Yonsei Med J.
2018 Jan;59(1):85-91. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.85.
Adipogenic and Lipolytic Effects of Ascorbic Acid in Ovariectomized Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mingoolee@korea.ac.kr
- 2Neuroscience Research Institute, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Reproductive Endocrinology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Korea Polar Research Institute, Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2418853
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.85
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Ascorbic acid has been reported to have an adipogenic effect on 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, while evidence also suggests that ascorbic acid reduces body weight in humans. In this study, we tested the effects of ascorbic acid on adipogenesis and the balance of lipid accumulation in ovariectomized rats, in addition to long-term culture of differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Murine 3T3-L1 fibroblasts and ovariectomized rats were treated with ascorbic acid at various time points. In vitro adipogenesis was analyzed by Oil Red O staining, and in vivo body fat was measured by a body composition analyzer using nuclear magnetic resonance.
RESULTS
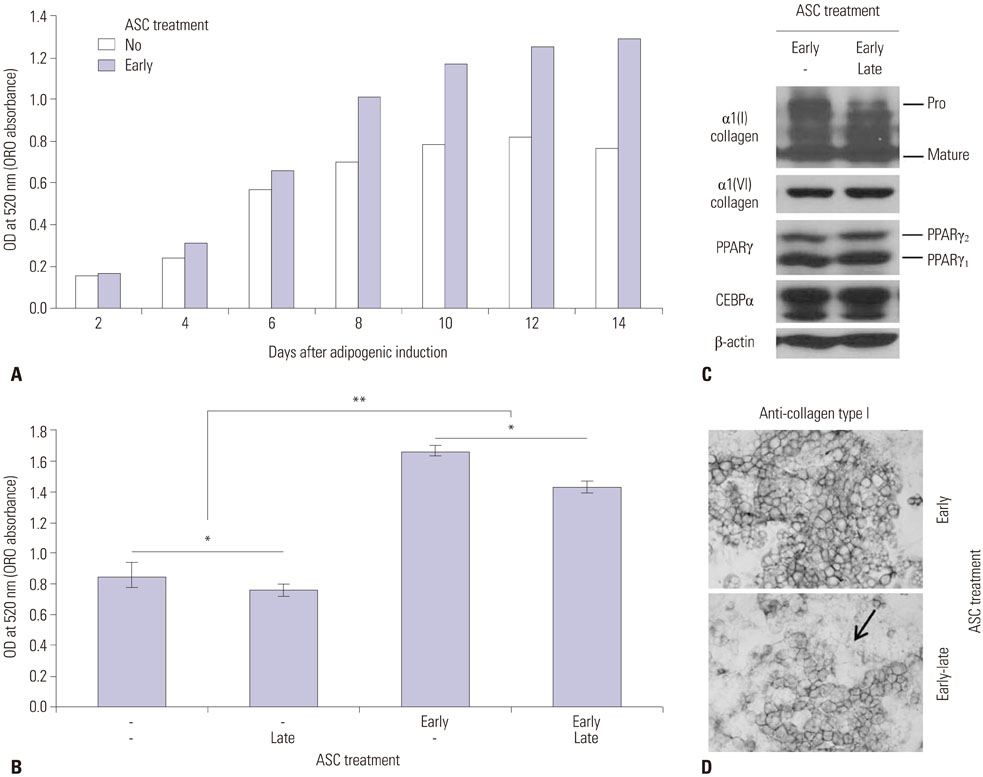
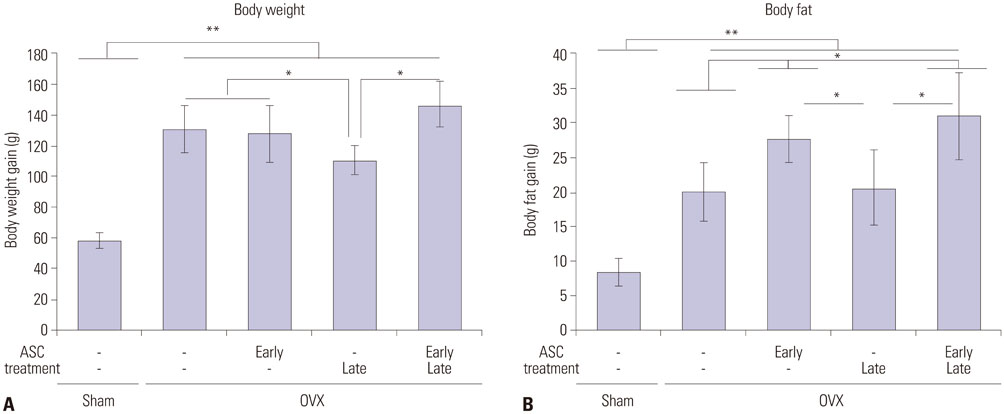
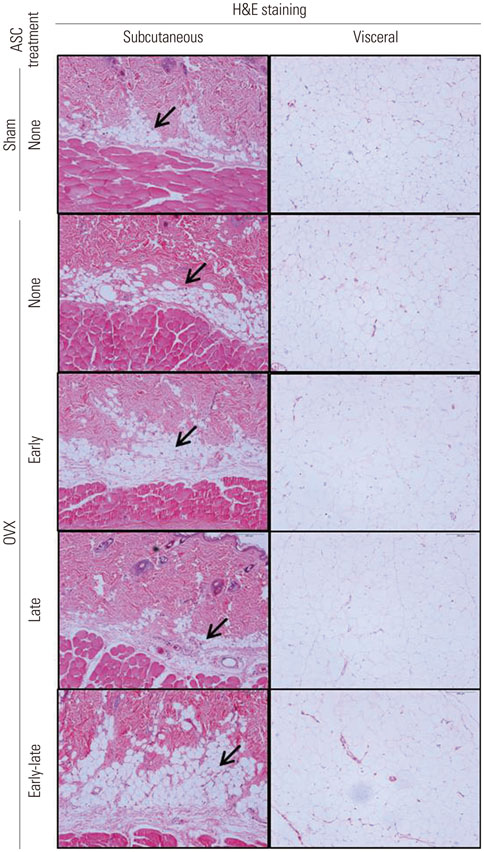
When ascorbic acid was applied during an early time point in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation and after bilateral ovariectomy (OVX) in rats, adipogenesis and fat mass gain significantly increased, respectively. However, lipid accumulation in well-differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes showed a significant reduction when ascorbic acid was applied after differentiation (10 days after induction). Also, oral ascorbic acid administration 4 weeks after OVX in rats significantly reduced both body weight and subcutaneous fat layer. In comparison to the results of ascorbic acid, which is a well-known cofactor for an enzyme of collagen synthesis, and the antioxidant ramalin, a potent antioxidant but not a cofactor, showed only a lipolytic effect in well-differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes, not an adipogenic effect.
CONCLUSION
Taking these results into account, we concluded that ascorbic acid has both an adipogenic effect as a cofactor of an enzymatic process and a lipolytic effect as an antioxidant.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
3T3-L1 Cells
Adipocytes/drug effects/metabolism
Adipogenesis/*drug effects
Animals
Antioxidants/pharmacology
Ascorbic Acid/*pharmacology
Body Composition/drug effects
Body Weight/drug effects
Cell Differentiation/drug effects
Female
Fibroblasts/drug effects/metabolism
Lipolysis/*drug effects
Mice
*Ovariectomy
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Antioxidants
Ascorbic Acid
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parker WH, Broder MS, Liu Z, Shoupe D, Farquhar C, Berek JS. Ovarian conservation at the time of hysterectomy for benign disease. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2007; 50:354–361.
Article2. Rivera CM, Grossardt BR, Rhodes DJ, Brown RD Jr, Roger VL, Melton LJ 3rd, et al. Increased cardiovascular mortality after early bilateral oophorectomy. Menopause. 2009; 16:15–23.
Article3. McCarthy AM, Menke A, Ouyang P, Visvanathan K. Bilateral oophorectomy, body mass index, and mortality in U.S. women aged 40 years and older. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012; 5:847–854.
Article4. Singh PN, Haddad E, Knutsen SF, Fraser GE. The effect of menopause on the relation between weight gain and mortality among women. Menopause. 2001; 8:314–320.
Article5. Barnes MJ. Function of ascorbic acid in collagen metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975; 258:264–277.
Article6. Kim B, Choi KM, Yim HS, Lee MG. Ascorbic acid enhances adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 murine preadipocyte through differential expression of collagens. Lipids Health Dis. 2013; 12:182.
Article7. Ono M, Aratani Y, Kitagawa I, Kitagawa Y. Ascorbic acid phosphate stimulates type IV collagen synthesis and accelerates adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1990; 187:309–314.
Article8. Padayatty SJ, Katz A, Wang Y, Eck P, Kwon O, Lee JH, et al. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003; 22:18–35.
Article9. Zhu LL, Cao J, Sun M, Yuen T, Zhou R, Li J, et al. Vitamin C prevents hypogonadal bone loss. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e47058.
Article10. Sugiura M, Nakamura M, Ogawa K, Ikoma Y, Yano M. High Vitamin C intake with high serum β-cryptoxanthin associated with lower risk for osteoporosis in post-menopausal Japanese female subjects: Mikkabi Cohort Study. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2016; 62:185–191.
Article11. Kim DE, Cho SH, Park HM, Chang YK. Relationship between bone mineral density and dietary intake of β-carotene, vitamin C, zinc and vegetables in postmenopausal Korean women: a cross-sectional study. J Int Med Res. 2016; 44:1103–1114.
Article12. Garcia-Diaz DF, Lopez-Legarrea P, Quintero P, Martinez JA. Vitamin C in the treatment and/or prevention of obesity. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2014; 60:367–379.
Article13. Hasegawa N, Niimi N, Odani F. Vitamin C is one of the lipolytic substances in green tea. Phytother Res. 2002; 16:Suppl 1. S91–S92.
Article14. Ji H, Om AD, Yoshimatsu T, Umino T, Nakagawa H, Sakamoto S. Effect of dietary ascorbate on lipogenesis and lipolysis activities in black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2010; 36:749–755.
Article15. Campión J, Milagro FI, Fernández D, Martínez JA. Diferential gene expression and adiposity reduction induced by ascorbic acid supplementation in a cafeteria model of obesity. J Physiol Biochem. 2006; 62:71–80.
Article16. Ponec M, Weerheim A, Kempenaar J, Mulder A, Gooris GS, Bouwstra J, et al. The formation of competent barrier lipids in reconstructed human epidermis requires the presence of vitamin C. J Invest Dermatol. 1997; 109:348–355.
Article17. Lutz TA, Woods SC. Overview of animal models of obesity. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2012; Chapter 5:Unit5.61.
Article18. Chen Y, Heiman ML. Increased weight gain after ovariectomy is not a consequence of leptin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 280:E315–E322.
Article19. Wegorzewska IN, Walters K, Weiser MJ, Cruthirds DF, Ewell E, Larco DO, et al. Postovariectomy weight gain in female rats is reversed by estrogen receptor alpha agonist, propylpyrazoletriol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008; 199:67.e1–67.e5.20. Paudel B, Bhattarai HD, Koh HY, Lee SG, Han SJ, Lee HK, et al. Ramalin, a novel nontoxic antioxidant compound from the Antarctic lichen Ramalina terebrata. Phytomedicine. 2011; 18:1285–1290.
Article21. Kim SY, Jang YJ, Park B, Yim JH, Lee HK, Rhee DK, et al. Ramalin inhibits differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and suppresses adiposity and body weight in a high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Chem Biol Interact. 2016; 257:71–80.
Article22. Naylor GJ, Grant L, Smith C. A double blind placebo controlled trial of ascorbic acid in obesity. Nutr Health. 1985; 4:25–28.
Article23. Johnston CS, Beezhold BL, Mostow B, Swan PD. Plasma vitamin C is inversely related to body mass index and waist circumference but not to plasma adiponectin in nonsmoking adults. J Nutr. 2007; 137:1757–1762.
Article24. Kurl S, Tuomainen TP, Laukkanen JA, Nyyssönen K, Lakka T, Sivenius J, et al. Plasma vitamin C modifies the association between hypertension and risk of stroke. Stroke. 2002; 33:1568–1573.
Article25. Larsen SC, Angquist L, Ahluwalia TS, Skaaby T, Roswall N, Tjønneland A, et al. Dietary ascorbic acid and subsequent change in body weight and waist circumference: associations may depend on genetic predisposition to obesity–a prospective study of three independent cohorts. Nutr J. 2014; 13:43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Berberine reduces the expression of adipogenic enzymes and inflammatory molecules of 3T3-L1 adipocyte
- Vitamin C causes lung damages in diabetic rats
- Effects of ascorbic acid on the phagocytosis of murine peritoneal macrophages and the activities of lymphocytes
- Ascorbic Acid Determination in Aqueous and Vitreous Humor of the Rabbit
- The Effects of Ascorbic Acids on the Proliferation of the Human & Rabbit Tenon's Fibroblasts