Lab Anim Res.
2018 Mar;34(1):37-43. 10.5625/lar.2018.34.1.37.
Protective effects of cultured and fermented ginseng extracts against scopolamine-induced memory loss in a mouse model
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine and Research Institute of Veterinary Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. beomjun@cbu.ac.kr
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine and Institute of Animal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Chinju, Korea. hujang@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2430884
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2018.34.1.37
Abstract
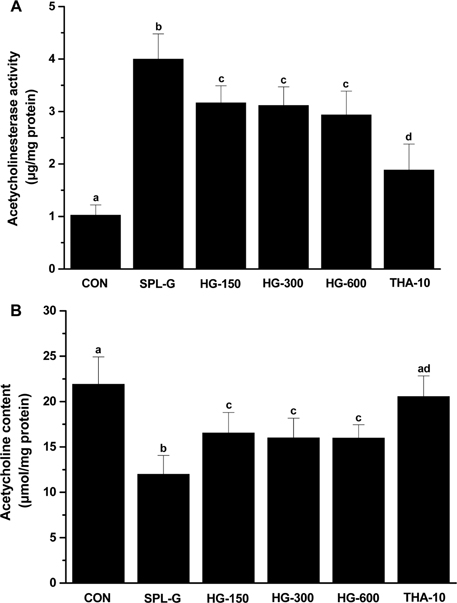
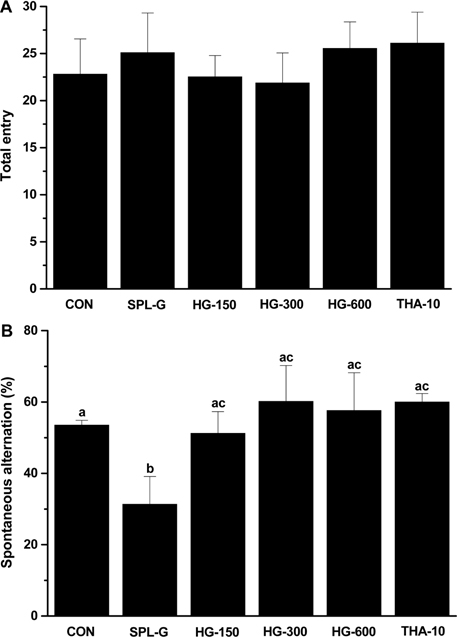
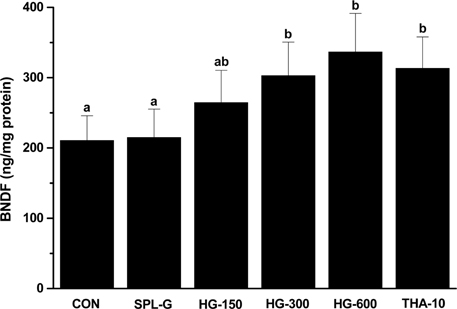
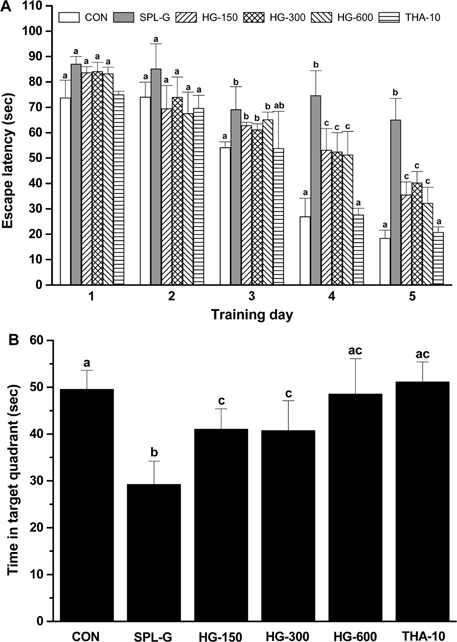
- This study was performed to investigate the effect of a concentrate of fermented wild ginseng root culture (HLJG0701) on memory improvement in the scopolamine (SPL)-induced memory-deficient mouse model. Eight-week-old male ICR mice were used to evaluate the protective effect of HLJG0701 against the SPL-induced memory loss animal model. The Morris water maze test, which measures hippocampus-dependent learning ability, and the Y-maze test, a short-term memory assessment test, were performed and related markers were analyzed. HLJG0701-treated groups displayed significantly reduced acetylcholinesterase activity and increased acetylcholine level compared with the SPL-administered group (SPL-G) (P < 0.05). In the Y-maze test, the spontaneous alternation in al HLJG0711-treated groups was significantly increased compared with that in SPL-G (P < 0.05). In the Morris water maze test, the escape latency and time spent in the target quadrant in all HLJG0701-treated groups were significantly decreased and increased, respectively, compared with those in SPL-G (P < 0.05). In addition, the brain-derived neurotrophic factor level in groups treated with HLJG0701 300 and 600 mg/kg body weight was significantly increased compared with that in SPL-G (P < 0.05). These results suggest that the HLJG0701 may protect against memory loss by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase activity and preventing acetylcholine deficiency.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholinesterase
Animals
Body Weight
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
Ginsenosides
Humans
Learning
Male
Memory Disorders*
Memory*
Memory, Short-Term
Mice*
Mice, Inbred ICR
Models, Animal
Panax*
Scopolamine Hydrobromide
United Nations
Water
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholinesterase
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
Ginsenosides
Scopolamine Hydrobromide
Water
Figure
Reference
-
1. Monti JM, Baym CL, Cohen NJ. Identifying and characterizing the effects of nutrition on hippocampal memory. Adv Nutr. 2014; 5(3):337S–343S.
Article2. Oh SK. Neurotransmitters and brain disease. Seoul: Shinil Books Company;2005. p. 345–364.3. Fratiglioni L, Winblad B, von Strauss E. Prevention of Alzheimer's disease and dementia. Major findings from the Kungsholmen Project. Physiol Behav. 2007; 92(1-2):98–104.
Article4. Bohnen NI, Albin RL. The cholinergic system and Parkinson disease. Behav Brain Res. 2011; 221(2):564–573.
Article5. Schliebs R, Arendt T. The cholinergic system in aging and neuronal degeneration. Behav Brain Res. 2011; 221(2):555–563.
Article6. Klinkenberg I, Blokland A. The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: a review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010; 34(8):1307–1350.
Article7. Oh JH, Choi BJ, Chang MS, Park SK. Nelumbo nucifera semen extract improves memory in rats with scopolamine-induced amnesia through the induction of choline acetyltransferase expression. Neurosci Lett. 2009; 461(1):41–44.
Article8. Han JY, Chung KH, Ryu GH. Comparison of physicochemical properties and release characteristics of extruded tissue cultured mountain ginseng. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2008; 37(8):1018–1024.
Article9. Zhu G, Wang Y, Li J, Wang J. Chronic treatment with ginsenoside Rg1 promotes memory and hippocampal long-term potentiation in middle-aged mice. Neuroscience. 2015; 292:81–89.
Article10. Niu J, Pi ZF, Yue H, Yang H, Wang Y, Yu Q, Liu SY. Effect of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 on streptozotocin-induced experimental type 2 diabetic rats: A urinary metabonomics study by rapid-resolution liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2012; 26(23):2683–2689.
Article11. Leung KW, Wong AS. Pharmacology of ginsenosides: a literature review. Chin Med. 2010; 5:20.
Article12. Bai Y, Gänzle MG. Conversion of ginsenosides by Lactobacillus plantarum studied by liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole trap mass spectrometry. Food Res Int. 2015; 76(Pt 3):709–718.13. Shin EJ, Cho CW, Kim YE, Han D, Hong HD, Rhee YK. Evaluation of functional properties of the tissue cultured wild ginseng fermented by Lactobacillus sp. Korean J Food Cult. 2012; 27(6):743–750.14. Panza F, Lozupone M, Solfrizzi V, Stallone R, Bellomo A, Greco A, Daniele A, Seripa D, Logroscino G. Cognitive frailty: a potential target for secondary prevention of dementia. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017; 13(10):1023–1027.
Article15. Rakesh G, Szabo ST, Alexopoulos GS, Zannas AS. Strategies for dementia prevention: latest evidence and implications. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2017; 8(8-9):121–136.
Article16. Wittstock M, Zettl UK. Adverse effects of treatment with intravenous immunoglobulins for neurological diseases. J Neurol. 2006; 253:Suppl 5. V75–V79.
Article17. Farlow M, Gracon SI, Hershey LA, Lewis KW, Sadowsky CH, Dolan-Ureno J. A controlled trial of tacrine in Alzheimer's disease. JAMA. 1992; 268(18):2523–2529.
Article18. Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1984; 11(1):47–60.
Article19. Kim DH, Jeon SJ, Son KH, Jung JW, Lee S, Yoon BH, Lee JJ, Cho YW, Cheong JH, Ko KH, Ryu JH. The ameliorating effect of oroxylin A on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007; 87(4):536–546.
Article20. Jahn H. Memory loss in Alzheimer's disease. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2013; 15(4):445–454.
Article21. Terry AV Jr, Mahadik SP. Time-dependent cognitive deficits associated with first and second generation antipsychotics: cholinergic dysregulation as a potential mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007; 320(3):961–968.
Article22. Remya C, Dileep KV, Tintu I, Variyar EJ, Sadasivan C. Flavanone glycosides as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: computational and experimental evidence. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2014; 76(6):567–570.23. Colović MB, Krstić DZ, Lazarević-Pašti TD, Bondžić AM, Vasiæ VM. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: pharmacology and toxicology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2013; 11(3):315–335.24. Wang Q, Sun LH, Jia W, Liu XM, Dang HX, Mai WL, Wang N, Steinmetz A, Wang YQ, Xu CL. Comparison of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1 for their effects on improving scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment in mice. Phytother Res. 2010; 24(12):1748–1754.
Article25. Kim J, Shim J, Lee S, Cho WH, Hong E, Lee JH, Han JS, Lee HJ, Lee KW. Rg3-enriched ginseng extract ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning deficits in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016; 16:66.
Article26. Al-Hazmi MA, Rawi SM, Arafa NM, Wagas A, Montasser AO. The potent effects of ginseng root extract and memantine on cognitive dysfunction in male albino rats. Toxicol Ind Health. 2015; 31(6):494–509.
Article27. Jeong HS, Lim CS, Cha BC, Choi SH, Kwon KR. Component analysis of cultivated ginseng, cultivated wild ginseng, and wild ginseng and the change of ginsenoside components in the process of red ginseng. J Pharmacopuncture. 2010; 13(1):63–77.
Article28. Nagahara AH, Merrill DA, Coppola G, Tsukada S, Schroeder BE, Shaked GM, Wang L, Blesch A, Kim A, Conner JM, Rockenstein E, Chao MV, Koo EH, Geschwind D, Masliah E, Chiba AA, Tuszynski MH. Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med. 2009; 15(3):331–337.
Article29. Konar A, Shah N, Singh R, Saxena N, Kaul SC, Wadhwa R, Thakur MK. Protective role of Ashwagandha leaf extract and its component withanone on scopolamine-induced changes in the brain and brain-derived cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6(11):e27265.
Article30. Zhao HF, Li Q, Li Y. Long-term ginsenoside administration prevents memory loss in aged female C57BL/6J mice by modulating the redox status and up-regulating the plasticity-related proteins in hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2011; 183:189–202.
Article31. Lee Y, Oh S. Administration of red ginseng ameliorates memory decline in aged mice. J Ginseng Res. 2015; 39(3):250–256.
Article32. Dela Peña IJI, Kim HJ, Botanas CJ, de la Peña JB, Van Le TH, Nguyen MD, Park JH, Cheong JH. The psychopharmacological activities of Vietnamese ginseng in mice: characterization of its psychomotor, sedative-hypnotic, antistress, anxiolytic, and cognitive effects. J Ginseng Res. 2017; 41(2):201–208.
Article33. Peña ID, Yoon SY, Kim HJ, Park S, Hong EY, Ryu JH, Park IH, Cheong JH. Effects of ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in mice. J Ginseng Res. 2014; 38(1):1–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Withdrawal: Protective effects of cultured and fermented ginseng extracts against scopolamine-induced memory loss in a mouse model
- Erratum: Protective effects of cultured and fermented ginseng extracts against scopolamine-induced memory loss in a mouse model
- A Novel Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor, 4-FHA, Improves Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive and Memory Impairment in Mice
- Vanillin and 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol attenuate cognitive impairment and the reduction of cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of scopolamine-induced amnesia
- Protective Effect of Ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 Against beta Amyloid ( 25-35 )-Induced Neurotoxicity on B103 cells