Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2017 Mar;25(1):21-27. 10.12793/tcp.2017.25.1.21.
Validated UPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of tadalafil in human plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon 22332, South Korea. shcho123@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon 22332, South Korea.
- 3Clinical Research Center of H PLUS Yangji Hospital, Sillim-dong, Gwanak-gu, Seoul 08779, South Korea.
- KMID: 2411415
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2017.25.1.21
Abstract
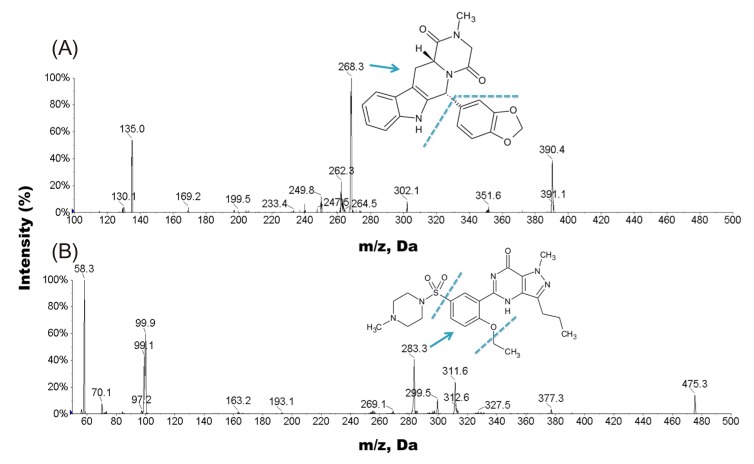
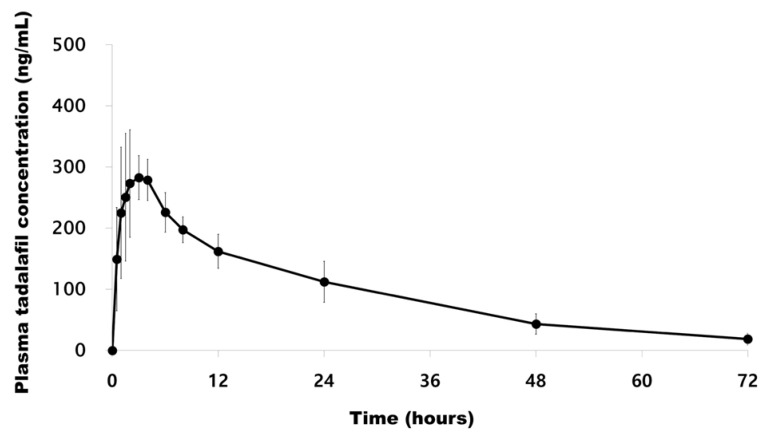
- A simple, rapid, and reliable UPLC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the determination of tadalafil in human plasma. The plasma samples were deproteinized with acetonitrile. Chromatographic separation was performed on a Shiseido C18 (100 × 2.1 mm, 2.7 µm) column with isocratic elution using 2.0 mM ammonium acetate and acetonitrile (55:45, v/v) with 0.1% formic acid at a flow rate of 0.7 mL/min. The total run time was 1 min per sample. The quantitative analysis was performed using multiple reaction monitoring at transition of m/z 390.4 → 268.3 for tadalafil and m/z 475.3 → 283.3 for sildenafil as an internal standard. The method was fully validated over a concentration range of 5-1,000 ng/mL with a lower quantification limit of 5 ng/mL. Intra- and inter-day precision (relative standard deviation, %RSD) were within 8.4% and accuracy (relative error, %RE) was lower than -3.2%. The developed and validated method was successfully applied to a pharmacokinetic study of tadalafil (20 mg) in Korean healthy male subjects (n = 12).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kuan J, Brock G. Selective phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition using tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2002; 11:1605–1613.
Article2. Meuleman EJ. Review of tadalafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003; 4:2049–2056. PMID: 14596658.
Article3. Rotella DP. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors: current status and potential applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002; 1:674–682. PMID: 12209148.
Article4. Rosen RC, Kostis JB. Overview of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition in erectile dysfunction. Am J Cardiol. 2003; 92:9M–18M.
Article5. Corbin JD. Mechanisms of action of PDE5 inhibition in erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2004; 16(Suppl 1):S4–S7. PMID: 15224127.
Article6. Doggrell SA. Comparison of clinical trials with sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil in erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005; 6:75–84. PMID: 15709885.
Article7. Bruzziches R, Francomano D, Gareri P, Lenzi A, Aversa A. An update on pharmacological treatment of erectile dysfunction with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013; 14:1333–1344. DOI: 10.1517/14656566.2013.799665.PMID: 23675780.
Article8. Cleves AE, Jain AN. Effects of inductive bias on computational evaluations of ligand-based modeling and on drug discovery. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2008; 22:147–159. PMID: 18074107.
Article9. Cheng CL, Chou CH. Determination of tadalafil in small volumes of plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005; 822:278–284.
Article10. Shakya AK, Abu-awwad AN, Arafat TA, Melhim M. Validated liquid chromatographic-ultraviolet method for the quantitation of tadalafil in human plasma using liquid-liquid extraction. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007; 852:403–408.
Article11. Farthing CA, Farthing DE, Koka S, Larus T, Fakhry I, Xi L, et al. A simple and sensitive HPLC fluorescence method for determination of tadalafil in mouse plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010; 878:2891–2895. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.07.022.
Article12. Ramakrishna NV, Vishwottam KN, Puran S, Koteshwara M, Manoj S, Santosh M, et al. Quantitation of tadalafil in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004; 809:243–249.
Article13. Lee JH, Oh JH, Lee YJ. Simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry methods for quantification of tadalafil in rat plasma: application to pharmacokinetic study in rats. Arch Pharm Res. 2013; 36:457–463. DOI: 10.1007/s12272-013-0046-1. PMID: 23435913.
Article14. Rust KY, Wilkens H, Kaiser R, Bregel D, Wilske J, Kraemer T. Detection and validated quantification of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, and 2 of their metabolites in human blood plasma by LC-MS/MS--application to forensic and therapeutic drug monitoring cases. Ther Drug Monit. 2012; 34:729–735. DOI: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e31827318b8. PMID: 23128911.
Article15. Ma B, Shang X, Zhang Q, Li J, Liu Y, Cao X, et al. Rapid analysis of tadalafil in human blood plasma and seminal plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013; 77:149–157. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.01.019. PMID: 23416369.
Article16. Yokoyama Y, Tomatsuri M, Hayashi H, Hirai K, Ono Y, Yamada Y, et al. Simultaneous microdetermination of bosentan, ambrisentan, sildenafil, and tadalafil in plasma using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for pediatric patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014; 89:227–232. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.11.007. PMID: 24309556.
Article17. Proenca P, Mustra C, Marcos M, Franco JM, Corte-Real F, Vieira DN. Validated UPLC-MS/MS assay for the determination of synthetic phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitors in postmortem blood samples. J Forensic Leg Med. 2013; 20:655–658. DOI: 10.1016/j.jflm.2013.03.002. PMID: 23910856.18. Lee S, Choi B, Kim J, In S, Baeck S, Oh SM, et al. An LC-MS/MS method for the determination of five erectile dysfunction drugs and their selected metabolites in hair. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015; 978-979:1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.11.024.
Article19. Karavadi T, Challa BR. Determination of Tadalafil in rat plasma by liquid chromatography tandam mass spectrometry: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Pharm Lett. 2012; 4:1401–1413.20. de Boer T, Wieling J. Incurred sample accuracy assessment: design of experiments based on standard addition. Bioanalysis. 2011; 3:983–992. DOI: 10.4155/bio.11.36. PMID: 21545346.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and validation of a UPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of acetaminophen in human plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic studies
- Qualification and application of liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-offlight mass spectrometric method for the determination of carisbamate in rat plasma and prediction of its human pharmacokinetics using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling
- Development and validation of analytical method for the determination of radotinib in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Determination of donepezil in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Determination of sumatriptan in human plasma using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for pharmacokinetic study in healthy Korean volunteers