J Korean Med Assoc.
2018 Sep;61(9):557-565. 10.5124/jkma.2018.61.9.557.
Storage and use of cord blood
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cord@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2420367
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2018.61.9.557
Abstract
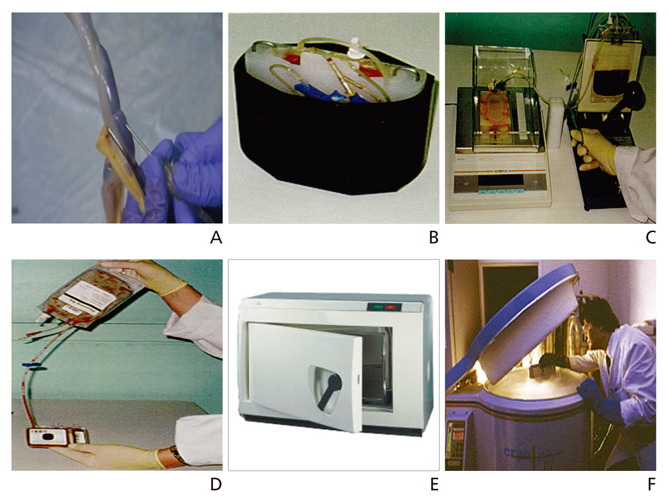
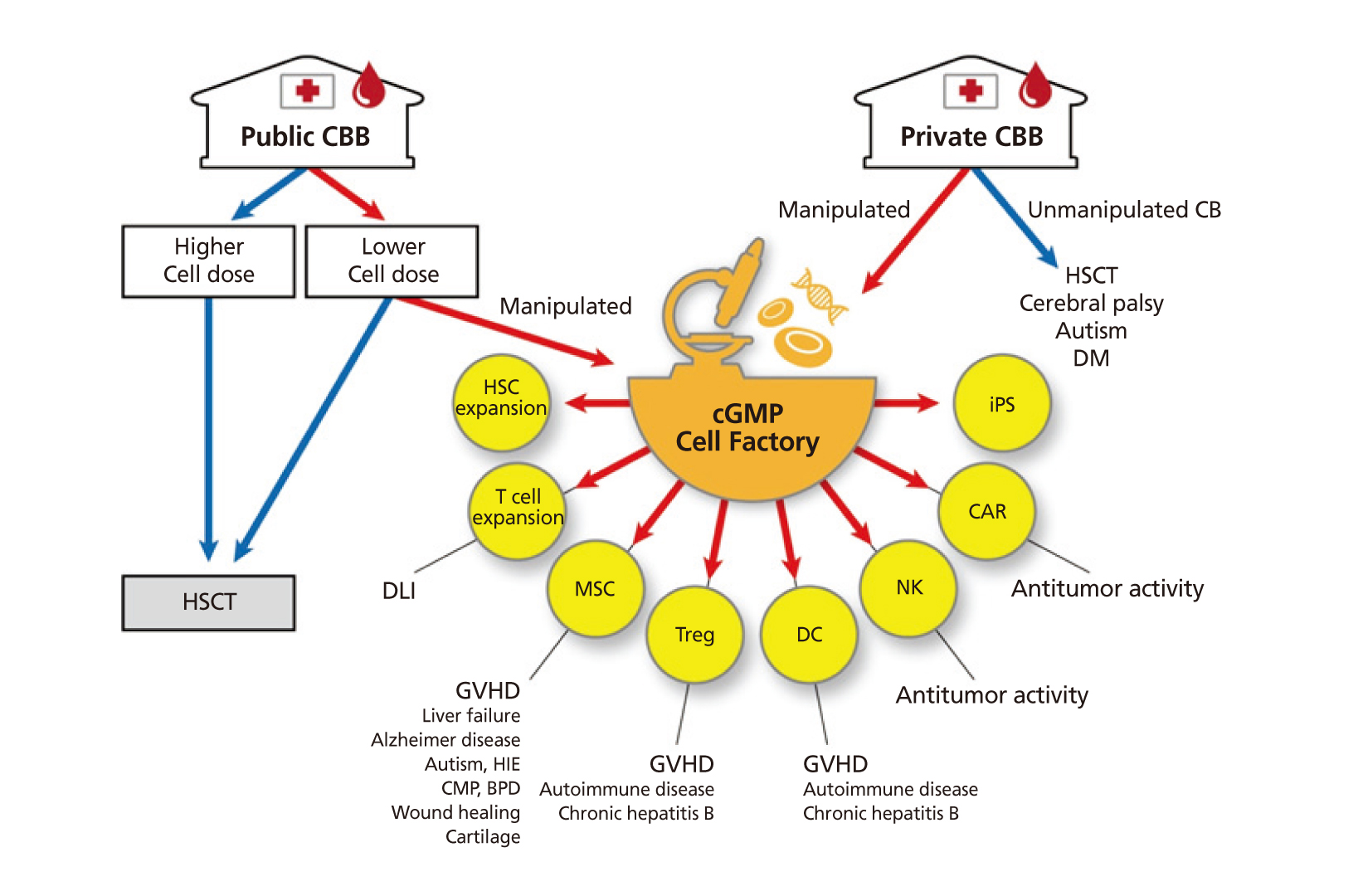
- Cord blood (CB) has been used as an important source for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and has been stored in public CB banks (CBBs) worldwide since the mid-1990s. Recently, the application of cell-based therapy using CB has expanded its clinical utility for various refractory diseases and immunologic diseases through the manufacture of mesenchymal stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells and the isolation of mononuclear cells from CB. In this review, I briefly summarize the biologic characteristics and banking process of CB, as well as the current status of public and private CBBs. I also review the current status of stem cell transplantation and cell-based therapy using CBs. Finally, I suggest strategies of banking CBs in anticipation of future medical advances.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Broxmeyer HE, Douglas GW, Hangoc G, Cooper S, Bard J, English D, Arny M, Thomas L, Boyse EA. Human umbilical cord blood as a potential source of transplantable hemato-poietic stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989; 86:3828–3832.
Article2. Gluckman E, Broxmeyer HA, Auerbach AD, Friedman HS, Douglas GW, Devergie A, Esperou H, Thierry D, Socie G, Lehn P, Cooper S, English D, Kurtzberg J, Bard J, Boyse EA. Hematopoietic reconstitution in a patient with Fanconi's anemia by means of umbilical-cord blood from an HLA-identical sibling. N Engl J Med. 1989; 321:1174–1178.
Article3. World Marrow Donor Association [Internet]. Leiden: World Marrow Donor Association;cited 2018 Jul 30. Available from: https://collaboration.wmda.info/.4. Huss R. Isolation of primary and immortalized CD34-hema-topoietic and mesenchymal stem cells from various sources. Stem Cells. 2000; 18:1–9.
Article5. Rizk M, Aziz J, Shorr R, Allan DS. Cell-based therapy using umbilical cord blood for novel indications in regenerative therapy and immune modulation: an updated systematic scoping review of the literature. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017; 23:1607–1613.
Article6. Brunstein CG, Miller JS, McKenna DH, Hippen KL, DeFor TE, Sumstad D, Curtsinger J, Verneris MR, MacMillan ML, Levine BL, Riley JL, June CH, Le C, Weisdorf DJ, McGlave PB, Blazar BR, Wagner JE. Umbilical cord blood-derived T regulatory cells to prevent GVHD: kinetics, toxicity profile, and clinical effect. Blood. 2016; 127:1044–1051.
Article7. Mehta RS, Shpall EJ, Rezvani K. Cord blood as a source of natural killer cells. Front Med (Lausanne). 2016; 2:93.
Article8. Marek-Trzonkowska N, Mysliwiec M, Dobyszuk A, Grabo-wska M, Derkowska I, Juscinska J, Owczuk R, Szadkowska A, Witkowski P, Młynarski W, Jarosz-Chobot P, Bossowski A, Siebert J, Trzonkowski P. Therapy of type 1 diabetes with CD4(+)CD25(high)CD127-regulatory T cells prolongs sur-vival of pancreatic islets: results of one year follow-up. Clin Immunol. 2014; 153:23–30.
Article9. Schaub B, Tantisira KG, Gibbons FK, He H, Litonjua AA, Gillman MW, Weiss S, Perkins DL, Gold DR, Finn PW. Fetal cord blood: aspects of heightened immune responses. J Clin Immunol. 2005; 25:329–337.
Article10. Broxmeyer HE, Lee MR, Hangoc G, Cooper S, Prasain N, Kim YJ, Mallett C, Ye Z, Witting S, Cornetta K, Cheng L, Yoder MC. Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, generation of induced pluripotent stem cells, and isolation of endothelial progenitors from 21- to 23.5-year cryopreserved cord blood. Blood. 2011; 117:4773–4777.
Article11. Mitchell R, Wagner JE, Brunstein CG, Cao Q, McKenna DH, Lund TC, Verneris MR. Impact of long-term cryopreservation on single umbilical cord blood transplantation outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015; 21:50–54.
Article12. Otsubo K, Nosaki K, Imamura CK, Ogata H, Fujita A, Sakata S, Hirai F, Toyokawa G, Iwama E, Harada T, Seto T, Takenoyama M, Ozeki T, Mushiroda T, Inada M, Kishimoto J, Tsuchihashi K, Suina K, Nagano O, Saya H, Nakanishi Y, Okamoto I. Phase I study of salazosulfapyridine in combina-tion with cisplatin and pemetrexed for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017; 108:1843–1849.
Article13. Lee YH, Kwon YH, Hwang K, Jun H, Lee MA, Jang HI, Nah JH, Koo HH, Hwang TJ. Analysis of stored and transplanted cord blood units from KoreaCORD: reappraisal of banking guidelines and selection strategy. Transfusion. 2013; 53:123–127.
Article14. Lee YH, Cho NC, Je KH, Han H, Han JY, Kim JS, Kim HJ, Cho B, Kim HK. Successful sibling cord blood stem cell trans-plantation for relapsed acute mixed lineage leukemia. Korean J Hematol. 1999; 34:471–476.15. Yoo KH, Lee SH, Sung KW, Koo HH, Chung NG, Cho B, Kim HK, Kang HJ, Shin HY, Ahn HS, Baek HJ, Han DK, Kook H, Hwang TJ, Kim SY, Lee YH, Hah JO, Im HJ, Seo JJ, Park SK, Jung HJ, Park JE, Lim YJ, Park SS, Lim YT, Yoo ES, Ryu KH, Park HJ, Park BK. Current status of pediatric umbilical cord blood transplantation in Korea: a multicenter retrospective analysis of 236 cases. Am J Hematol. 2011; 86:12–17.
Article16. Eapen M, Rubinstein P, Zhang MJ, Stevens C, Kurtzberg J, Scaradavou A, Loberiza FR, Champlin RE, Klein JP, Horowitz MM, Wagner JE. Outcomes of transplantation of unrelated donor umbilical cord blood and bone marrow in children with acute leukaemia: a comparison study. Lancet. 2007; 369:1947–1954.
Article17. Wagner JE Jr, Eapen M, Carter S, Wang Y, Schultz KR, Wall DA, Bunin N, Delaney C, Haut P, Margolis D, Peres E, Verneris MR, Walters M, Horowitz MM, Kurtzberg J. Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network. One-unit versus two-unit cord-blood transplantation for hematologic cancers. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:1685–1694.
Article18. Mehta RS, Saliba RM, Cao K, Kaur I, Rezvani K, Chen J, Olson A, Parmar S, Shah N, Marin D, Alousi A, Hosing C, Popat U, Kebriaei P, Champlin R, de Lima M, Skerrett D, Burke E, Shpall EJ, Oran B. Ex vivo mesenchymal precursor cell-expanded cord blood transplantation after reduced-intensity conditioning regimens improves time to neutrophil recovery. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017; 23:1359–1366.
Article19. Kiernan J, Damien P, Monaghan M, Shorr R, McIntyre L, Fergusson D, Tinmouth A, Allan D. Clinical studies of ex vivo expansion to accelerate engraftment after umbilical cord blood transplantation: a systematic review. Transfus Med Rev. 2017; 31:173–182.
Article20. Bari S, Seah KK, Poon Z, Cheung AM, Fan X, Ong SY, Li S, Koh LP, Hwang WY. Expansion and homing of umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells for clinical transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015; 21:1008–1019.
Article21. Okada M, Tasaka T, Ikegame K, Aotsuka N, Kobayashi T, Najima Y, Matsuhashi Y, Wada H, Tokunaga H, Masuda S, Utsu Y, Yoshihara S, Kaida K, Daimon T, Ogawa H. A pro-spective multicenter phase II study of intrabone marrow tran-splantation of unwashed cord blood using reduced-intensity conditioning. Eur J Haematol. 2018; 100:335–343.
Article22. Park YB, Ha CW, Lee CH, Yoon YC, Park YG. Cartilage rege-neration in osteoarthritic patients by a composite of allogeneic umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronate hydrogel: results from a clinical trial for safety and proof-of-concept with 7 years of extended follow-up. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017; 6:613–621.
Article23. Lee YH, Choi KV, Moon JH, Jun HJ, Kang HR, Oh SI, Kim HS, Um JS, Kim MJ, Choi YY, Lee YJ, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Son SM, Choi SJ, Oh W, Yang YS. Safety and feasibility of countering neurological impairment by intravenous admini-stration of autologous cord blood in cerebral palsy. J Transl Med. 2012; 10:58.
Article24. Min K, Song J, Kang JY, Ko J, Ryu JS, Kang MS, Jang SJ, Kim SH, Oh D, Kim MK, Kim SS, Kim M. Umbilical cord blood therapy potentiated with erythropoietin for children with cerebral palsy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-control-led trial. Stem Cells. 2013; 31:581–591.
Article25. Rah WJ, Lee YH, Moon JH, Jun HJ, Kang HR, Koh H, Eom HJ, Lee JY, Lee YJ, Kim JY, Choi YY, Park K, Kim MJ, Kim SH. Neuroregenerative potential of intravenous G-CSF and autologous peripheral blood stem cells in children with cere-bral palsy: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over study. J Transl Med. 2017; 15:16.
Article26. Koh H, Hwang K, Lim HY, Kim YJ, Lee YH. Mononuclear cells from the cord blood and granulocytecolony stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood: is there a potential for treatment of cerebral palsy? Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10:2018–2024.
Article27. Berglund S, Gertow J, Uhlin M, Mattsson J. Expanded umbili-cal cord blood T cells used as donor lymphocyte infusions after umbilical cord blood transplantation. Cytotherapy. 2014; 16:1528–1536.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Cord Blood Banks in Korea
- Improving Storage Policy in Korean Public Cord Blood Banks: Comparison of Quality between Long-Term and Short-Term Storage of Cord Blood
- Analysis of Blood Gas, K and Glucose Levels of ACD Banked Blood
- The Effect of Cord Blood Plasma on Hematopoietic Colony Formation
- Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation