J Rheum Dis.
2018 Jul;25(3):207-211. 10.4078/jrd.2018.25.3.207.
Case of Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Articular Involvement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. leeyn35@gmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3WCU Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Medical Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2415610
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2018.25.3.207
Abstract
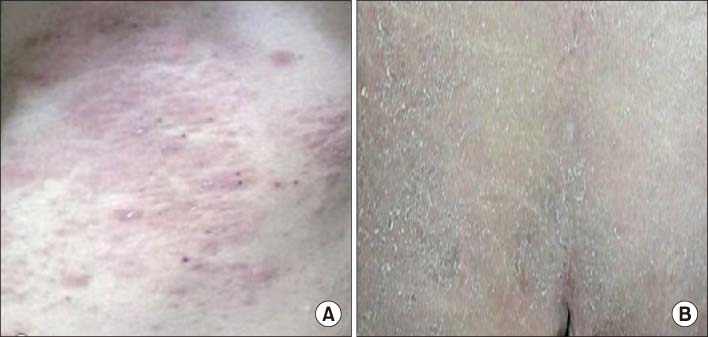
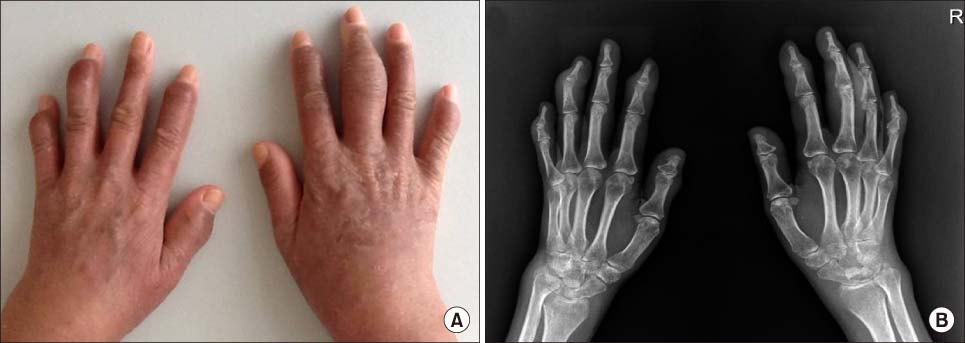
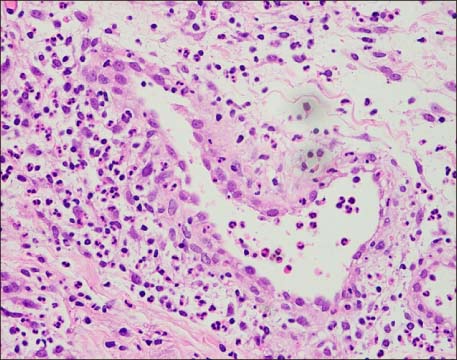
- Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (IHES) is a rare disease that is characterized by otherwise unexplained persistent eosinophilia and organ damage caused by eosinophilic infiltration. Its manifestations are highly variable but clinically apparent arthritis is uncommonly observed. Although Korean cases of severe eosinophilia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or IHES concurrent with RA have been published, there are no reports of IHES with joint involvement. This paper reports a case of IHES presenting with persistent peripheral eosinophilia, fever, skin rash, multiple lymphadenopathy, and polyarthritis, including the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Curtis C, Ogbogu P. Hypereosinophilic Syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016; 50:240–251.
Article2. Weller PF, Bubley GJ. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood. 1994; 83:2759–2779.
Article3. Brogadir SP, Goldwein MI, Schumacher HR. A hypereosinophilic syndrome mimicking rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1980; 69:799–802.
Article4. Spry CJ, Davies J, Tai PC, Olsen EG, Oakley CM, Goodwin JF. Clinical features of fifteen patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Q J Med. 1983; 52:1–22.5. Martín-Santos JM, Mulero J, Andréu JL, de Villa LF, Bernaldo-de Quirós L, Noguera E. Arthritis in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:120–125.6. Anders HJ, Schattenkirchner M. Destructive joint lesions and bursitis in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38:185–186.
Article7. Chaudhuri K, Dubey S, Zaphiropoulos G. Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome in a patient with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41:349–350.
Article8. Choi JH, Jung JW, Song HJ, Song KE, Choi JH, Suh YJ, et al. A case of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2003; 10:200–205.9. Park JH, Lee WS, Park SJ, Yoo WH. Hypereosinophilic syndrome associated with the onset of rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. J Rheum Dis. 2017; 24:165–168.
Article10. Sohn CI, Kim MK, Lee KC, Jung SS, Lee IH, Bae SC, et al. A case of rheumatoid arthritis accompanied by severe eosinophilia. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 1994; 1:98–102.11. Tay C. Eosinophilic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38:1188–1194.
Article12. Guellec D, Milin M, Cornec D, Tobon GJ, Marhadour T, Jousse-Joulin S, et al. Eosinophilia predicts poor clinical outcomes in recent-onset arthritis: results from the ESPOIR cohort. RMD Open. 2015; 1:e000070.
Article13. Chen Z, Andreev D, Oeser K, Krljanac B, Hueber A, Kleyer A, et al. Th2 and eosinophil responses suppress inflammatory arthritis. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:11596.
Article14. Kita H. Eosinophils: multifaceted biological properties and roles in health and disease. Immunol Rev. 2011; 242:161–177.
Article15. Ogbogu PU, Bochner BS, Butterfield JH, Gleich GJ, Huss-Marp J, Kahn JE, et al. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: a multicenter, retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:1319–1325.e3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome presenting multiple organ injuries with eyeball involvement
- A Case of the Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Evolving to Malignant Lymphoma
- Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Involving Thoracic Spine
- A case of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome manifested as regional wall motion abnormalities in echocardiogram and pericardial effusion
- A Case of Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Hepatic Involvement in a 5-Year-Old Boy