Korean J Radiol.
2018 Dec;19(6):1187-1195. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1187.
Impact of Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction on the Correlation between Computed Tomography Quantification of a Low Lung Attenuation Area and Airway Measurements and Pulmonary Function Test Results in Normal Subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan 15355, Korea. kiylee@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pulmonology, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan 15355, Korea.
- 3Institute for Human Genomic Study, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan 15355, Korea.
- KMID: 2424858
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1187
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare correlations between pulmonary function test (PFT) results and different reconstruction algorithms and to suggest the optimal reconstruction protocol for computed tomography (CT) quantification of low lung attenuation areas and airways in healthy individuals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
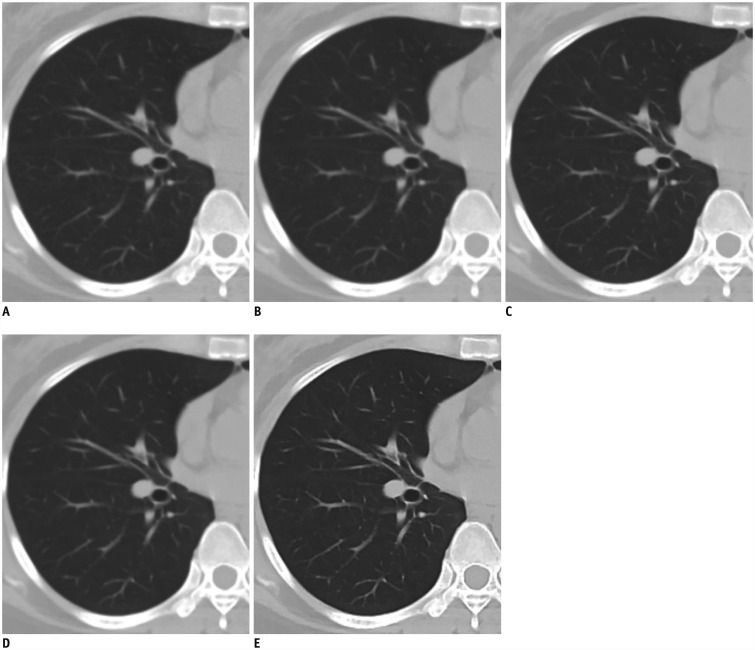
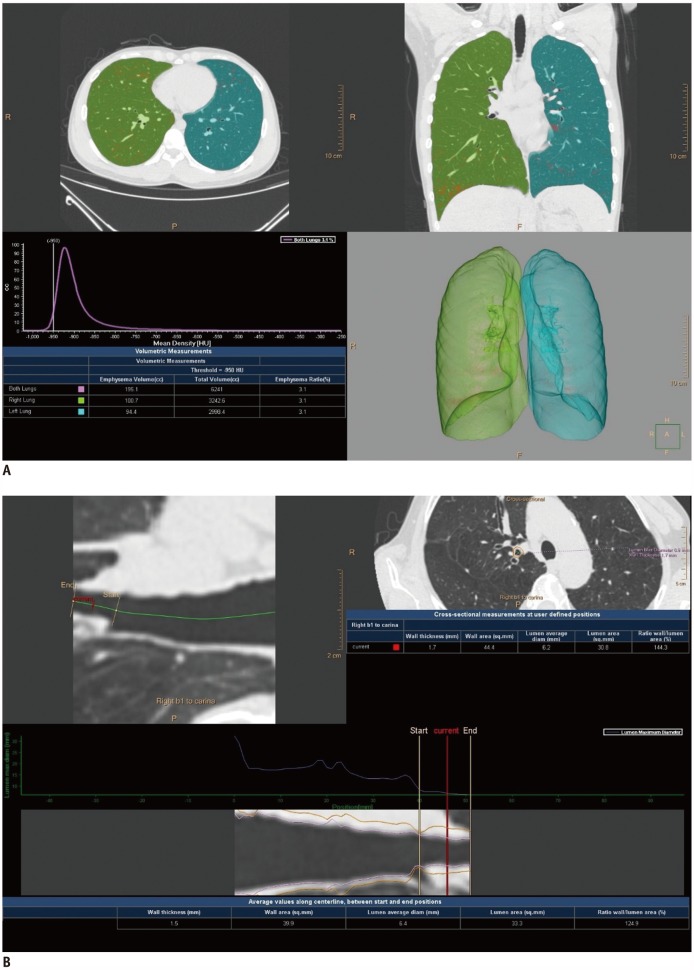
A total of 259 subjects with normal PFT and chest CT results were included. CT scans were reconstructed using filtered back projection, hybrid-iterative reconstruction, and model-based IR (MIR). For quantitative analysis, the emphysema index (EI) and wall area percentage (WA%) were determined. Subgroup analysis according to smoking history was also performed.
RESULTS
The EIs of all the reconstruction algorithms correlated significantly with the forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1)/forced vital capacity (FVC) (all p < 0.001). The EI of MIR showed the strongest correlation with FEV1/FVC (r = −0.437). WA% showed a significant correlation with FEV1 in all the reconstruction algorithms (all p < 0.05) correlated significantly with FEV1/FVC for MIR only (p < 0.001). The WA% of MIR showed the strongest correlations with FEV1 (r = −0.205) and FEV1/FVC (r = −0.250). In subgroup analysis, the EI of MIR had the strongest correlation with PFT in both ever-smoker and never-smoker subgroups, although there was no significant difference in the EI between the reconstruction algorithms. WA% of MIR showed a significantly thinner airway thickness than the other algorithms (49.7 ± 7.6 in ever-smokers and 49.5 ± 7.5 in never-smokers, all p < 0.001), and also showed the strongest correlation with PFT in both ever-smoker and never-smoker subgroups.
CONCLUSION
CT quantification of low lung attenuation areas and airways by means of MIR showed the strongest correlation with PFT results among the algorithms used, in normal subjects.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:2277–2284. PMID: 18046031.2. Hackx M, Bankier AA, Gevenois PA. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: CT quantification of airways disease. Radiology. 2012; 265:34–48. PMID: 22993219.
Article3. Ceresa M, Bastarrika G, de Torres JP, Montuenga LM, Zulueta JJ, Ortiz-de-Solorzano C, et al. Robust, standardized quantification of pulmonary emphysema in low dose CT exams. Acad Radiol. 2011; 18:1382–1390. PMID: 21852160.
Article4. Newell JD Jr, Hogg JC, Snider GL. Report of a workshop: quantitative computed tomography scanning in longitudinal studies of emphysema. Eur Respir J. 2004; 23:769–775. PMID: 15176695.
Article5. Xie X, de Jong PA, Oudkerk M, Wang Y, Ten Hacken NH, Miao J, et al. Morphological measurements in computed tomography correlate with airflow obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22:2085–2093. PMID: 22699870.
Article6. Chen H, Chen RC, Guan YB, Li W, Liu Q, Zeng QS. Correlation of pulmonary function indexes determined by low-dose MDCT with spirometric pulmonary function tests in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014; 202:711–718. PMID: 24660696.
Article7. Park KJ, Bergin CJ, Clausen JL. Quantitation of emphysema with three-dimensional CT densitometry: comparison with two-dimensional analysis, visual emphysema scores, and pulmonary function test results. Radiology. 1999; 211:541–547. PMID: 10228540.
Article8. Kim SS, Jin GY, Li YZ, Lee JE, Shin HS. CT quantification of lungs and airways in normal Korean subjects. Korean J Radiol. 2017; 18:739–748. PMID: 28670169.
Article9. Hara AK, Paden RG, Silva AC, Kujak JL, Lawder HJ, Pavlicek W. Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:764–771. PMID: 19696291.
Article10. Mayo-Smith WW, Hara AK, Mahesh M, Sahani DV, Pavlicek W. How I do it: managing radiation dose in CT. Radiology. 2014; 273:657–672. PMID: 25420167.
Article11. Geyer LL, Schoepf UJ, Meinel FG, Nance JW Jr, Bastarrika G, Leipsic JA, et al. State of the art: iterative CT reconstruction techniques. Radiology. 2015; 276:339–357. PMID: 26203706.
Article12. Kuo Y, Lin YY, Lee RC, Lin CJ, Chiou YY, Guo WY. Comparison of image quality from filtered back projection, statistical iterative reconstruction, and model-based iterative reconstruction algorithms in abdominal computed tomography. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e4456. PMID: 27495078.
Article13. Singh S, Kalra MK, Do S, Thibault JB, Pien H, O'Connor OJ, et al. Comparison of hybrid and pure iterative reconstruction techniques with conventional filtered back projection: dose reduction potential in the abdomen. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2012; 36:347–353. PMID: 22592622.14. Szilveszter B, Elzomor H, Károlyi M, Kolossváry M, Raaijmakers R, Benke K, et al. The effect of iterative model reconstruction on coronary artery calcium quantification. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016; 32:153–160. PMID: 26285899.
Article15. Padole A, Ali Khawaja RD, Kalra MK, Singh S. CT radiation dose and iterative reconstruction techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 204:W384–W392. PMID: 25794087.
Article16. Boedeker KL, McNitt-Gray MF, Rogers SR, Truong DA, Brown MS, Gjertson DW, et al. Emphysema: effect of reconstruction algorithm on CT imaging measures. Radiology. 2004; 232:295–301. PMID: 15220511.
Article17. Choo JY, Goo JM, Lee CH, Park CM, Park SJ, Shim MS. Quantitative analysis of emphysema and airway measurements according to iterative reconstruction algorithms: comparison of filtered back projection, adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction and model-based iterative reconstruction. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24:799–806. PMID: 24275806.
Article18. Nishio M, Koyama H, Ohno Y, Negi N, Seki S, Yoshikawa T, et al. Emphysema quantification using ultralow-dose CT with iterative reconstruction and filtered back projection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016; 206:1184–1192. PMID: 27058307.
Article19. Nishio M, Matsumoto S, Ohno Y, Sugihara N, Inokawa H, Yoshikawa T, et al. Emphysema quantification by low-dose CT: potential impact of adaptive iterative dose reduction using 3D processing. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 199:595–601. PMID: 22915399.
Article20. Martin SP, Gariani J, Hachulla AL, Botsikas D, Adler D, Karenovics W, et al. Impact of iterative reconstructions on objective and subjective emphysema assessment with computed tomography: a prospective study. Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:2950–2956. PMID: 27847999.
Article21. Yamashiro T, Miyara T, Honda O, Tomiyama N, Ohno Y, Noma S, et al. Iterative reconstruction for quantitative computed tomography analysis of emphysema: consistent results using different tube currents. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015; 10:321–327. PMID: 25709426.
Article22. Nishio M, Matsumoto S, Seki S, Koyama H, Ohno Y, Fujisawa Y, et al. Emphysema quantification on low-dose CT using percentage of low-attenuation volume and size distribution of low-attenuation lung regions: effects of adaptive iterative dose reduction using 3D processing. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:2268–2276. PMID: 25445899.
Article23. Yuki H, Oda S, Utsunomiya D, Funama Y, Kidoh M, Namimoto T, et al. Clinical impact of model-based type iterative reconstruction with fast reconstruction time on image quality of low-dose screening chest CT. Acta Radiol. 2016; 57:295–302. PMID: 25817455.
Article24. Neroladaki A, Botsikas D, Boudabbous S, Becker CD, Montet X. Computed tomography of the chest with model-based iterative reconstruction using a radiation exposure similar to chest X-ray examination: preliminary observations. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:360–366. PMID: 22892722.
Article25. Laqmani A, Avanesov M, Butscheidt S, Kurfürst M, Sehner S, Schmidt-Holtz J, et al. Comparison of image quality and visibility of normal and abnormal findings at submillisievert chest CT using filtered back projection, iterative model reconstruction (IMR) and iDose4TM. Eur J Radiol. 2016; 85:1971–1979. PMID: 27776648.26. Katsura M, Matsuda I, Akahane M, Yasaka K, Hanaoka S, Akai H, et al. Model-based iterative reconstruction technique for ultralow-dose chest CT: comparison of pulmonary nodule detectability with the adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique. Invest Radiol. 2013; 48:206–212. PMID: 23344517.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CT Densitometry of the Lung in Healthy Nonsmokers with Normal Pulmonary Function
- Quantification of Emphysema with a Three-Dimensional Chest CT Scan: Correlation with the Visual Emphysema Scoring on Chest CT, Pulmonary Function Tests and Dyspnea Severity
- CT Quantification of Lungs and Airways in Normal Korean Subjects
- Comparison of Filtered Back Projection, Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction, Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction, and Virtual Monoenergetic Reconstruction Images at Both Low- and Standard-Dose Settings in Measurement of Emphysema Volume and Airway Wall Thickness: A CT Phantom Study
- High-Resolution CT Appearance of Pulmonary Parenchymal Abnormalities Associated with Bronchiectasis: Correlation with Pulmonary Function Tests