Hip Pelvis.
2018 Jun;30(2):115-119. 10.5371/hp.2018.30.2.115.
Sequential Bilateral Rapid Destructive Inflammatory Coxarthrosis in a Patient with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. hyeonjun@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2412693
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.2.115
Abstract
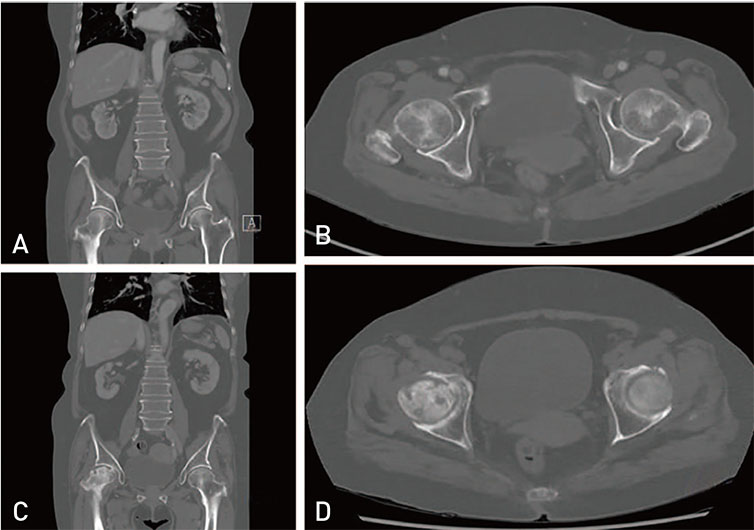
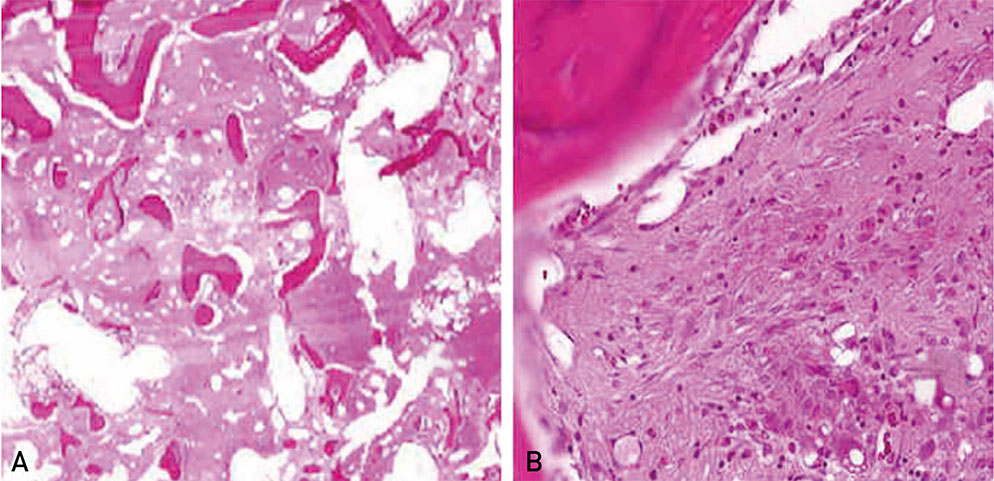
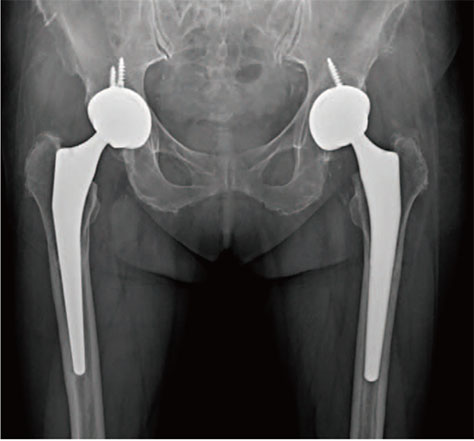
- The diagnostic criteria for sequential rapidly destructive coxarthrosis remain unclear and this condition is rarely reported in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Here, we report a case of an HIV-infected 73-year old female who experienced hip joint destruction. The patient was diagnosed with HIV in 2012 (at age 68 years) and began continuous treatment with nucleoside reverse transcriptase and protease inhibitors. Twenty-nine months after her HIV diagnosis, the patient experienced osteonecrosis of the right hip and underwent a total hip arthroplasty (THA). Twelve months post right-hip THA, X-ray results showed good outcomes. Eight months later (20 months post THA), however, osteolysis of the left femoral head was detected upon radiological exam and THA of the left hip was performed; chronic inflammation and fibrosis were identified in the resultant biopsy. Favorable results were obtained at 3 months after the second surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. UNAIDS/WHO global AIDS statistics. AIDS Care. 1999; 11:253–264.2. Gutiérrez F, Padilla S, Masiá M, et al. Osteonecrosis in patients infected with HIV: clinical epidemiology and natural history in a large case series from Spain. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006; 42:286–292.3. Matos MA, Alencar RW, Matos SS. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head in HIV infected patients. Braz J Infect Dis. 2007; 11:31–34.
Article4. Deshayes P, Thomine JM, Hemet J, Seruzier E, Biga N, Ducastelle C. Hip diseases with rapid chondrolysis. Clinical and anatomical comparison. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1975; 42:345–353. French.5. Rosenberg ZS, Shankman S, Steiner GC, Kastenbaum DK, Norman A, Lazansky MG. Rapid destructive osteoarthritis: clinical, radiographic, and pathologic features. Radiology. 1992; 182:213–216.
Article6. Komiya S, Inoue A, Sasaguri Y, Minamitani K, Morimatsu M. Rapidly destructive arthropathy of the hip. Studies on bone resorptive factors in joint fluid with a theory of pathogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; (284):273–282.7. Postel M, Kerboull M. Total prosthetic replacement in rapidly destructive arthrosis of the hip joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970; 72:138–144.8. Allison GT, Bostrom MP, Glesby MJ. Osteonecrosis in HIV disease: epidemiology, etiologies, and clinical management. AIDS. 2003; 17:1–9.9. Yoo MC, Lee SH, Cho YJ, Kim YH, Lee YS, Kang CH. Rapidly destructive coxarthrosis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1997; 32:1566–1574.
Article10. Glesby MJ, Hoover DR, Vaamonde CM. Osteonecrosis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: a case-control study. J Infect Dis. 2001; 184:519–523.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rapidly Destructive Coxarthrosis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Report on 3 Cases
- Rapidly Destructive Coxarthrosis
- A Case of Ankylosing Spondylitis in a Patient with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Rapid Destruction of the Hip Joint Accompanied by an Enlarged Iliopsoas Bursa in a Healthy Man
- A Case of Sequential Lymphoma in an Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Patient