussis infection than after vaccination with an acellular pertussis vaccine. J Med Microbiol. 2010; 59(Pt 9):1029–1036. PMID: 20508003.
Article6. Friedman RL, Paulaitis S, McMillan JW. Development of a rapid diagnostic test for pertussis: direct detection of pertussis toxin in respiratory secretions. J Clin Microbiol. 1989; 27:2466–2470. PMID: 2808670.
Article7. Sato H, Sato Y. Bordetella pertussis infection in mice: correlation of specific antibodies against two antigens, pertussis toxin, and filamentous hemagglutinin with mouse protectivity in an intracerebral or aerosol challenge system. Infect Immun. 1984; 46:415–421. PMID: 6542069.
Article8. Redhead K, Watkins J, Barnard A, Mills KH. Effective immunization against Bordetella pertussis respiratory infection in mice is dependent on induction of cell-mediated immunity. Infect Immun. 1993; 61:3190–3198. PMID: 8335349.
Article9. Gates I, DuVall M, Ju H, Tondella ML, Pawloski L. Pertussis Working Group. Development of a qualitative assay for screening of Bordetella pertussis isolates for pertussis toxin production. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0175326. PMID: 28394915.
Article10. Menzies SL, Kadwad V, Pawloski LC, et al. Development and analytical validation of an immunoassay for quantifying serum anti-pertussis toxin antibodies resulting from Bordetella pertussis infection. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009; 16:1781–1788. PMID: 19864485.11. Poirier B, Bornstein N, Andre M, et al. Collaborative study for the establishment of a European Phamacopoeia Biological reference preparation for Bordetella pertussis mouse antiserum for serological potency testing of acellular pertussis vaccines. Biologicals. 2003; 31:25–38. PMID: 12623057.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Investigation on the Immunity to Pertussis in the Korea
- Development and implementation of standardized method for detecting immunogenicity of acellular pertussis vaccines in Korea
- Detection of anti-borrelia burgdorferi antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in Korea
- Immunoassay of Pertussis According to Ages
- Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, indirect immunofluorescent antibody test and indirect immunoperoxidase antibody test in setecting antibodies to rickettsia tsutsugamushi