Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Jan;51(1):408-412. 10.4143/crt.2018.138.
Rare Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in Korean Patients with EGFR-mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. silkahn@skku.edu
- 2Samsung Genome Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Health Science and Technology, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2437631
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.138
Abstract
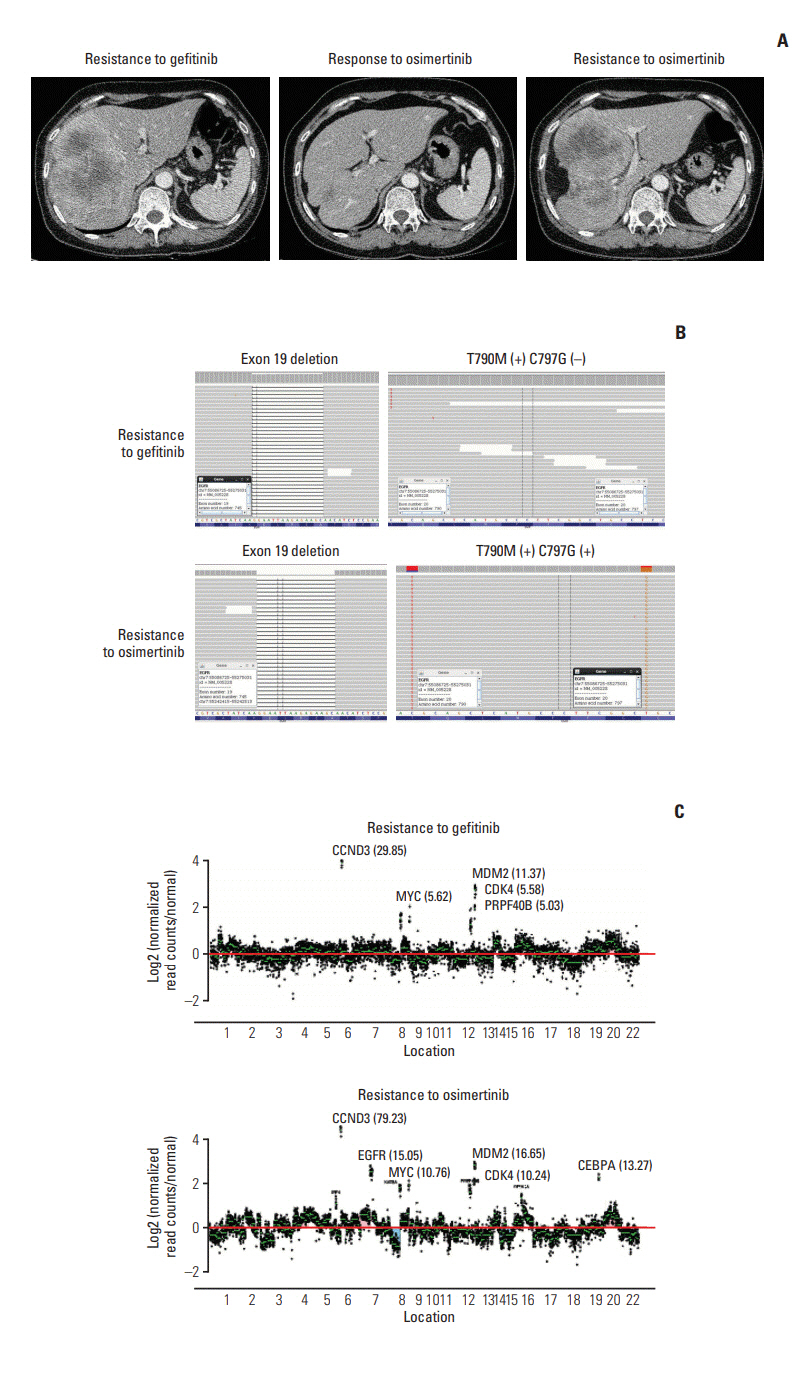
- Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)"’tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are effective clinical therapeutics for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Osimertinib, a thirdgeneration EGFR TKI, has proven effective against T790M mutations. However, the vast majority of patients acquire resistance following successful treatment. A 59-year-old female patient with metastatic NSCLC developed resistance after 43 weeks of osimertinib. CancerSCAN of the metastatic liver lesion revealed a EGFR C797G mutation at an allele frequency of 72%, a preexisting T790M mutation (73%) in cis and an exon 19 deletion (87%). Another 53-year-old female patient developed systemic progression after 10 months of osimertinib. CancerSCAN of the lung biopsy identified an EGFR L718Q mutation at an allele frequency of 7%, concomitant PIK3CA E545K (12.90%) and preexisting EGFR L858R (38%), but loss of the T790M mutation. The heterogeneity of osimertinib resistance mechanisms warrants further investigation into novel or combination agents to overcome the rare acquired resistances.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ohashi K, Maruvka YE, Michor F, Pao W. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant disease. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:1070–80.
Article2. Huang YH, Hsu KH, Tseng JS, Chen KC, Hsu CH, Su KY, et al. The association of acquired T790M mutation with clinical characteristics after resistance to first-line epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 50:1294–303.
Article3. Wang S, Tsui ST, Liu C, Song Y, Liu D. EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to third-generation inhibitors in T790Mpositive non-small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2016; 9:59.
Article4. Ercan D, Choi HG, Yun CH, Capelletti M, Xie T, Eck MJ, et al. EGFR mutations and resistance to irreversible pyrimidinebased EGFR inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 21:3913–23.
Article5. Shin HT, Choi YL, Yun JW, Kim NK, Kim SY, Jeon HJ, et al. Prevalence and detection of low-allele-fraction variants in clinical cancer samples. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:1377.
Article6. Scheffler M, Bos M, Gardizi M, Konig K, Michels S, Fassunke J, et al. PIK3CA mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): genetic heterogeneity, prognostic impact and incidence of prior malignancies. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:1315–26.
Article7. Engelman JA, Mukohara T, Zejnullahu K, Lifshits E, Borras AM, Gale CM, et al. Allelic dilution obscures detection of a biologically significant resistance mutation in EGFR-amplified lung cancer. J Clin Invest. 2006; 116:2695–706.
Article8. Wang J, Wang B, Chu H, Yao Y. Intrinsic resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with activating EGFR mutations. Onco Targets Ther. 2016; 9:3711–26.9. Sun Z, Li Q, Zhang S, Chen J, Huang L, Ren J, et al. NVPBEZ235 overcomes gefitinib-acquired resistance by down-regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR phosphorylation. Onco Targets Ther. 2015; 8:269–77.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acquired Resistance Mechanism of EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication to EGFR TKIs in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Osimertinib Combined with Systemic Chemotherapy for EGFR Mutant, T790M-Negative, Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Who Develop Leptomeningeal Metastases with Extracranial Progression to Prior EGFR TKI
- EGFR C797S as a Resistance Mechanism of Lazertinib in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR T790M Mutation
- Assessment of Anti-tumor Efficacy of Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients by Liquid Biopsy Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid, Plasma, or Pleural Effusion
- Real-World Analysis of the Efficacy of Rebiopsy and EGFR Mutation Test of Tissue and Plasma Samples in Drug-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer