J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 Jan;78(1):69-72. 10.3348/jksr.2018.78.1.69.
Transient Orbitofacial Angioedema due to Intravenous Iodinated Contrast Media During Computed Tomography: CT Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. silwater007@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2399308
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.78.1.69
Abstract
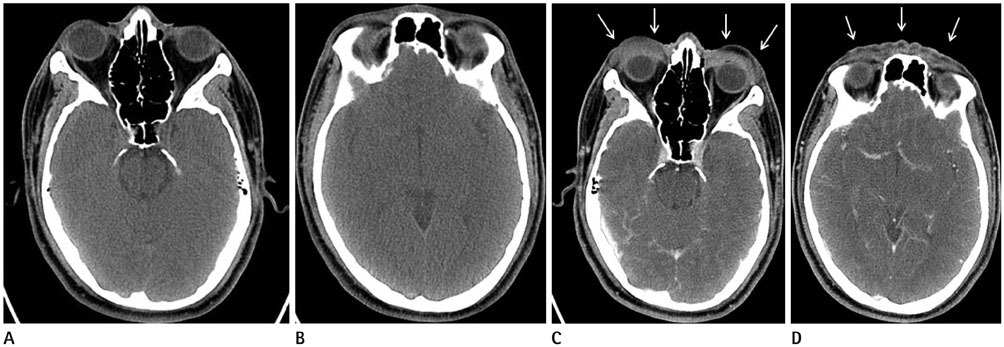
- Orbitofacial angioedema is one of the common contrast-induced adverse reactions. The symptoms are recognized, based on the patient's clinical complaints. Based on prior research findings, there were no reports about contrast-induced orbitofacial angioedema that was confirmed on image findings. The researchers herein report on contrast-induced orbitofacial angioedema presented on enhanced computed tomography, following intravenous administration of iodine contrast media.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bae K, Lee SM, Ha JY, Jeon KN, Moon JI, Choi BH, et al. Adverse drug reactions to CT contrast media in South Korea: incidence and risk factors. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2016; 75:41–48.
Article2. Andreucci M, Solomon R, Tasanarong A. Side effects of radiographic contrast media: pathogenesis, risk factors, and prevention. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:741018.
Article3. Morcos SK, Thomsen HS. Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media. Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:1267–1275.
Article4. Wang CL, Cohan RH, Ellis JH, Caoili EM, Wang G, Francis IR. Frequency, outcome, and appropriateness of treatment of nonionic iodinated contrast media reactions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 191:409–415.
Article5. Kulthanan K, Jiamton S, Boochangkool K, Jongjarearnprasert K. Angioedema: clinical and etiological aspects. Clin Dev Immunol. 2007; 2007:26438.
Article6. Kaplan AP, Greaves MW. Angioedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005; 53:373–388. quiz 389-392.7. Ishigami K, Averill SL, Pollard JH, McDonald JM, Sato Y. Radiologic manifestations of angioedema. Insights Imaging. 2014; 5:365–374.
Article8. Sharma S, Aggarwal S. Unilateral orbital edema following the intravascular injection of contrast medium. Clin Radiol. 1989; 40:108.9. Fry EL, Fante RG. Acute orbital edema causing reversible blindness after the administration of intravenous contrast agent in a patient with thyroid eye disease. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 24:330–331.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recurrent Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia Triggered by Deep Inspiration During Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography
- Prescreening skin test effectiveness in predicting hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast media
- Risk Factors for Adverse Reactions to Iodinated Contrast Media in Computed Tomography
- Management of adverse reaction to iodinated radiocontrast media
- Optimization of the Contrast Mixture Ratio for Simultaneous Direct MR and CT Arthrography: an in Vitro Study