J Bone Metab.
2018 Aug;25(3):153-159. 10.11005/jbm.2018.25.3.153.
Linkage of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Phosphate in Serum: Phosphate and Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Reduction by Increasing Dose of Sevelamer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Biotechnology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran. rozag2001@gmail.com
- 2Urology and Nephrology Research Center, Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 3Connective Tissue Diseases Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
- 4Drug Applied Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
- KMID: 2419842
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2018.25.3.153
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
High serum phosphate and fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23) levels are well-recognized independent risk factors of mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic kidney diseases (CKDs). Sevelamer, as a phosphate chelating agent, reduces serum phosphate and FGF-23 levels produced by bone osteocytes. This study aimed to determine the best dose at which sevelamer could successfully reduce serum phosphate and FGF-23 levels in rat models of adenine-induced CKD.
METHODS
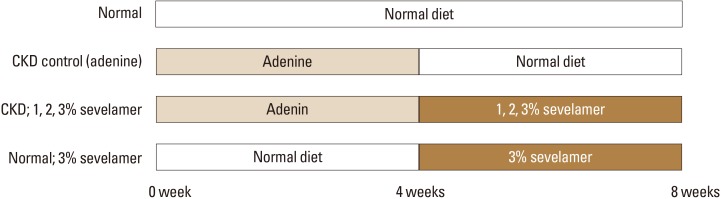
CKD was induced using adenine. Healthy and CKD-induced rats were divided into 6 groups as follows: healthy controls; CKD controls; rats treated with 1%, 2%, and 3% sevelamer for CKDs; and healthy rats administered 3% sevelamer. Biochemical factors and serum FGF-23 levels were measured using spectrophotometry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay methods.
RESULTS
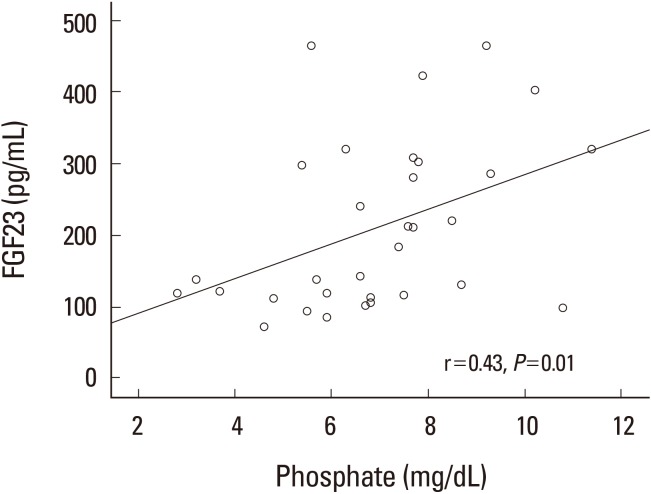
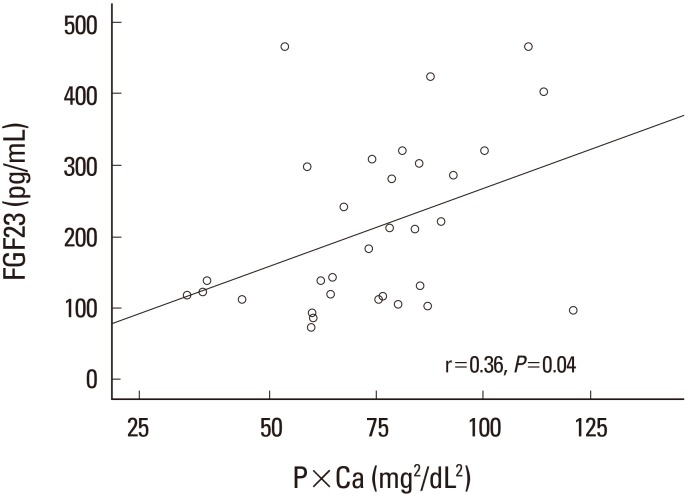
Serum phosphate levels were best decreased in rats receiving 3% sevelamer in their diet (5.91±1.48 mg/dL vs. 8.09±1.70 mg/dL, P < 0.05) compared with the CKD control rats. A dose-dependent decrease in serum FGF-23 levels was observed, and the most significant results were obtained in rats receiving 3% sevelamer compared with the CKD control rats (142.60±83.95 pg/mL vs. 297.15±131.10 pg/mL, P < 0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
Higher sevelamer doses significantly reduced serum phosphate and FGF-23 levels in adenine-induced CKD rats.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Denker M, Boyle S, Anderson AH, et al. Chronic renal insufficiency cohort study (CRIC): overview and summary of selected findings. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015; 10:2073–2083. PMID: 26265715.
Article2. Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Amin MG, et al. Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: a pooled analysis of community-based studies. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:1307–1315. PMID: 15100371.
Article3. Oliveira RB, Cancela AL, Graciolli FG, et al. Early control of PTH and FGF23 in normophosphatemic CKD patients: a new target in CKD-MBD therapy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010; 5:286–291. PMID: 19965540.
Article4. Munoz Mendoza J, Isakova T, Ricardo AC, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and Inflammation in CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012; 7:1155–1162. PMID: 22554719.
Article5. Gutiérrez OM, Mannstadt M, Isakova T, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and mortality among patients undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:584–592. PMID: 18687639.
Article6. Wesseling-Perry K. FGF23: is it ready for prime time? Clin Chem. 2011; 57:1476–1477. PMID: 21914788.
Article7. Burnett SM, Gunawardene SC, Bringhurst FR, et al. Regulation of C-terminal and intact FGF-23 by dietary phosphate in men and women. J Bone Miner Res. 2006; 21:1187–1196. PMID: 16869716.
Article8. Muñoz-García B, Martín-Ventura JL, Martínez E, et al. Fn14 is upregulated in cytokine-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells and is expressed in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques: modulation by atorvastatin. Stroke. 2006; 37:2044–2053. PMID: 16809572.9. Isakova T, Xie H, Yang W, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and risks of mortality and end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. JAMA. 2011; 305:2432–2439. PMID: 21673295.
Article10. Gutiérrez OM, Wolf M, Taylor EN. Fibroblast growth factor 23, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and phosphorus intake in the health professionals follow-up study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011; 6:2871–2878. PMID: 22034506.
Article11. Cozzolino M, Dusso AS, Liapis H, et al. The effects of sevelamer hydrochloride and calcium carbonate on kidney calcification in uremic rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:2299–2308. PMID: 12191974.
Article12. Ketteler M, Petermann AT. Phosphate and FGF23 in early CKD: on how to tackle an invisible foe. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:2430–2432. PMID: 21803732.
Article13. Ferrari SL, Bonjour JP, Rizzoli R. Fibroblast growth factor-23 relationship to dietary phosphate and renal phosphate handling in healthy young men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:1519–1524. PMID: 15613425.
Article14. Antoniucci DM, Yamashita T, Portale AA. Dietary phosphorus regulates serum fibroblast growth factor-23 concentrations in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91:3144–3149. PMID: 16735491.
Article15. Ito N, Fukumoto S, Takeuchi Y, et al. Effect of acute changes of serum phosphate on fibroblast growth factor (FGF)23 levels in humans. J Bone Miner Metab. 2007; 25:419–422. PMID: 17968495.
Article16. Rodríguez-Osorio L, Zambrano DP, Gracia-Iguacel C, et al. Use of sevelamer in chronic kidney disease: beyond phosphorus control. Nefrologia. 2015; 35:207–217. PMID: 26300515.
Article17. Koiwa F, Kazama JJ, Tokumoto A, et al. Sevelamer hydrochloride and calcium bicarbonate reduce serum fibroblast growth factor 23 levels in dialysis patients. Ther Apher Dial. 2005; 9:336–339. PMID: 16076378.
Article18. Nagano N, Miyata S, Abe M, et al. Effects of intermittent treatment with sevelamer hydrochloride on parathyroid hyperplasia and vascular calcification in rats with chronic kidney disease. Clin Calcium. 2005; 15(Suppl 1):35–39. discussion 9-40.19. Spaia S. Phosphate binders: sevelamer in the prevention and treatment of hyperphosphataemia in chronic renal failure. Hippokratia. 2011; 15:22–26.20. Tamagaki K, Yuan Q, Ohkawa H, et al. Severe hyperparathyroidism with bone abnormalities and metastatic calcification in rats with adenine-induced uraemia. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006; 21:651–659. PMID: 16311258.
Article21. Nagano N, Miyata S, Abe M, et al. Effect of manipulating serum phosphorus with phosphate binder on circulating PTH and FGF23 in renal failure rats. Kidney Int. 2006; 69:531–537. PMID: 16395276.
Article22. Nagano N, Miyata S, Obana S, et al. Sevelamer hydrochloride, a phosphate binder, protects against deterioration of renal function in rats with progressive chronic renal insufficiency. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003; 18:2014–2023. PMID: 13679475.
Article23. Cancela AL, Oliveira RB, Graciolli FG, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 in hemodialysis patients: effects of phosphate binder, calcitriol and calcium concentration in the dialysate. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011; 117:c74–c82. PMID: 20689328.
Article24. Bansal S. New insights into regulation of FGF23 in chronic kidney disease and its role in cardiovascular disease. SM J Cardiolog and Cardiovasc Disord. 2015; 1:1003.25. Liu S, Tang W, Zhou J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is a counter-regulatory phosphaturic hormone for vitamin D. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17:1305–1315. PMID: 16597685.
Article26. Spatz C, Roe K, Lehman E, et al. Effect of a non-calcium-based phosphate binder on fibroblast growth factor 23 in chronic kidney disease. Nephron Clin Pract. 2013; 123:61–66. PMID: 23774446.
Article27. Yilmaz MI, Sonmez A, Saglam M, et al. Comparison of calcium acetate and sevelamer on vascular function and fibroblast growth factor 23 in CKD patients: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012; 59:177–185. PMID: 22137672.
Article28. Ketteler M, Biggar PH. Use of phosphate binders in chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013; 22:413–420. PMID: 23736841.
Article29. Yokota H, Pires A, Raposo JF, et al. Model-based analysis of FGF23 regulation in chronic kidney disease. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2010; 4:53–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Transforming Growth Factor-beta and Mannose-6-Phosphate on the Proliferation of Subconjunctival Fibroblast of Rabbit
- Effects of Single Vitamin D₃ Injection (200,000 Units) on Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Sclerostin Levels in Subjects with Vitamin D Deficiency
- Kidney and Phosphate Metabolism
- An Experimental Study of the Effect of Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor on Nerve Regeneration
- A FGF23-Positive Maxillary Sinus Tumor Associated with Oncogenic Osteomalacia