J Pathol Transl Med.
2018 Sep;52(5):275-282. 10.4132/jptm.2018.07.29.
Differential MicroRNA Expression between EGFR T790M and L858R Mutated Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea. cnlee@pusan.ac.kr
- 5Department of Pathology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2422093
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.07.29
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, non-coding RNAs that mediate post-transcriptional gene regulation. They are commonly deregulated in human malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The aim of this study is to investigate miRNA expression in T790M-mutated NSCLC resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
METHODS
Six cases of resected NSCLC harboring the T790M mutation were examined. We performed miRNA time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) array profiling using EGFR T790M-mutated NSCLC and L858R-mutated NSCLC. Once identified, miRNAs that were differentially expressed between the two groups were validated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
RESULTS
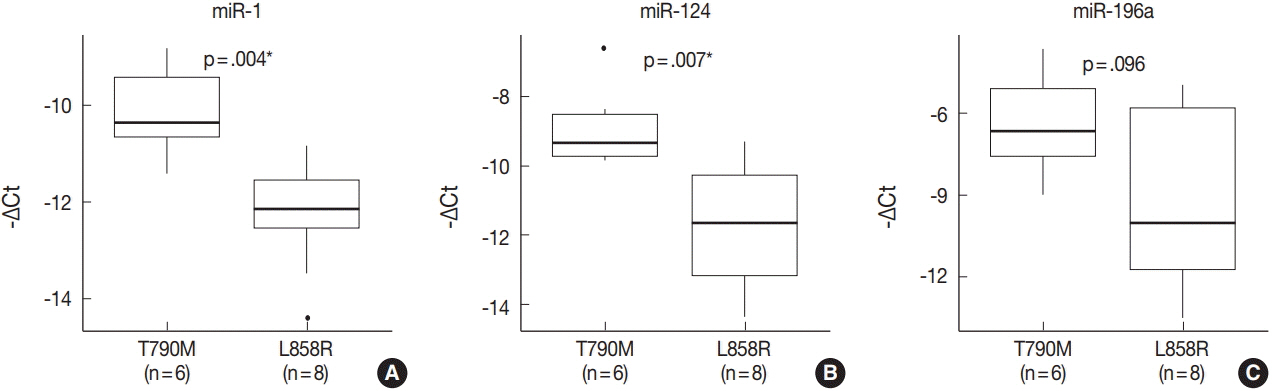
miRNA PCR array profiling revealed three up-regulated miRNAs whose expression levels were altered 4.0-fold or more in the EGFR T790M mutation group than in the L858R group: miR-1 (fold change, 4.384), miR-196a (fold change, 4.138), and miR-124 (fold change, 4.132). The three differentially expressed miRNAs were validated by qRT-PCR, and they were found to be overexpressed in the T790M group relative to L858R group. In particular, expression levels of miR-1 and miR-124 were significantly higher in the T790M group (p-value of miR-1 = .004, miR-124 = .007, miR-196a = .096).
CONCLUSIONS
MiR-1, miR-124, and miR-196a are overexpressed in EGFR T790M mutated NSCLC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016; 66:271–89.
Article2. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:947–57.
Article3. Denis MG, Vallée A, Théoleyre S. EGFR T790M resistance mutation in non small-cell lung carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 2015; 444:81–5.4. Engelman JA, Jänne PA. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:2895–9.5. Remon J, Morán T, Majem M, et al. Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a new era begins. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014; 40:93–101.6. Garzon R, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2006; 12:580–7.
Article7. Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, et al. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA. 2007; 297:1901–8.
Article8. Kanaan Z, Rai SN, Eichenberger MR, et al. Plasma miR-21: a potential diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2012; 256:544–51.9. Hu Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, et al. Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:1721–6.
Article10. Pignot G, Cizeron-Clairac G, Vacher S, et al. microRNA expression profile in a large series of bladder tumors: identification of a 3-miRNA signature associated with aggressiveness of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013; 132:2479–91.
Article11. Xu F, Zhang H, Su Y, Kong J, Yu H, Qian B. Up-regulation of microRNA-183-3p is a potent prognostic marker for lung adenocarcinoma of female non-smokers. Clin Transl Oncol. 2014; 16:980–5.
Article12. Cho WC, Chow AS, Au JS. Restoration of tumour suppressor hsamiR-145 inhibits cancer cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:2197–206.
Article13. Gao Y, Fan X, Li W, Ping W, Deng Y, Fu X. miR-138-5p reverses gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells via negatively regulating G protein-coupled receptor 124. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014; 446:179–86.
Article14. Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, et al. Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:5923–30.
Article15. Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS, Sander C. The microRNA. org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008; 36:D149–53.16. Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genomewide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:15545–50.
Article17. Sequist LV, Martins RG, Spigel D, et al. First-line gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring somatic EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:2442–9.18. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–39.
Article19. Sos ML, Rode HB, Heynck S, et al. Chemogenomic profiling provides insights into the limited activity of irreversible EGFR inhibitors in tumor cells expressing the T790M EGFR resistance mutation. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:868–74.20. Yun CH, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV, et al. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:2070–5.21. Chong CR, Jänne PA. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med. 2013; 19:1389–400.
Article22. Camidge DR, Pao W, Sequist LV. Acquired resistance to TKIs in solid tumours: learning from lung cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014; 11:473–81.
Article23. Yang JC, Ahn MJ, Kim DW, et al. Osimertinib in pretreated T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: AURA study phase II extension component. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:1288–96.
Article24. Sin TK, Wang F, Meng F, et al. Implications of microRNAs in the treatment of gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:237.
Article25. Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Enokida H, Seki N. microRNA-1/133a and microRNA-206/133b clusters: dysregulation and functional roles in human cancers. Oncotarget. 2012; 3:9–21.
Article26. Xiao H, Zeng J, Li H, et al. MiR-1 downregulation correlates with poor survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma where it interferes with cell cycle regulation and metastasis. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:13201–15.
Article27. Han C, Yu Z, Duan Z, Kan Q. Role of microRNA-1 in human cancer and its therapeutic potentials. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:428371.
Article28. Chen Z, Liu S, Tian L, et al. miR-124 and miR-506 inhibit colorectal cancer progression by targeting DNMT3B and DNMT1. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:38139–50.
Article29. Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S, Imoto I, Inazawa J. miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2010; 31:766–76.
Article30. Dong LL, Chen LM, Wang WM, Zhang LM. Decreased expression of microRNA-124 is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor for patients with breast cancer. Diagn Pathol. 2015; 10:45.
Article31. Lee Y, Lee GK, Hwang JA, Yun T, Kim HT, Lee JS. Clinical likelihood of sporadic primary EGFR T790M mutation in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015; 16:46–50.32. Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS, et al. Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:1616–22.33. Hata A, Katakami N, Yoshioka H, et al. Rebiopsy of non-small cell lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: Comparison between T790M mutation-positive and mutation-negative populations. Cancer. 2013; 119:4325–32.34. Rosell R, Molina-Vila MA, Taron M, et al. EGFR compound mutants and survival on erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (p) in the EURTAC study. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30(15 Suppl):7522.
Article35. Fujita Y, Suda K, Kimura H, et al. Highly sensitive detection of EGFR T790M mutation using colony hybridization predicts favorable prognosis of patients with lung cancer harboring activating EGFR mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:1640–4.36. Panarelli NC, Chen YT, Zhou XK, Kitabayashi N, Yantiss RK. MicroRNA expression aids the preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2012; 41:685–90.
Article37. Steele CW, Oien KA, McKay CJ, Jamieson NB. Clinical potential of microRNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2011; 40:1165–71.
Article38. Chen C, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Weakley SM, Yao Q. MicroRNA-196: critical roles and clinical applications in development and cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2011; 15:14–23.
Article39. Kim SM, Kwon OJ, Hong YK, et al. Activation of IL-6R/JAK1/STAT3 signaling induces de novo resistance to irreversible EGFR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M resistance mutation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012; 11:2254–64.
Article40. Cheung HW, Du J, Boehm JS, et al. Amplification of CRKL induces transformation and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor resistance in human non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Discov. 2011; 1:608–25.41. Wu Z, Huang W, Chen B, Bai PD, Wang XG, Xing JC. Up-regulation of miR-124 inhibits invasion and proliferation of prostate cancer cells through mediating JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017; 21:2338–45.42. Lv Z, Yang L. MiR-124 inhibits the growth of glioblastoma through the downregulation of SOS1. Mol Med Rep. 2013; 8:345–9.
Article43. Chen LY, Molina-Vila MA, Ruan SY, et al. Coexistence of EGFR T790M mutation and common activating mutations in pretreatment non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Lung Cancer. 2016; 94:46–53.44. Inukai M, Toyooka S, Ito S, et al. Presence of epidermal growth factor receptor gene T790M mutation as a minor clone in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:7854–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronicles of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeting EGFR C797S Containing Triple Mutations
- Tissue and Plasma-Based Highly Sensitive Blocker Displacement Amplicon Nanopore Sequencing for EGFR Mutations in Lung Cancer
- Rare Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in Korean Patients with EGFR-mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Acquired Resistance Mechanism of EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication to EGFR TKIs in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Should We Perform Repeated Re-biopsy for the Detection of T790M Mutation?