Korean J Radiol.
2017 ;18(4):699-709. 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.4.699.
Efficacy of Maximum Intensity Projection of Contrast-Enhanced 3D Turbo-Spin Echo Imaging with Improved Motion-Sensitized Driven-Equilibrium Preparation in the Detection of Brain Metastases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Korea. byungse.choi@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul 02447, Korea.
- KMID: 2427239
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2017.18.4.699
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
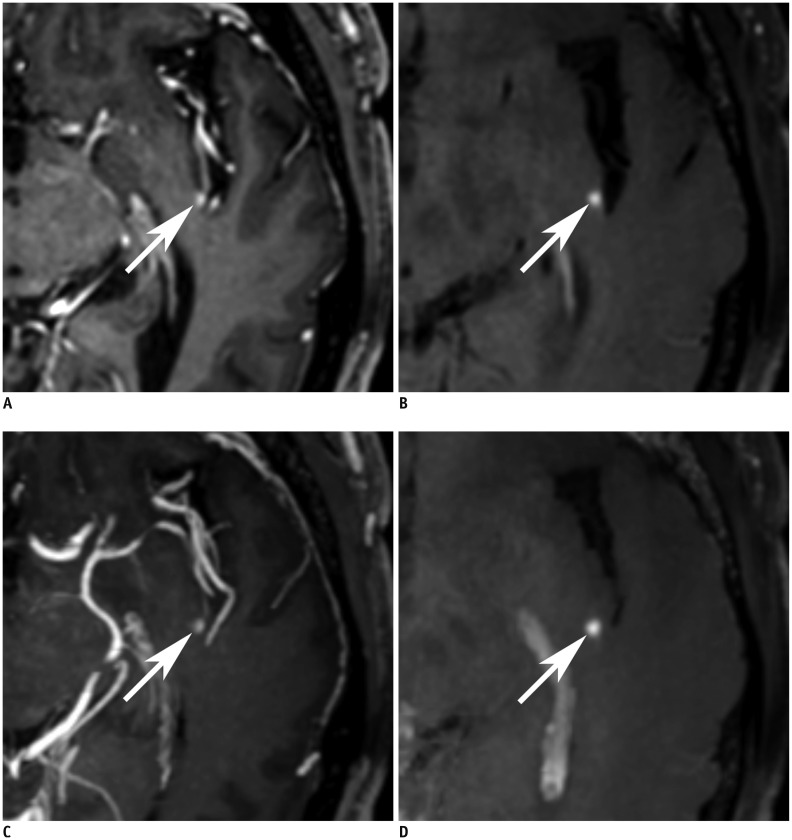
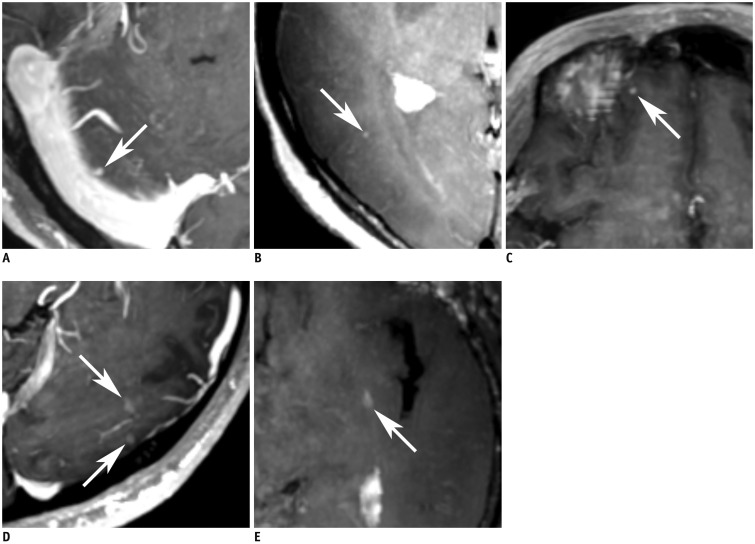
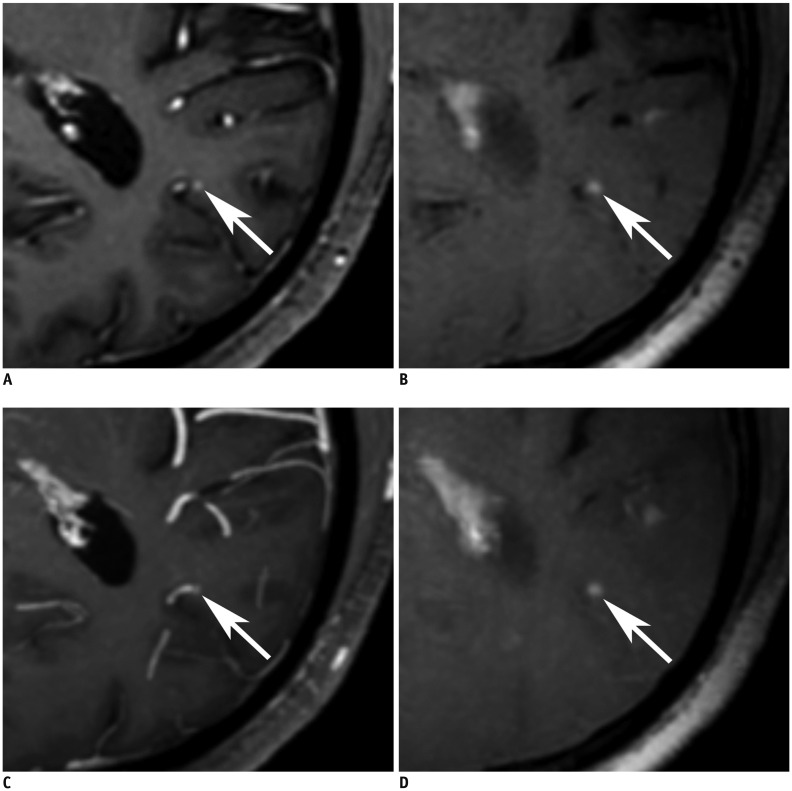
To evaluate the diagnostic benefits of 5-mm maximum intensity projection of improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium prepared contrast-enhanced 3D T1-weighted turbo-spin echo imaging (MIP iMSDE-TSE) in the detection of brain metastases. The imaging technique was compared with 1-mm images of iMSDE-TSE (non-MIP iMSDE-TSE), 1-mm contrast-enhanced 3D T1-weighted gradient-echo imaging (non-MIP 3D-GRE), and 5-mm MIP 3D-GRE.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
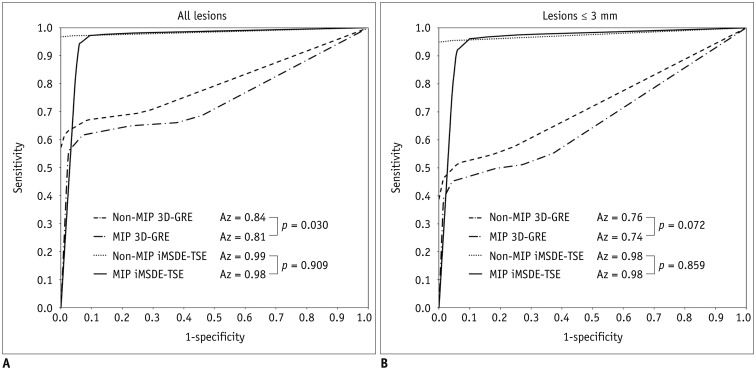
From October 2014 to July 2015, 30 patients with 460 enhancing brain metastases (size > 3 mm, n = 150; size ≤ 3 mm, n = 310) were scanned with non-MIP iMSDE-TSE and non-MIP 3D-GRE. We then performed 5-mm MIP reconstruction of these images. Two independent neuroradiologists reviewed these four sequences. Their diagnostic performance was compared using the following parameters: sensitivity, reading time, and figure of merit (FOM) derived by jackknife alternative free-response receiver operating characteristic analysis. Interobserver agreement was also tested.
RESULTS
The mean FOM (all lesions, 0.984; lesions ≤ 3 mm, 0.980) and sensitivity ([reader 1: all lesions, 97.3%; lesions ≤ 3 mm, 96.2%], [reader 2: all lesions, 97.0%; lesions ≤ 3 mm, 95.8%]) of MIP iMSDE-TSE was comparable to the mean FOM (0.985, 0.977) and sensitivity ([reader 1: 96.7, 99.0%], [reader 2: 97, 95.3%]) of non-MIP iMSDE-TSE, but they were superior to those of non-MIP and MIP 3D-GREs (all, p < 0.001). The reading time of MIP iMSDE-TSE (reader 1: 47.7 ± 35.9 seconds; reader 2: 44.7 ± 23.6 seconds) was significantly shorter than that of non-MIP iMSDE-TSE (reader 1: 78.8 ± 43.7 seconds, p = 0.01; reader 2: 82.9 ± 39.9 seconds, p < 0.001). Interobserver agreement was excellent (κ> 0.75) for all lesions in both sequences.
CONCLUSION
MIP iMSDE-TSE showed high detectability of brain metastases. Its detectability was comparable to that of non-MIP iMSDE-TSE, but it was superior to the detectability of non-MIP/MIP 3D-GREs. With a shorter reading time, the false-positive results of MIP iMSDE-TSE were greater. We suggest that MIP iMSDE-TSE can provide high diagnostic performance and low false-positive rates when combined with 1-mm sequences.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Age of Data in Contemporary Research Articles Published in Representative General Radiology Journals
Ji Hun Kang, Dong Hwan Kim, Seong Ho Park, Jung Hwan Baek
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(6):1172-1178. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1172.
Reference
-
1. Posner JB, Chernik NL. Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol. 1978; 19:579–592. PMID: 570349.2. Nagao E, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A, Obara M, Yamashita K, Kamano H, et al. 3D turbo spin-echo sequence with motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium preparation for detection of brain metastases on 3T MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:664–670. PMID: 21292797.
Article3. Kwak HS, Hwang S, Chung GH, Song JS, Choi EJ. Detection of small brain metastases at 3 T: comparing the diagnostic performances of contrast-enhanced T1-weighted SPACE, MPRAGE, and 2D FLASH imaging. Clin Imaging. 2015; 39:571–575. PMID: 25770904.
Article4. Nussbaum ES, Djalilian HR, Cho KH, Hall WA. Brain metastases. Histology, multiplicity, surgery, and survival. Cancer. 1996; 78:1781–1788. PMID: 8859192.
Article5. Chang WS, Kim HY, Chang JW, Park YG, Chang JH. Analysis of radiosurgical results in patients with brain metastases according to the number of brain lesions: is stereotactic radiosurgery effective for multiple brain metastases? J Neurosurg. 2010; 113(Suppl):73–78. PMID: 21121789.
Article6. Yoshida A, Tha KK, Fujima N, Zaitsu Y, Yoshida D, Tsukahara A, et al. Detection of brain metastases by 3-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging at 3 T: comparison between T1-weighted volume isotropic turbo spin echo acquisition and 3-dimensional T1-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2013; 37:84–90. PMID: 23321838.7. Sills AK. Current treatment approaches to surgery for brain metastases. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57(5 Suppl):S24–S32. discusssion S1-S4. PMID: 16237284.
Article8. Linskey ME, Andrews DW, Asher AL, Burri SH, Kondziolka D, Robinson PD, et al. The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol. 2010; 96:45–68. PMID: 19960227.
Article9. Suh CH, Jung SC, Kim KW, Pyo J. The detectability of brain metastases using contrast-enhanced spin-echo or gradient-echo images: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurooncol. 2016; 129:363–371. PMID: 27324495.
Article10. Kakeda S, Korogi Y, Hiai Y, Ohnari N, Moriya J, Kamada K, et al. Detection of brain metastasis at 3T: comparison among SE, IR-FSE and 3D-GRE sequences. Eur Radiol. 2007; 17:2345–2351. PMID: 17318603.
Article11. Furutani K, Harada M, Mawlan M, Nishitani H. Difference in enhancement between spin echo and 3-dimensional fast spoiled gradient recalled acquisition in steady state magnetic resonance imaging of brain metastasis at 3-T magnetic resonance imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008; 32:313–319. PMID: 18379324.
Article12. Komada T, Naganawa S, Ogawa H, Matsushima M, Kubota S, Kawai H, et al. Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of metastatic brain tumor at 3 tesla: utility of T(1)-weighted SPACE compared with 2D spin echo and 3D gradient echo sequence. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2008; 7:13–21. PMID: 18460844.
Article13. Park J, Kim J, Yoo E, Lee H, Chang JH, Kim EY. Detection of small metastatic brain tumors: comparison of 3D contrast-enhanced whole-brain black-blood imaging and MP-RAGE imaging. Invest Radiol. 2012; 47:136–141. PMID: 22104961.14. Yoneyama M, Nakamura M, Tabuchi T, Takemura A, Obara M, Tatsuno S, et al. Whole-brain black-blood imaging with magnetization-transfer prepared spin echo-like contrast: a novel sequence for contrast-enhanced brain metastasis screening at 3T. Radiol Phys Technol. 2013; 6:431–436. PMID: 23645471.
Article15. Yoneyama M, Nakamura M, Takahara T, Takemura A, Obara M, Tabuchi T, et al. Improvement of T1 contrast in whole-brain black-blood imaging using motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium prepared 3D turbo spin echo (3D MSDE-TSE). Magn Reson Med Sci. 2014; 13:61–65. PMID: 24492739.
Article16. Lee S, Park DW, Lee JY, Lee YJ, Kim T. Improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium preparation for 3D turbo spin echo T1 weighted imaging after gadolinium administration for the detection of brain metastases on 3T MRI. Br J Radiol. 2016; 89:20150176. PMID: 27187597.17. Obara M, Van Cauteren M, Honda M, Imai Y, Kuroda K. Assessment of improved motion-sensitized driven equilibrium (iMSDE) for multi-contrast vessel wall screening. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2014; 13:139–144. PMID: 24769630.
Article18. Wang J, Yarnykh VL, Yuan C. Enhanced image quality in black-blood MRI using the improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium (iMSDE) sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010; 31:1256–1263. PMID: 20432365.
Article19. Jankowski A, Martinelli T, Timsit JF, Brambilla C, Thony F, Coulomb M, et al. Pulmonary nodule detection on MDCT images: evaluation of diagnostic performance using thin axial images, maximum intensity projections, and computer-assisted detection. Eur Radiol. 2007; 17:3148–3156. PMID: 17763856.
Article20. Jensen CT, Vicens-Rodriguez RA, Wagner-Bartak NA, Fox PS, Faria SC, Carrion I, et al. Multidetector CT detection of peritoneal metastases: evaluation of sensitivity between standard 2.5 mm axial imaging and maximum-intensity-projection (MIP) reconstructions. Abdom Imaging. 2015; 40:2167–2172. PMID: 25666971.21. Park EA, Goo JM, Lee JW, Kang CH, Lee HJ, Lee CH, et al. Efficacy of computer-aided detection system and thin-slab maximum intensity projection technique in the detection of pulmonary nodules in patients with resected metastases. Invest Radiol. 2009; 44:105–113. PMID: 19034026.
Article22. Yoneda K, Ueno J, Nishihara S, Tsujikawa T, Morita N, Otsuka H, et al. Postprocessing technique with MDCT data improves the accuracy of the detection of lung nodules. Radiat Med. 2007; 25:511–515. PMID: 18085401.
Article23. Chakraborty DP, Berbaum KS. Observer studies involving detection and localization: modeling, analysis, and validation. Med Phys. 2004; 31:2313–2330. PMID: 15377098.
Article24. Chakraborty DP. Analysis of location specific observer performance data: validated extensions of the jackknife free-response (JAFROC) method. Acad Radiol. 2006; 13:1187–1193. PMID: 16979067.
Article25. Kim M, Kim HS. Emerging techniques in brain tumor imaging: what radiologists need to know. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:598–619. PMID: 27587949.
Article26. Gruden JF, Ouanounou S, Tigges S, Norris SD, Klausner TS. Incremental benefit of maximum-intensity-projection images on observer detection of small pulmonary nodules revealed by multidetector CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:149–157. PMID: 12076925.
Article27. Valencia R, Denecke T, Lehmkuhl L, Fischbach F, Felix R, Knollmann F. Value of axial and coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP) images in the detection of pulmonary nodules by multislice spiral CT: comparison with axial 1-mm and 5-mm slices. Eur Radiol. 2006; 16:325–332. PMID: 16086181.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced T2 FLAIR and 3D T1 Black-Blood Fast Spin-Echo for Detection of Leptomeningeal Metastases
- Usefulness of Fluid Attenuated Inve rsion Re c overy(FLAIR) Image
- Single-Slab 3D Fast Spin Echo Imaging: T1 -Contrast Perspective
- The Detection of Gallstones on MR Cholangiopancreatography: Comparison between the Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo Pulse Sequence and the Three-Dimensional Turbo Spin-Echo Pulse Sequence with the SENSE Technique
- Projection-type Fast Spin Echo Imaging