Urogenit Tract Infect.
2018 Dec;13(3):51-57. 10.14777/uti.2018.13.3.51.
Preventive Effect of Lactobacillus Fermentation Extract on Inflammation and Cytokine Production in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cystitis in Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wowhana@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2431248
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2018.13.3.51
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The effects of Lactobacillus fermentation extract (LFE) on cystitis induced by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the mouse bladder were investigated by pathological analyses and measurement of the levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-18 (IL-18).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
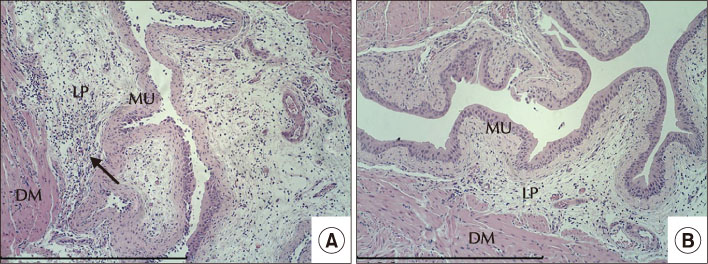
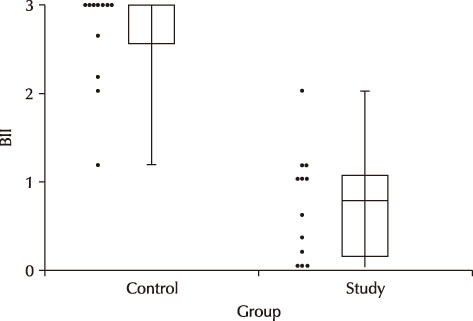
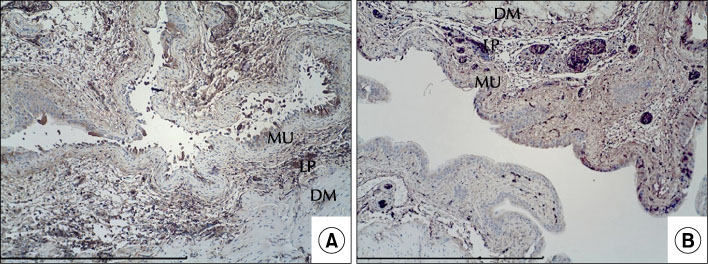
LFE was administered orally (5 µg/L) to mice for 10 days after which the study group (n=12) received transurethral injection of 5 µg/L LPS. The bladder tissue was then harvested after 24 hours and subjected to hematoxylin and eosin staining. A semi-quantitative score was used to evaluate inflammation (bladder inflammation index, BII). TNF-α immunohistochemical staining and multiplex cytokine assays were also performed. TNF-α and IL-18 levels were determined. The results were compared with those of the control group (n=12).
RESULTS
The BII in the control and study groups was 2.7±0.5 and 1.1±0.7, respectively, with the control group scores differing significantly from the study group scores (p<0.001). TNF-α immunohistochemical staining results were similar. The TNF-α levels determined by the multiplex cytokine assay were 2.82±1.35 pg/mg and 1.55±0.56 pg/mg for the control and study groups, respectively, and the difference between these groups was statistically significant (p=0.007).
CONCLUSIONS
Oral administration of LFE appears to have a preventive effect against the inflammatory responses and TNF-α expression induced by transurethral instillation of LPS in the mouse bladder. Further studies are required to determine the clinical application of this finding.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pai H. Treatment of community-acquired uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Korean J Med. 2011; 81:685–689.2. Kim TH. The choice of empirical treatment of uncomplicated cystitis: no longer free ride. Infect Chemother. 2012; 44:323–327.
Article3. Barrons R, Tassone D. Use of Lactobacillus probiotics for bacterial genitourinary infections in women: a review. Clin Ther. 2008; 30:453–468.
Article4. Ryu KH, Kim MK, Jeong YB. A recent study on the antimicrobial sensitivity of the organisms that cause urinary tract infection. Korean J Urol. 2007; 48:638–645.
Article5. Kim HY, Yim SH, Cho HJ, Kim JS, Ha US, Kim DB, et al. Changes in causative organisms and antibiotic sensitivity in intensive care unit-acquired urinary tract infection. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:1108–1113.
Article6. Olson NC, Hellyer PW, Dodam JR. Mediators and vascular effects in response to endotoxin. Br Vet J. 1995; 151:489–522.7. Jerde TJ, Bjorling DE, Steinberg H, Warner T, Saban R. Determination of mouse bladder inflammatory response to E. coli lipopolysaccharide. Urol Res. 2000; 28:269–273.
Article8. Saban MR, Saban R, Hammond TG, Haak-Frendscho M, Steinberg H, Tengowski MW, et al. LPS-sensory peptide communication in experimental cystitis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002; 282:F202–F210.
Article9. Gracie JA, Robertson SE, McInnes IB. Interleukin-18. J Leukoc Biol. 2003; 73:213–224.
Article10. Hochholzer P, Lipford GB, Wagner H, Pfeffer K, Heeg K. Role of interleukin-18 (IL-18) during lethal shock: decreased lipopolysaccharide sensitivity but normal superantigen reaction in IL-18-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 2000; 68:3502–3508.
Article11. Smaldone MC, Vodovotz Y, Tyagi V, Barclay D, Philips BJ, Yoshimura N, et al. Multiplex analysis of urinary cytokine levels in rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Urology. 2009; 73:421–426.
Article12. Corcoran AT, Yoshimura N, Tyagi V, Jacobs B, Leng W, Tyagi P. Mapping the cytokine profile of painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis in human bladder and urine specimens. World J Urol. 2013; 31:241–246.
Article13. Lewis RE, Kunz AL, Bell RE. Error of intraperitoneal injections in rats. Lab Anim Care. 1966; 16:505–509.14. Larsson PG, Forsum U. Bacterial vaginosis--a disturbed bacterial flora and treatment enigma. APMIS. 2005; 113:305–316.
Article15. Lee NS, Lee SJ, Cho YH, Han CH. Antimicrobial effect of Lactobacillus in a rat model of Escherichia coli urinary tract infection: a preliminary study. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:1253–1257.
Article16. Asahara T, Nomoto K, Watanuki M, Yokokura T. Antimicrobial activity of intraurethrally administered probiotic Lactobacillus casei in a murine model of Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:1751–1760.
Article17. Kontiokari T, Sundqvist K, Nuutinen M, Pokka T, Koskela M, Uhari M. Randomised trial of cranberry-lingonberry juice and Lactobacillus GG drink for the prevention of urinary tract infections in women. BMJ. 2001; 322:1571.
Article18. Lee SJ, Lee CH, Kim SW, Cho YH, Yoon MS. Immunostimulating and prophylactic effect of Escherichia coli extract in a mouse model of lipopolysaccharide-induced cystitis. Korean J Urol. 2004; 45:1049–1055.19. Lee JW, Kim YW, Huh JS, Lee SJ. Protective effect of hyaluronic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in rats. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:797–804.
Article20. Schiffrin EJ, Rochat F, Link-Amster H, Aeschlimann JM, Donnet-Hughes A. Immunomodulation of human blood cells following the ingestion of lactic acid bacteria. J Dairy Sci. 1995; 78:491–497.
Article21. Fischer S, Scheffler A, Kabelitz D. Stimulation of the specific immune system by mistletoe extracts. Anticancer Drugs. 1997; 8:Suppl 1. S33–S37.
Article22. Hathout AS, Mohamed SR, El-Nekeety AA, Hassan NS, Aly SE, Abdel-Wahhab MA. Ability of Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus reuteri to protect against oxidative stress in rats fed aflatoxinscontaminated diet. Toxicon. 2011; 58:179–186.
Article23. Kim HJ, Vazquez Roque MI, Camilleri M, Stephens D, Burton DD, Baxter K, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a probiotic combination VSL# 3 and placebo in irritable bowel syndrome with bloating. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2005; 17:687–696.
Article24. Takano T. Anti-hypertensive activity of fermented dairy products containing biogenic peptides. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002; 82:333–340.
Article25. Meisel H, Bockelmann W. Bioactive peptides encrypted in milk proteins: proteolytic activation and thropho-functional properties. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1999; 76:207–215.
Article26. Leblanc J, Fliss I, Matar C. Induction of a humoral immune response following an Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection with an immunomodulatory peptidic fraction derived from Lactobacillus helveticus-fermented milk. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004; 11:1171–1181.
Article27. Thomas CM, Hong T, van Pijkeren JP, Hemarajata P, Trinh DV, Hu W, et al. Histamine derived from probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri suppresses TNF via modulation of PKA and ERK signaling. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e31951.
Article28. Stein PC, Pham H, Ito T, Parsons CL. Bladder injury model induced in rats by exposure to protamine sulfate followed by bacterial endotoxin. J Urol. 1996; 155:1133–1138.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunostimulating and Prophylactic Effect of Escherichia coli Extract in a Mouse Model of Lipopolysaccharide-induced Cystitis
- Anti-inflammatory Effect of Escherichia coli Extract and Green Tea in a Mouse Model of Cystitis
- Coptis chinensis Extract Inhibits the Production of Inflammatory Mediators and Delayed Type Hypersensitivity in Mice
- Mitigation effects of red Platycodon grandiflorum extract on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in splenocytes isolated from mice
- The effect of rosehip extract on TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-8 production in THP-1-derived macrophages infected with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans