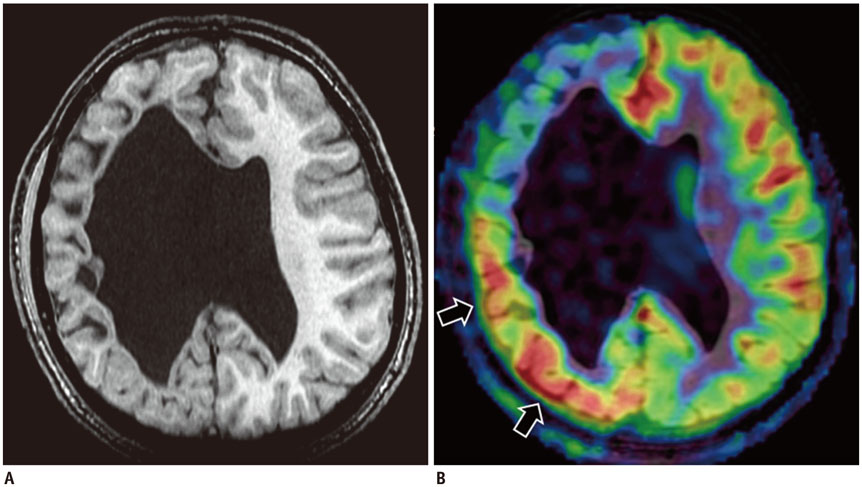
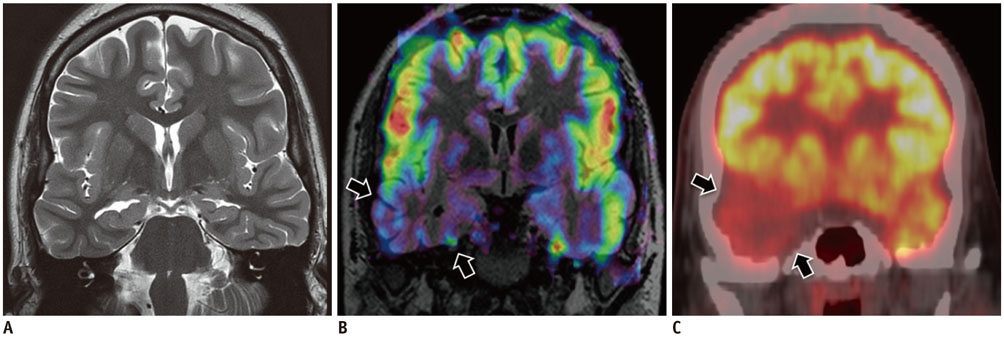
Korean J Radiol.
2018 Oct;19(5):965-977. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.5.965.
The Imaging of Localization Related Symptomatic Epilepsies: The Value of Arterial Spin Labelling Based Magnetic Resonance Perfusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Imaging Sciences & Interventional Radiology, Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences & Technology (SCTIMST), Trivandrum 695011, India. kesav@sctimst.ac.in
- 2Comprehensive Epilepsy Centre, Department of Neurology, Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences & Technology (SCTIMST), Trivandrum 695011, India.
- KMID: 2418561
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.5.965
Abstract
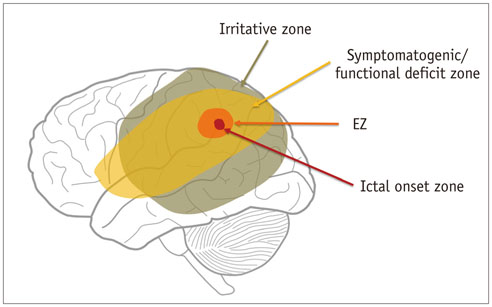
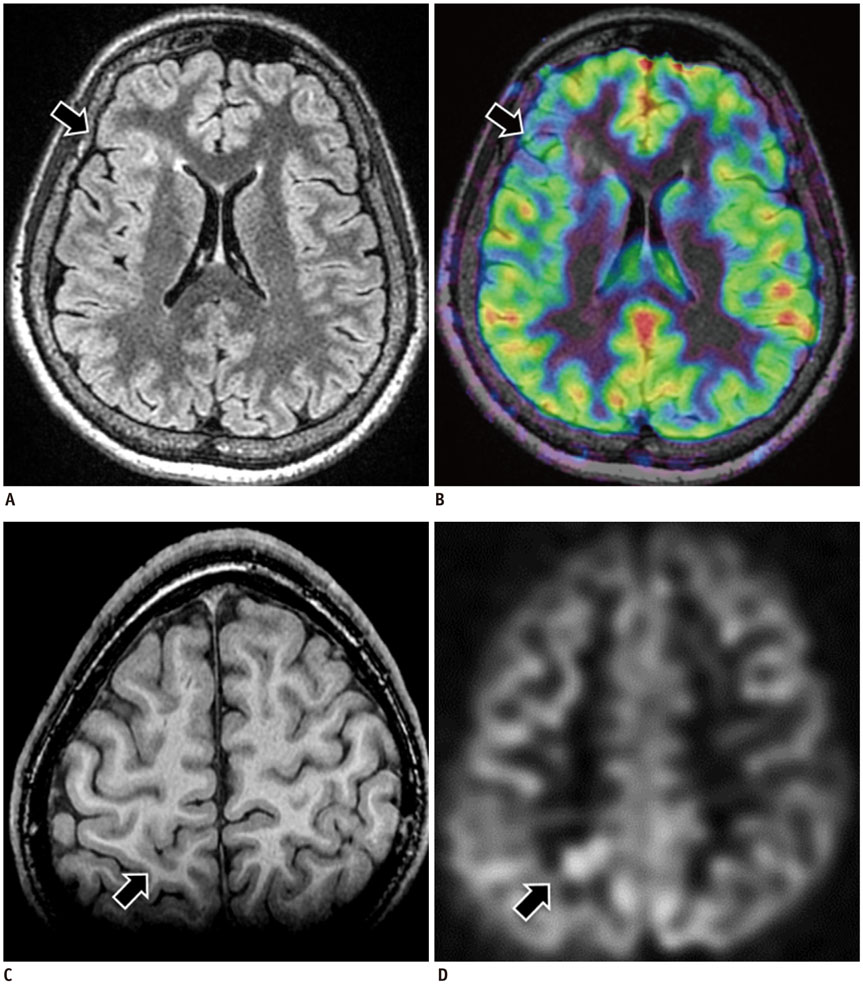
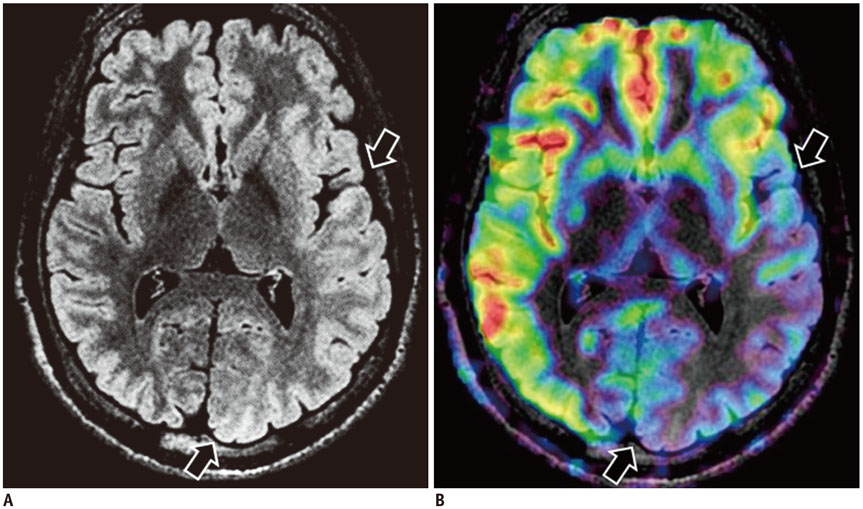
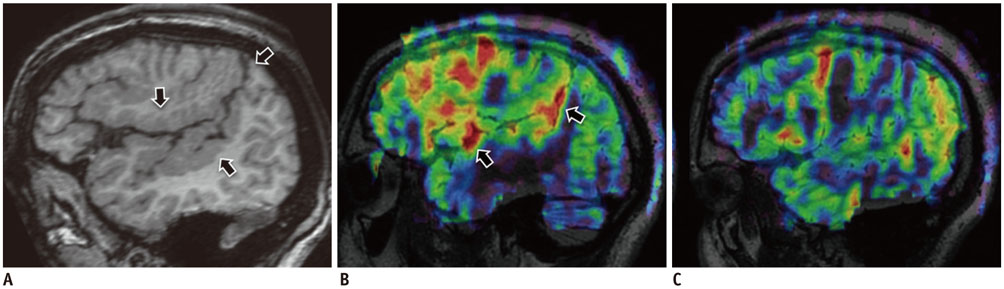
- Accurate identification of the epileptogenic zone is an important prerequisite in presurgical evaluation of refractory epilepsy since it affects seizure-free outcomes. Apart from structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI), delineation has been traditionally done with electroencephalography and nuclear imaging modalities. Arterial spin labelling (ASL) sequence is a non-contrast magnetic resonance perfusion technique capable of providing similar information. Similar to single-photon emission computed tomography, its utility in epilepsy is based on alterations in perfusion linked to seizure activity by neurovascular coupling. In this article, we discuss complementary value that ASL can provide in the evaluation and characterization of some basic substrates underlying epilepsy. We also discuss the role that ASL may play in sMRI negative epilepsy and acute scenarios such as status epilepticus.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shorvon SD. The etiologic classification of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2011; 52:1052–1057.
Article2. Koepp MJ, Woermann FG. Imaging structure and function in refractory focal epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2005; 4:42–53.
Article3. Woermann FG, Vollmar C. Clinical MRI in children and adults with focal epilepsy: a critical review. Epilepsy Behav. 2009; 15:40–49.
Article4. Tao JX, Baldwin M, Hawes-Ebersole S, Ebersole JS. Cortical substrates of scalp EEG epileptiform discharges. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 24:96–100.
Article5. Shorvon S, Perucca E, Engel J Jr. The treatment of epilepsy. 4th ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell;2015. p. 714–715.6. Deibler AR, Pollock JM, Kraft RA, Tan H, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA. Arterial spin-labeling in routine clinical practice, part 1: technique and artifacts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1228–1234.
Article7. Blumenfeld H, McNally KA, Vanderhill SD, Paige AL, Chung R, Davis K, et al. Positive and negative network correlations in temporal lobe epilepsy. Cereb Cortex. 2004; 14:892–902.
Article8. Spencer SS. Neural networks in human epilepsy: evidence of and implications for treatment. Epilepsia. 2002; 43:219–227.
Article9. Englot DJ, Raygor KP, Molinaro AM, Garcia PA, Knowlton RC, Auguste KI, et al. Factors associated with failed focal neocortical epilepsy surgery. Neurosurgery. 2014; 75:648–656. discussion 655; quiz 656.
Article10. Chassoux F, Artiges E, Semah F, Laurent A, Landré E, Turak B, et al. 18F-FDG-PET patterns of surgical success and failure in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology. 2017; 88:1045–1053.11. Theodore WH. Presurgical focus localization in epilepsy: PET and SPECT. Semin Nucl Med. 2017; 47:44–53.
Article12. Kim BS, Lee ST, Yun TJ, Lee SK, Paeng JC, Jun J, et al. Capability of arterial spin labeling MR imaging in localizing seizure focus in clinical seizure activity. Eur J Radiol. 2016; 85:1295–1303.
Article13. Huneau C, Benali H, Chabriat H. Investigating human neurovascular coupling using functional neuroimaging: a critical review of dynamic models. Front Neurosci. 2015; 9:467.
Article14. Gaillard WD, Fazilat S, White S, Malow B, Sato S, Reeves P, et al. Interictal metabolism and blood flow are uncoupled in temporal lobe cortex of patients with complex partial epilepsy. Neurology. 1995; 45:1841–1847.
Article15. Hamandi K, Laufs H, Nöth U, Carmichael DW, Duncan JS, Lemieux L. BOLD and perfusion changes during epileptic generalised spike wave activity. Neuroimage. 2008; 39:608–618.
Article16. Stefanovic B, Warnking JM, Kobayashi E, Bagshaw AP, Hawco C, Dubeau F, et al. Hemodynamic and metabolic responses to activation, deactivation and epileptic discharges. Neuroimage. 2005; 28:205–215.
Article17. Pizzini FB, Farace P, Manganotti P, Zoccatelli G, Bongiovanni LG, Golay X, et al. Cerebral perfusion alterations in epileptic patients during peri-ictal and post-ictal phase: PASL vs DSC-MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 31:1001–1005.
Article18. Menon RN, Radhakrishnan A, Parameswaran R, Thomas B, Kesavadas C, Abraham M, et al. Does F-18 FDG-PET substantially alter the surgical decision-making in drug-resistant partial epilepsy? Epilepsy Behav. 2015; 51:133–139.
Article19. Madan N, Grant PE. New directions in clinical imaging of cortical dysplasias. Epilepsia. 2009; 50:Suppl 9. 9–18.
Article20. Jones AL, Cascino GD. Evidence on use of neuroimaging for surgical treatment of temporal lobe epilepsy: a systematic review. JAMA Neurol. 2016; 73:464–470.21. Gaillard WD, Zeffiro T, Fazilat S, DeCarli C, Theodore WH. Effect of valproate on cerebral metabolism and blood flow: an 18F-2-deoxyglucose and 15O water positron emission tomography study. Epilepsia. 1996; 37:515–521.22. Guo X, Xu S, Wang G, Zhang Y, Guo L, Zhao B. Asymmetry of cerebral blood flow measured with three-dimensional pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling mr imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 42:1386–1397.
Article23. Wolf RL, Alsop DC, Levy-Reis I, Meyer PT, Maldjian JA, Gonzalez-Atavales J, et al. Detection of mesial temporal lobe hypoperfusion in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy by use of arterial spin labeled perfusion MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1334–1341.24. Storti SF, Boscolo Galazzo I, Del Felice A, Pizzini FB, Arcaro C, Formaggio E, et al. Combining ESI, ASL and PET for quantitative assessment of drug-resistant focal epilepsy. Neuroimage. 2014; 102(Pt 1):49–59.
Article25. Boscolo Galazzo I, Storti SF, Del Felice A, Pizzini FB, Arcaro C, Formaggio E, et al. Patient-specific detection of cerebral blood flow alterations as assessed by arterial spin labeling in drug-resistant epileptic patients. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0123975.
Article26. Lim YM, Cho YW, Shamim S, Solomon J, Birn R, Luh WM, et al. Usefulness of pulsed arterial spin labeling MR imaging in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2008; 82:183–189.
Article27. Cianfoni A, Caulo M, Cerase A, Della Marca G, Falcone C, Di Lella GM, et al. Seizure-induced brain lesions: a wide spectrum of variably reversible MRI abnormalities. Eur J Radiol. 2013; 82:1964–1972.
Article28. Provenzale JM, Barboriak DP, VanLandingham K, MacFall J, Delong D, Lewis DV. Hippocampal MRI signal hyperintensity after febrile status epilepticus is predictive of subsequent mesial temporal sclerosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:976–983.
Article29. Vattipally VR, Bronen RA. MR imaging of epilepsy: strategies for successful interpretation. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2006; 14:225–247.
Article30. Bast T, Ramantani G, Seitz A, Rating D. Focal cortical dysplasia: prevalence, clinical presentation and epilepsy in children and adults. Acta Neurol Scand. 2006; 113:72–81.
Article31. Stanescu L, Ishak GE, Khanna PC, Biyyam DR, Shaw DW, Parisi MT. FDG PET of the brain in pediatric patients: imaging spectrum with MR imaging correlation. Radiographics. 2013; 33:1279–1303.
Article32. Wintermark P, Lechpammer M, Warfield SK, Kosaras B, Takeoka M, Poduri A, et al. Perfusion imaging of focal cortical dysplasia using arterial spin labeling: correlation with histopathological vascular density. J Child Neurol. 2013; 28:1474–1482.33. Wissmeyer M, Altrichter S, Pereira VM, Viallon M, Federspiel A, Seeck M, et al. Arterial spin-labeling MRI perfusion in tuberous sclerosis: correlation with PET. J Neuroradiol. 2010; 37:127–130.
Article34. Rintahaka PJ, Chugani HT, Messa C, Phelps ME. Hemimegalencephaly: evaluation with positron emission tomography. Pediatr Neurol. 1993; 9:21–28.
Article35. Altrichter S, Pendse N, Wissmeyer M, Jägersberg M, Federspiel A, Viallon M, et al. Arterial spin-labeling demonstrates ictal cortical hyperperfusion in epilepsy secondary to hemimegalencephaly. J Neuroradiol. 2009; 36:303–305.
Article36. Wintermark P, Roulet-Perez E, Maeder-Ingvar M, Moessinger AC, Gudinchet F, Meuli R. Perfusion abnormalities in hemimegalencephaly. Neuropediatrics. 2009; 40:92–96.
Article37. Van Bogaert P, David P, Gillain CA, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Scalais E, et al. Perisylvian dysgenesis. Clinical, EEG, MRI and glucose metabolism features in 10 patients. Brain. 1998; 121(Pt 12):2229–2238.
Article38. De Volder AG, Gadisseux JF, Michel CJ, Maloteaux JM, Bol AC, Grandin CB, et al. Brain glucose utilization in band heterotopia: synaptic activity of “double cortex”. Pediatr Neurol. 1994; 11:290–294.
Article39. Seniaray N, Jain A. PET MRI coregistration in intractable epilepsy and gray matter heterotopia. Clin Nucl Med. 2017; 42:e171–e172.
Article40. Conrad GR, Sinha P. FDG PET imaging of subependymal gray matter heterotopia. Clin Nucl Med. 2005; 30:35–36.
Article41. Thom M, Blümcke I, Aronica E. Long-term epilepsy-associated tumors. Brain Pathol. 2012; 22:350–379.
Article42. Radhakrishnan A, Abraham M, Vilanilam G, Menon R, Menon D, Kumar H, et al. Surgery for “long-term epilepsy associated tumors (LEATs)”: seizure outcome and its predictors. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016; 141:98–105.
Article43. Yeom KW, Mitchell LA, Lober RM, Barnes PD, Vogel H, Fisher PG, et al. Arterial spin-labeled perfusion of pediatric brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35:395–401.
Article44. Hamer HM, Hong SB. Is an epilepsy presurgical evaluation necessary for mid-grade and high-grade brain tumors presenting with seizures? Epilepsia. 2013; 54:Suppl 9. 56–60.
Article45. Josephson CB, Rosenow F, Al-Shahi Salman R. Intracranial vascular malformations and epilepsy. Semin Neurol. 2015; 35:223–234.
Article46. Le TT, Fischbein NJ, André JB, Wijman C, Rosenberg J, Zaharchuk G. Identification of venous signal on arterial spin labeling improves diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistulas and small arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:61–68.
Article47. Wolf RL, Wang J, Detre JA, Zager EL, Hurst RW. Arteriovenous shunt visualization in arteriovenous malformations with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:681–687.
Article48. Blauwblomme T, Naggara O, Brunelle F, Grévent D, Puget S, Di Rocco F, et al. Arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging: toward noninvasive diagnosis and follow-up of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015; 15:451–458.
Article49. Yoo RE, Yun TJ, Yoon BW, Lee SK, Lee ST, Kang KM, et al. Identification of cerebral perfusion using arterial spin labeling in patients with seizures in acute settings. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0173538.
Article50. Dussaule C, Masnou P, Nasser G, Archambaud F, Cauquil-Michon C, Gagnepain JP, et al. Can developmental venous anomalies cause seizures? J Neurol. 2017; 264:2495–2505.
Article51. Iv M, Fischbein NJ, Zaharchuk G. Association of developmental venous anomalies with perfusion abnormalities on arterial spin labeling and bolus perfusion-weighted imaging. J Neuroimaging. 2015; 25:243–250.
Article52. Pinto A, Sahin M, Pearl PL. Epileptogenesis in neurocutaneous disorders with focus in Sturge Weber syndrome. F1000Res. 2016; 5:pii: F1000 Faculty Rev-370.
Article53. Varadkar S, Cross JH. Rasmussen syndrome and other inflammatory epilepsies. Semin Neurol. 2015; 35:259–268.
Article54. Hauf M, Wiest R, Nirkko A, Strozzi S, Federspiel A. Dissociation of epileptic and inflammatory activity in Rasmussen encephalitis. Epilepsy Res. 2009; 83:265–268.
Article55. Kumar S, Nagesh CP, Thomas B, Radhakrishnan A, Menon RN, Kesavadas C. Arterial spin labeling hyperperfusion in Rasmussen's encephalitis: is it due to focal brain inflammation or a postictal phenomenon? J Neuroradiol. 2018; 45:6–14.
Article56. Graus F, Titulaer MJ, Balu R, Benseler S, Bien CG, Cellucci T, et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016; 15:391–404.
Article57. Kelley BP, Patel SC, Marin HL, Corrigan JJ, Mitsias PD, Griffith B. Autoimmune encephalitis: pathophysiology and imaging review of an overlooked diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017; 38:1070–1078.
Article58. Sachs JR, Zapadka ME, Popli GS, Burdette JH. Arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging demonstrates cerebral hyperperfusion in anti-NMDAR encephalitis. Radiol Case Rep. 2017; 12:833–837.
Article59. Espinosa-Jovel C, Toledano R, García-Morales I, Álvarez-Linera J, Gil-Nagel A. Serial arterial spin labeling MRI in autonomic status epilepticus due to anti-LGI1 encephalitis. Neurology. 2016; 87:443–444.
Article60. Bonello M, Michael BD, Solomon T. Infective causes of epilepsy. Semin Neurol. 2015; 35:235–244.
Article61. Noguchi T, Yakushiji Y, Nishihara M, Togao O, Yamashita K, Kikuchi K, et al. Arterial spin-labeling in central nervous system infection. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2016; 15:386–394.
Article62. Ances BM, Sisti D, Vaida F, Liang CL, Leontiev O, Perthen JE, et al. HNRC group. Resting cerebral blood flow: a potential biomarker of the effects of HIV in the brain. Neurology. 2009; 73:702–770.
Article63. Khoury MN, Gheuens S, Ngo L, Wang X, Alsop DC, Koralnik IJ. Hyperperfusion in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy is associated with disease progression and absence of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Brain. 2013; 136(Pt 11):3441–3450.
Article64. Topolnik L, Steriade M, Timofeev I. Partial cortical deafferentation promotes development of paroxysmal activity. Cereb Cortex. 2003; 13:883–893.
Article65. Deibler AR, Pollock JM, Kraft RA, Tan H, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA. Arterial spin-labeling in routine clinical practice, part 2: hypoperfusion patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1235–1241.
Article66. Miyaji Y, Kawabata Y, Joki H, Seki S, Mori K, Kamide T, et al. Arterial spin-labeling magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosis of early seizure after stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 354:127–128.
Article67. Miyaji Y, Yokoyama M, Kawabata Y, Joki H, Kushi Y, Yokoi Y, et al. Arterial spin-labeling magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosis of late seizure after stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2014; 339:87–90.
Article68. Nagesh C, Asranna A, K P D, Cherian A, Nanda S, Thomas B. Culpable brain lesion causing complex partial status in Wilson's disease: deduction by arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI. Seizure. 2017; 46:50–52.
Article69. So EL, Ryvlin P. MRI-negative epilepsy. 1st ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press;2015. p. 255.70. Wang ZI, Alexopoulos AV, Jones SE, Jaisani Z, Najm IM, Prayson RA. The pathology of magnetic-resonance-imaging-negative epilepsy. Mod Pathol. 2013; 26:1051–1058.
Article71. Jeon TY, Kim JH, Lee J, Yoo SY, Hwang SM, Lee M. Value of repeat brain MRI in children with focal epilepsy and negative findings on initial MRI. Korean J Radiol. 2017; 18:729–738.
Article72. Rheims S, Jung J, Ryvlin P. Combination of PET and magnetoencephalography in the presurgical assessment of MRI-negative epilepsy. Front Neurol. 2013; 4:188.
Article73. Boscolo Galazzo I, Mattoli MV, Pizzini FB, De Vita E, Barnes A, Duncan JS, et al. Cerebral metabolism and perfusion in MR-negative individuals with refractory focal epilepsy assessed by simultaneous acquisition of (18)F-FDG PET and arterial spin labeling. Neuroimage Clin. 2016; 11:648–657.74. Mendes A, Sampaio L. Brain magnetic resonance in status epilepticus: a focused review. Seizure. 2016; 38:63–67.
Article75. Kanazawa Y, Morioka T, Arakawa S, Furuta Y, Nakanishi A, Kitazono T. Nonconvulsive partial status epilepticus mimicking recurrent infarction revealed by diffusion-weighted and arterial spin labeling perfusion magnetic resonance images. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015; 24:731–738.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arterial Spin Labelling Perfusion, Proton MR Spectroscopy and Susceptibility-Weighted MR Findings of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy: a Case Report
- Arterial Spin Labelling-Based Blood-Brain Barrier Assessment and Its Applications
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Arterial Spin Labeling: Techniques and Potential Clinical and Research Applications
- Simulations of Perfusion Signals of Pulsed Arterial Spin Labeling MRI
- Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion MRI Signal Processing Through Traditional Methods and Machine Learning