Yonsei Med J.
2018 Jan;59(1):158-161. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.158.
Life-Threatening Thrombocytopenia Following Intravenous Contrast Media Infusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Divison of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. henkengun@gmail.com
- KMID: 2418864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.158
Abstract
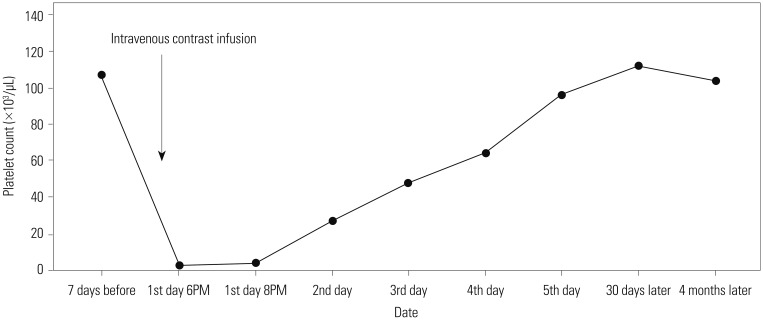
- Radiocontrast media-induced acute severe thrombocytopenia is a very rare complication and potentially life-threatening. Here, we report the case of a 63-year-old male patient with severe acute thrombocytopenia following first exposure to intravenous non-ionic contrast media without immediate allergic reactions. His platelet count dropped from 107000/µL to 2000/µL after six hours of radiocontrast infusion. After administration of corticosteroid and transfusion of platelet concentrates, the platelet count returned gradually to normal within 5 days. To the best of our knowledge, non-ionic contrast media-induced isolated acute severe thrombocytopenia following no signs or symptoms of immediate allergic reaction has never been described.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chang JC, Lee D, Gross HM. Acute thrombocytopenia after i.v. administration of a radiographic contrast medium. Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 152:947–949. PMID: 2705351.
Article2. Cubero-Gómez JM, Guerrero Márquez FJ, Diaz-de la-Llera L, Fernández-Quero M, Guisado-Rasco A, Villa-Gil-Ortega M. Severe thrombocytopenia induced by iodinated contrast after coronary angiography: The use of gadolinium contrast and intravascular ultrasound as an alternative to guide percutaneous coronary intervention. Rev Port Cardiol. 2017; 36:61.e1–61.e4. PMID: 27986390.
Article3. Wiemer M, Kreuzpaintner G, Lauer B, Kiefel V, Schultheiss HP, Horstkotte D, et al. [Recurrent immune thrombocytopenia: a rare complication after contrast medium injection]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1995; 120:1236–1240. PMID: 7671781.4. Bata P, Tarnoki AD, Tarnoki DL, Horvath E, Berczi V, Szalay F. Acute severe thrombocytopenia following non-ionic low-osmolarity intravenous contrast medium injection. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:505–509. PMID: 22778575.
Article5. McCaulley JA, Deering SH, Pates JA. Severe thrombocytopenia after contrast infusion in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2013; 121(2 Pt 2 Suppl 1):473–475. PMID: 23344413.6. Hunt CH, Hartman RP, Hesley GK. Frequency and severity of adverse effects of iodinated and gadolinium contrast materials: retrospective review of 456,930 doses. Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:1124–1127. PMID: 19770337.
Article7. Saitoh T, Saiki M, Sawada U, Kawamura N, Tohno H, Horie T. [Severe thrombocytopenia induced by radiographic non-ionic contrast medium]. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2001; 42:507–511. PMID: 11505531.8. Morcos SK, Thomsen HS. Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media. Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:1267–1275. PMID: 11471623.
Article9. Brockow K, Ring J. Classification and pathophysiology of radiocontrast media hypersensitivity. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2010; 95:157–169. PMID: 20519888.
Article10. Szebeni J. Hypersensitivity reactions to radiocontrast media: the role of complement activation. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004; 4:25–30. PMID: 14680617.
Article11. Szebeni J. Complement activation-related pseudoallergy: a new class of drug-induced acute immune toxicity. Toxicology. 2005; 216:106–121. PMID: 16140450.
Article12. Aster RH, Curtis BR, McFarland JG, Bougie DW. Drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7:911–918. PMID: 19344362.
Article13. Aster RH, Bougie DW. Drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:580–587. PMID: 17687133.
Article14. Simon RA, Schatz M, Stevenson DD, Curry N, Yamamoto F, Plow E, et al. Radiographic contrast media infusions. Measurement of histamine, complement, and fibrin split products and correlation with clinical parameters. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:281–288. PMID: 85650.15. Li X, Gabriel DA. Differences between contrast media in the inhibition of platelet activation by specific platelet agonists. Acad Radiol. 1997; 4:108–114. PMID: 9061083.16. Aspelin P, Stacul F, Thomsen HS, Morcos SK, van der. ESUR). Effects of iodinated contrast media on blood and endothelium. Eur Radiol. 2006; 16:1041–1049. PMID: 16395531.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anaphylaxis and Acute Coronary Syndrome Secondary to Intravenous Gadolinium-based Contrast Agent: Kounis Syndrome
- Acute Severe Thrombocytopenia Following Non-Ionic Low-Osmolarity Intravenous Contrast Medium Injection
- Acute Pulmonary Edema after Intravenous Administration of Nonionic Contrast Media: A Case Report
- A case of anaphylactoid reaction to nonionic contrast agent, Iodixanol (Visipaque(R)) during coronary angiography
- Transient Orbitofacial Angioedema due to Intravenous Iodinated Contrast Media During Computed Tomography: CT Findings