Intest Res.
2018 Oct;16(4):609-618. 10.5217/ir.2018.00044.
Seven days triple therapy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori does not alter the disease activity of patients with inflammatory bowel disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Suita, Japan. shinzaki@gh.med.osaka-u.ac.jp
- 2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan.
- 3Department of Medicine, Shiga University of Medical Science, Otsu, Japan.
- 4Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, The Jikei University School of Medicine Katsushika Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan.
- 5Center for Advanced IBD Research and Treatment, Kitasato University Kitasato Institute Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Osaka Police Hospital, Osaka, Japan.
- 7IBD Center, Sapporo Kosei General Hospital, Sapporo, Japan.
- 8Departments of Gastroenterology and Metabolism, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Nagoya, Japan.
- 9Department of Gastroenterology, Kagawa Prefectural Central Hospital, Takamatsu, Japan.
- 10Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, Kobe, Japan.
- 11Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Saitama Medical Center, Saitama Medical University, Kawagoe, Japan.
- 12Department of Gastroenterology and Hematology, Graduate School of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Toyama, Toyama, Japan.
- 13Department of Gastroenterology, Dokkyo Medical University, Mibu, Japan.
- 14Department of Gastroenterology, National Hospital Organization Osaka National Hospital, Osaka, Japan.
- 15Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama, Japan.
- 16Second Department of Internal Medicine, Osaka Medical College, Takatsuki, Japan.
- 17Department of Internal Medicine, Toho University Sakura Medical Center, Sakura, Japan.
- 18Department of Gastroenterology, Mitoyo General Hospital, Kanonji, Japan.
- 19Department of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Division of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College of Medicine, Nishinomiya, Japan.
- 20Division of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Digestive Disease Center, Kitano Hospital, Osaka, Japan.
- 21Department of Gastroenterology, Toranomon Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
- 22Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mie University Graduate School of Medicine, Tsu, Japan.
- 23Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Gunma University, Maebashi, Japan.
- 24Department of Gastroenterology, Tobata Kyoritsu Hospital, Kitakyushu, Japan.
- 25Department of Gastroenterology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan.
- KMID: 2434163
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2018.00044
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
The influences of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy on the disease course of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are still unclear. We therefore conducted a multicenter, retrospective cohort study to evaluate the safety of H. pylori eradication therapy for IBD patients.
METHODS
IBD patients with H. pylori eradication from 2005 to 2015 (eradication group) and control patients (non-eradication group; 2 paired IBD patients without H. pylori eradication matched with each eradicated patient) were included. IBD exacerbation (increased/additional IBD drug or IBD-associated hospitalization/surgery) and disease improvement based on the physicians' global assessment were investigated at baseline, and at 2 and 6 months after eradication or observation.
RESULTS
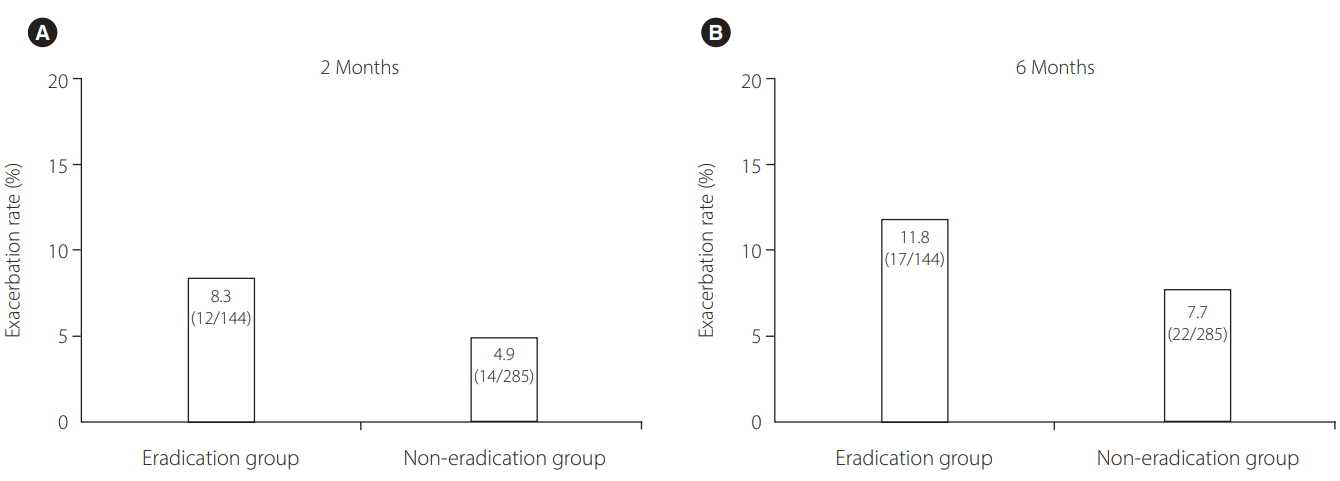
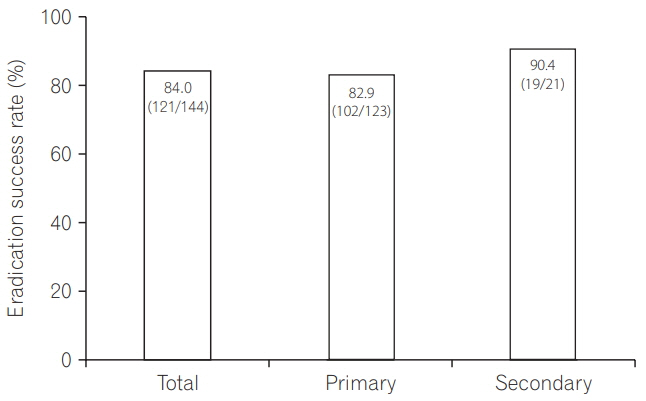
A total of 429 IBD (378 ulcerative colitis, 51 Crohn's disease) patients, comprising 144 patients in the eradication group and 285 patients in the non-eradication group, were enrolled at 25 institutions. IBD exacerbation was comparable between groups (eradication group: 8.3% at 2 months [odds ratio, 1.76; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-3.92; P=0.170], 11.8% at 6 months [odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.81-3.11; P=0.172]). Based on the physicians' global assessment at 2 months, none of the patients in the eradication group improved, whereas 3.2% of the patients in the non-eradication group improved (P=0.019). Multivariate analysis revealed that active disease at baseline, but not H. pylori eradication, was an independent factor for IBD exacerbation during 2 months' observation period. The overall eradication rate was 84.0%-comparable to previous reports in non-IBD patients.
CONCLUSIONS
H. pylori eradication therapy does not alter the short-term disease activity of IBD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kostic AD, Xavier RJ, Gevers D. The microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: current status and the future ahead. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:1489–1499.
Article2. Dave M, Purohit T, Razonable R, Loftus EV Jr. Opportunistic infections due to inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014; 20:196–212.
Article3. Ng SC, Chan FK. Infections and inflammatory bowel disease: challenges in Asia. J Dig Dis. 2013; 14:567–573.
Article4. Nagao-Kitamoto H, Kitamoto S, Kuffa P, Kamada N. Pathogenic role of the gut microbiota in gastrointestinal diseases. Intest Res. 2016; 14:127–138.
Article5. Warren JR, Marshall B. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983; 1:1273–1275.6. Marshall BJ, Goodwin CS, Warren JR, et al. Prospective doubleblind trial of duodenal ulcer relapse after eradication of Campylobacter pylori. Lancet. 1988; 2:1437–1442.
Article7. Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:784–789.
Article8. Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain CA, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut. 2017; 66:6–30.
Article9. Stolte M. Helicobacter pylori eradication in long-term users of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet. 1998; 352:2016.
Article10. Franchini M, Cruciani M, Mengoli C, Pizzolo G, Veneri D. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on platelet count in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:237–246.
Article11. Nishida T, Tsujii M, Tanimura H, et al. Comparative study of esomeprazole and lansoprazole in triple therapy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in Japan. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:4362–4369.
Article12. Asaoka D, Nagahara A, Matsuhisa T, et al. Trends of secondline eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori in Japan: a multicenter study in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Helicobacter. 2013; 18:468–472.
Article13. Miwa H, Ohkura R, Murai T, et al. Impact of rabeprazole, a new proton pump inhibitor, in triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection-comparison with omeprazole and lansoprazole. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999; 13:741–746.
Article14. Maldonado-Contreras A, Goldfarb KC, Godoy-Vitorino F, et al. Structure of the human gastric bacterial community in relation to Helicobacter pylori status. ISME J. 2011; 5:574–579.
Article15. Yap TW, Gan HM, Lee YP, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication causes perturbation of the human gut microbiome in young adults. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0151893. doi: 10.1371/journal. pone.0151893.
Article16. Sonnenberg A, Genta RM. Low prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 35:469–476.17. Ohkusa T, Kato K, Terao S, et al. Newly developed antibiotic combination therapy for ulcerative colitis: a double-blind placebo-controlled multicenter trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:1820–1829.
Article18. Asaka M, Kato M, Takahashi S, et al. Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: 2009 revised edition. Helicobacter. 2010; 15:1–20.
Article19. Rachmilewitz D. Coated mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid) versus sulphasalazine in the treatment of active ulcerative colitis: a randomised trial. BMJ. 1989; 298:82–86.
Article20. Lichtiger S, Present DH, Kornbluth A, et al. Cyclosporine in severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330:1841–1845.
Article21. Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F Jr. Development of a Crohn’s disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976; 70:439–444.22. Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, et al. Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of inflammatory bowel disease: report of a Working Party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005; 19 Suppl A:5A–36A.
Article23. Current European concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht Consensus report. European Helicobacter Pylori Study Group. Gut. 1997; 41:8–13.24. Lahat A, Kopylov U, Neuman S, et al. Helicobacter pylori prevalence and clinical significance in patients with quiescent Crohn’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017; 17:27.
Article25. Wu XW, Ji HZ, Yang MF, Wu L, Wang FY. Helicobacter pylori infection and inflammatory bowel disease in Asians: a metaanalysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:4750–4756.
Article26. Sustmann A, Okuda M, Koletzko S. Helicobacter pylori in children. Helicobacter. 2016; 21 Suppl 1:49–54.27. Freedberg DE, Toussaint NC, Chen SP, et al. Proton pump inhibitors alter specific taxa in the human gastrointestinal microbiome: a crossover trial. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149:883–885. e9.
Article28. Sartor RB. Therapeutic manipulation of the enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel diseases: antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1620–1633.
Article29. Loh G, Blaut M. Role of commensal gut bacteria in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut Microbes. 2012; 3:544–555.
Article30. Khan KJ, Ullman TA, Ford AC, et al. Antibiotic therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:661–673.
Article31. Lamouliatte H, Mégraud F, Delchier JC, et al. Second-line treatment for failure to eradicate Helicobacter pylori: a randomized trial comparing four treatment strategies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 18:791–797.
Article32. Nagahara A, Miwa H, Ohkura R, et al. Strategy for retreatment of therapeutic failure of eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 16:613–618.
Article33. Sharif F, McDermott M, Dillon M, et al. Focally enhanced gastritis in children with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:1415–1420.
Article34. Li Q, Liu J, Gong Y, Yuan Y. Association of CagA EPIYA-D or EPIYA-C phosphorylation sites with peptic ulcer and gastric cancer risks: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e6620. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006620.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- First-line Helicobacter pylori Eradication with Standard Triple Therapy and Concomitant Therapy: A Retrospective Study
- Helicobacter pylori and Other Gastrointestinal Diseases
- Changes in the Eradication Rate of Conventional Triple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection in Korea
- Ten Years Retrospective Study about Helicobacter pylori Eradication Rate
- Recent Trends of Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy: Focusing on First Line Treatment