Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Jun;10(2):240-247. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.240.
Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma-Derived Growth Factors Enhance Human Fibroblast Proliferation In Vitro
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. happyshoulder@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China.
- 3Gachon Medical Research Institute, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea. kokim67@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2411751
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.240
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Leukocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma (LP-PRP) from peripheral blood is currently used as a concentrated source of growth factors to stimulate repair at sites of soft tissue injury. Fibroblasts are primary mediators of wound healing. Thus, we aimed to assess the positive effect of LP-PRP on human fibroblast proliferation in vitro.
METHODS
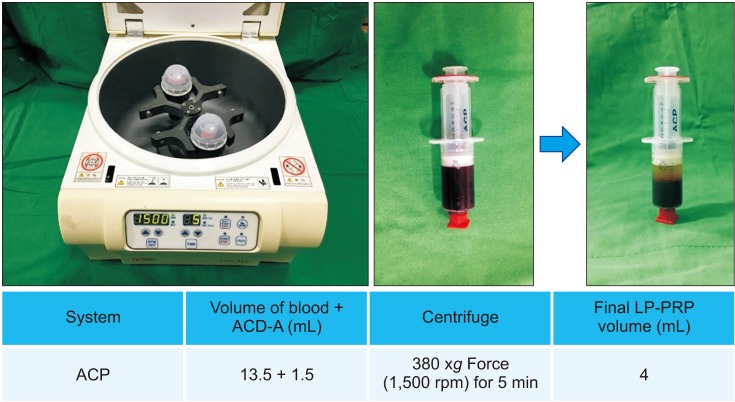
LP-PRP was prepared from 49 donors. The fibroblasts were seeded, and at 24 hours after seeding, 1 × 107/10 µL LP-PRP was added once to each well. The cells were harvested 10 times during study period at our planned points, and we examined cell proliferation using the water-soluble tetrazolium salt-1 assay. We collected the supernatants and measured the amount of growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-AB/BB, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which are known to be involved in wound healing processes, by multiplex assay.
RESULTS
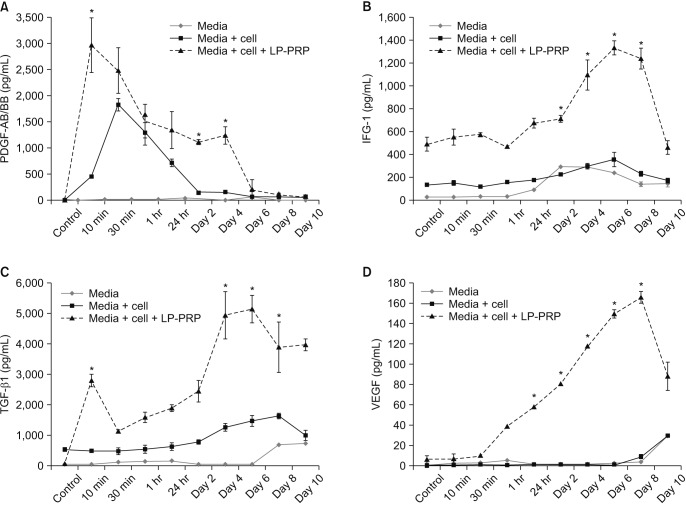
Human fibroblasts treated with LP-PRP showed a significant increase in proliferation when compared to untreated controls (p < 0.001 at days 4, 6, and 8). Multiplex cytokine assays revealed various secretion patterns. PDGF-AB/BB appeared at early time points and peaked before fibroblast proliferation. IGF-1 and TGF-β1 secretion gradually increased and peaked on days 4 and 6 post-treatment. The early VEGF concentration was lower than the concentration of other growth factors but increased along with cell proliferation.
CONCLUSIONS
Platelets in LP-PRP release growth factors such as PDGF, IGF-1, TGF-β1 and VEGF, and these growth factors have a promoting effect for human fibroblast proliferation, one of the important mediators of wound healing. These results suggest that growth factors derived from LP-PRP enhance the proliferation of human fibroblast.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cell Proliferation
Fibroblasts*
Humans*
In Vitro Techniques*
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins*
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor
Platelet-Rich Plasma
Soft Tissue Injuries
Tissue Donors
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Wound Healing
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Proteomic Classification and Identification of Proteins Related to Tissue Healing of Platelet-Rich Plasma
Ho Won Lee, Kyung-Ho Choi, Jung-Youn Kim, Kyung-Ok Kim, Bai Haotian, Liu Yuxuan, Kyu-Cheol Noh
Clin Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):120-129. doi: 10.4055/cios.2020.12.1.120.
Reference
-
1. Sundman EA, Cole BJ, Fortier LA. Growth factor and catabolic cytokine concentrations are influenced by the cellular composition of platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med. 2011; 39(10):2135–2140. PMID: 21846925.
Article2. Werner S, Grose R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev. 2003; 83(3):835–870. PMID: 12843410.
Article3. Yun JH, Han SH, Choi SH, et al. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma on bone regeneration for osseointegration of dental implants: preliminary study in canine three-wall intrabony defects. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014; 102(5):1021–1030. PMID: 24307497.
Article4. Kaigler D, Avila G, Wisner-Lynch L, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor applications in periodontal and peri-implant bone regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011; 11(3):375–385. PMID: 21288185.
Article5. Frechette JP, Martineau I, Gagnon G. Platelet-rich plasmas: growth factor content and roles in wound healing. J Dent Res. 2005; 84(5):434–439. PMID: 15840779.
Article6. Wasterlain AS, Braun HJ, Dragoo JL. Contents and formulations of platelet-rich plasma. Oper Tech Orthop. 2012; 22(1):33–42.
Article7. Sanchez M, Anitua E, Azofra J, Aguirre JJ, Andia I. Intra-articular injection of an autologous preparation rich in growth factors for the treatment of knee OA: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008; 26(5):910–913. PMID: 19032827.8. Radice F, Yanez R, Gutierrez V, Rosales J, Pinedo M, Coda S. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings in anterior cruciate ligament grafts with and without autologous platelet-derived growth factors. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26(1):50–57. PMID: 20117627.
Article9. McCarrel TM, Minas T, Fortier LA. Optimization of leukocyte concentration in platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of tendinopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(19):e143. PMID: 23032594.
Article10. Duif C, Vogel T, Topcuoglu F, Spyrou G, von Schulze Pellengahr C, Lahner M. Does intraoperative application of leukocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma during arthroscopy for knee degeneration affect postoperative pain, function and quality of life? A 12-month randomized controlled double-blind trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015; 135(7):971–977. PMID: 25957981.
Article11. Smith PA. Intra-articular autologous conditioned plasma injections provide safe and efficacious treatment for knee osteoarthritis: an FDA-sanctioned, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(4):884–891. PMID: 26831629.12. Behera P, Dhillon M, Aggarwal S, Marwaha N, Prakash M. Leukocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma versus bupivacaine for recalcitrant lateral epicondylar tendinopathy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015; 23(1):6–10. PMID: 25920634.
Article13. Osterman C, McCarthy MB, Cote MP, et al. Platelet-rich plasma increases anti-inflammatory markers in a human coculture model for osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43(6):1474–1484. PMID: 25716226.
Article14. Mazzucco L, Balbo V, Cattana E, Guaschino R, Borzini P. Not every PRP-gel is born equal. Evaluation of growth factor availability for tissues through four PRP-gel preparations: Fibrinet, RegenPRP-Kit, Plateltex and one manual procedure. Vox Sang. 2009; 97(2):110–118. PMID: 19392780.
Article15. DeLong JM, Russell RP, Mazzocca AD. Platelet-rich plasma: the PAW classification system. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28(7):998–1009. PMID: 22738751.
Article16. Magalon J, Bausset O, Serratrice N, et al. Characterization and comparison of 5 platelet-rich plasma preparations in a single-donor model. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30(5):629–638. PMID: 24725317.
Article17. Le Pillouer-Prost A. Fibroblasts: what's new in cellular biology? J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2003; 5(3-4):232–238. PMID: 14741842.18. Graziani F, Ivanovski S, Cei S, Ducci F, Tonetti M, Gabriele M. The in vitro effect of different PRP concentrations on osteoblasts and fibroblasts. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17(2):212–219. PMID: 16584418.
Article19. Boyce ST, Ham RG. Calcium-regulated differentiation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes in chemically defined clonal culture and serum-free serial culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1983; 81(1 Suppl):33s–40s. PMID: 6345690.
Article20. Kushida S, Kakudo N, Morimoto N, et al. Platelet and growth factor concentrations in activated platelet-rich plasma: a comparison of seven commercial separation systems. J Artif Organs. 2014; 17(2):186–192. PMID: 24748436.
Article21. Mazzocca AD, McCarthy MB, Chowaniec DM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma differs according to preparation method and human variability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(4):308–316. PMID: 22336969.
Article22. Mazzocca AD, McCarthy MB, Chowaniec DM, et al. The positive effects of different platelet-rich plasma methods on human muscle, bone, and tendon cells. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40(8):1742–1749. PMID: 22802273.
Article23. Everts PA, Hoffmann J, Weibrich G, et al. Differences in platelet growth factor release and leucocyte kinetics during autologous platelet gel formation. Transfus Med. 2006; 16(5):363–368. PMID: 16999760.
Article24. Tokunaga A, Oya T, Ishii Y, et al. PDGF receptor beta is a potent regulator of mesenchymal stromal cell function. J Bone Miner Res. 2008; 23(9):1519–1528. PMID: 18410236.25. Lynch SE, Nixon JC, Colvin RB, Antoniades HN. Role of platelet-derived growth factor in wound healing: synergistic effects with other growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987; 84(21):7696–7700. PMID: 3499612.
Article26. Bennett NT, Schultz GS. Growth factors and wound healing: biochemical properties of growth factors and their receptors. Am J Surg. 1993; 165(6):728–737. PMID: 8506974.
Article27. Olesen JL, Heinemeier KM, Haddad F, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor I, insulin-like growth factor binding proteins, and collagen mRNA in mechanically loaded plantaris tendon. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006; 101(1):183–188. PMID: 16782835.
Article28. Lind M, Overgaard S, Nguyen T, Ongpipattanakul B, Bunger C, Soballe K. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates bone ongrowth: hydroxyapatite-coated implants studied in dogs. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996; 67(6):611–616. PMID: 9065077.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of Platelet-rich Plasma
- Effect of Platelet-rich Plasma on Burn Wounds according to Time of Application: An Experimental Study on Rats
- The Effects of Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin and AdvancedPlatelet Rich Fibrin on Gingival Fibroblast Cell Vitality, Proliferation, Differentiation
- Platelet-rich plasma, platelet derivatives, and their therapeutic importance in veterinary medicine
- Enhanced skin wound healing by a sustained release of growth factors contained in platelet-rich plasma