Immune Netw.
2017 Dec;17(6):402-409. 10.4110/in.2017.17.6.402.
Polyvinylidene Fluoride Alters Inflammatory Responses by Activation-induced Cell Death in Macrophages
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacy, Korea University, Sejong 30019, Korea. yjung@korea.ac.kr, sachoi@korea.ac.kr
- 2School of Civil, Environmental and Architectural Engineering, Korea University, Seoul 02841, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 54907, Korea.
- 4Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Division of Health Sciences, Dongseo University, Busan 47011, Korea.
- KMID: 2400626
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2017.17.6.402
Abstract
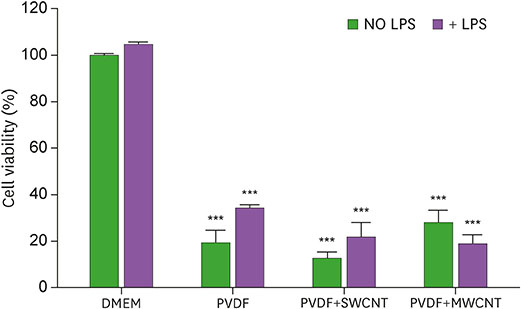
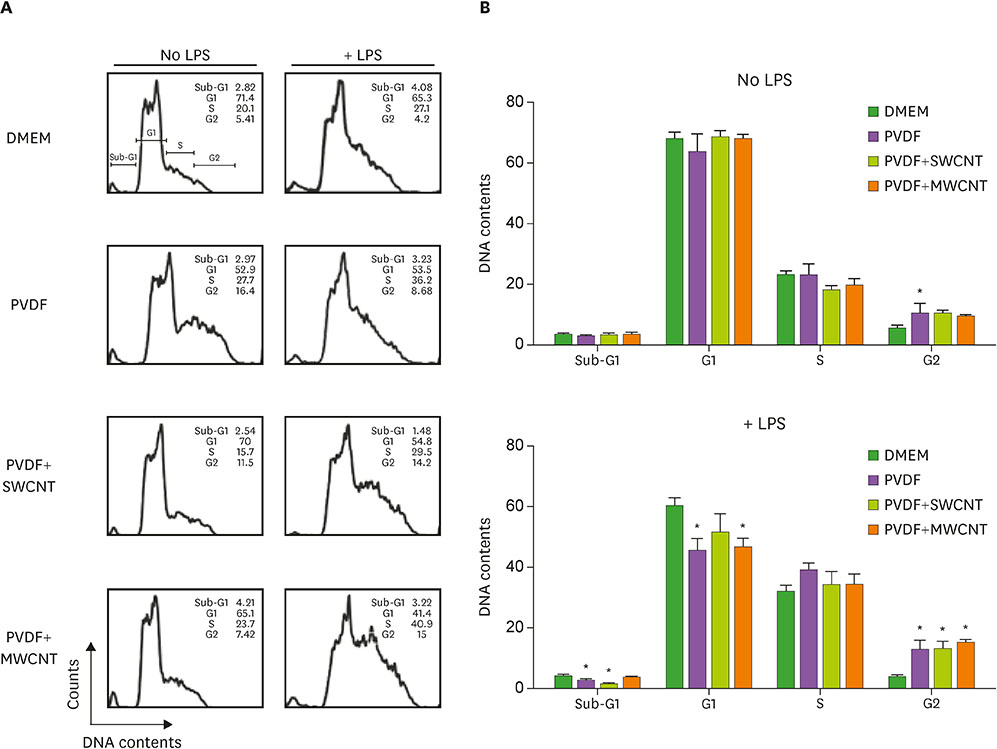
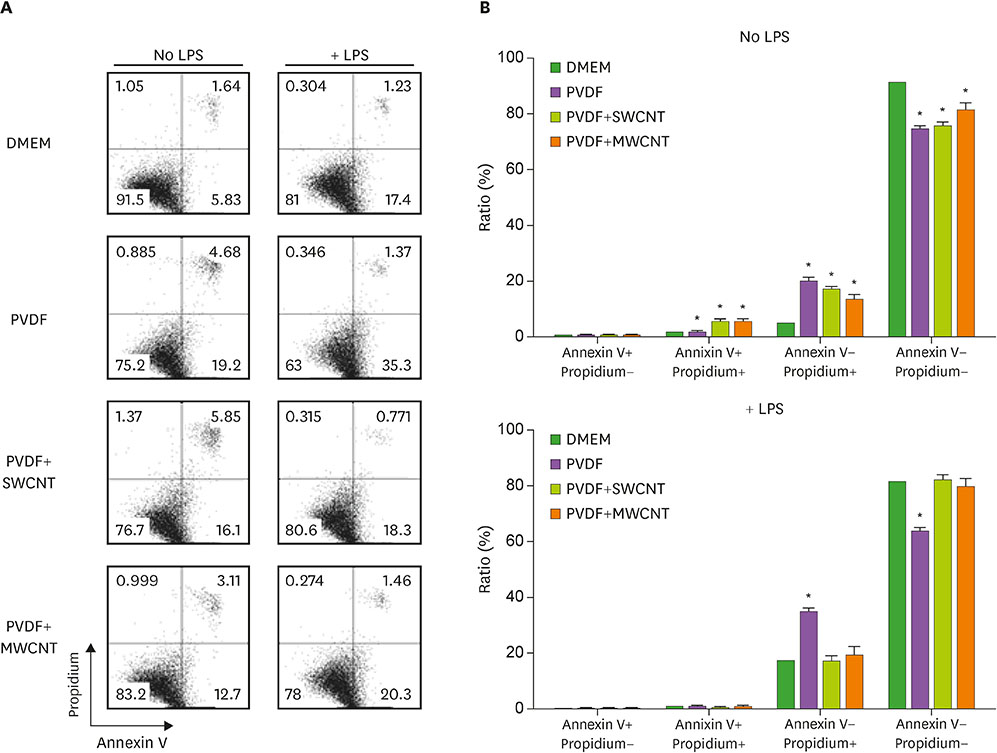
- Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are nanomaterials that have been employed in generating diverse materials. We previously reported that CNTs induce cell death in macrophages, possibly via asbestosis. Therefore, we generated CNT-attached polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which is an established polymer in membrane technology, and then examined whether CNT-attached PVDF is immunologically safe for medical purposes compared to CNT alone. To test this, we treated RAW 264.7 murine macrophages (RAW cells) with CNT-attached PVDF and analyzed the production of nitric oxide (NO), a potent proinflammatory mediator, in these cells. RAW cells treated with CNT-attached PVDF showed reduced NO production in response to lipopolysaccharide. However, the same treatment also decreased the cell number suggesting that this treatment can alter the homeostasis of RAW cells. Although cell cycle of RAW cells was increased by PVDF treatment with or without CNTs, apoptosis was enhanced in these cells. Taken together, these results indicate that PVDF with or without CNTs modulates inflammatory responses possibly due to activation-induced cell death in macrophages.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oh SJ, Kim N, Lee YT. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/TiO2 organic-inorganic composite membranes for fouling resistance improvement. J Membr Sci. 2009; 345:13–20.
Article2. Deng B, Yu M, Yang X, Zhang B, Li L, Xie L, Li J, Lu X. Antifouling microfiltration membranes prepared from acrylic acid or methacrylic acid grafted poly(vinylidene fluoride) powder synthesized via pre-irradiation induced graft polymerization. J Membr Sci. 2010; 350:252–258.
Article3. Chiang YC, Chang Y, Higuchi A, Chen WY, Ruaan RC. Sulfobetaine-grafted poly(vinylidene fluoride) ultrafiltration membranes exhibit excellent antifouling property. J Membr Sci. 2009; 339:151–159.
Article4. Lang WZ, Xu ZL, Yang H, Tong W. Preparation and characterization of PVDF-PFSA blend hollow fiber UF membrane. J Membr Sci. 2007; 288:123–131.
Article5. Flajnik MF, Du Pasquier L. Evolution of innate and adaptive immunity: can we draw a line? Trends Immunol. 2004; 25:640–644.
Article6. Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R. Introduction: the role of innate immunity in the adaptive immune response. Semin Immunol. 1998; 10:349–350.
Article7. Hoebe K, Janssen E, Beutler B. The interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5:971–974.
Article8. Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS. Recognition of gram-negative bacteria and endotoxin by the innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999; 11:19–22.
Article9. MacMicking J, Xie QW, Nathan C. Nitric oxide and macrophage function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997; 15:323–350.
Article10. Boscá L, Zeini M, Través PG, Hortelano S. Nitric oxide and cell viability in inflammatory cells: a role for NO in macrophage function and fate. Toxicology. 2005; 208:249–258.
Article11. Aderem A, Underhill DM. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999; 17:593–623.
Article12. Kim KH, Yeon SM, Kim HG, Lee H, Kim SK, Han SH, Min KJ, Byun Y, Lee EH, Lee KS, et al. Single-walled carbon nanotubes induce cell death and transcription of TNF-α in macrophages without affecting nitric oxide production. Inflammation. 2014; 37:44–54.
Article13. Kim HG, Yeon SM, Kim KH, Kim H, Park JI, Kang HJ, Cha EJ, Park HD, Kang HJ, Park TW, et al. Estrogenic endocrine-disrupting chemicals modulate the production of inflammatory mediators and cell viability of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Inflammation. 2015; 38:595–605.
Article14. Krishan A. Rapid flow cytofluorometric analysis of mammalian cell cycle by propidium iodide staining. J Cell Biol. 1975; 66:188–193.
Article15. Conze J, Junge K, Weiss C, Anurov M, Oettinger A, Klinge U, Schumpelick V. New polymer for intra-abdominal meshes--PVDF copolymer. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008; 87:321–328.
Article16. Binnebösel M, Ricken C, Klink CD, Junge K, Jansen M, Schumpelick V, Lynen Jansen P. Impact of gentamicin-supplemented polyvinylidenfluoride mesh materials on MMP-2 expression and tissue integration in a transgenic mice model. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2010; 395:413–420.
Article17. Klosterhalfen B, Junge K, Hermanns B, Klinge U. Influence of implantation interval on the long-term biocompatibility of surgical mesh. Br J Surg. 2002; 89:1043–1048.
Article18. Munn DH, Beall AC, Song D, Wrenn RW, Throckmorton DC. Activation-induced apoptosis in human macrophages: developmental regulation of a novel cell death pathway by macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1995; 181:127–136.
Article19. Donaldson K, Murphy FA, Duffin R, Poland CA. Asbestos, carbon nanotubes and the pleural mesothelium: a review of the hypothesis regarding the role of long fibre retention in the parietal pleura, inflammation and mesothelioma. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010; 7:5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CD11b Deficiency Exacerbates Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Sepsis by Upregulating Inflammatory Responses of Macrophages
- ZFP36L1 and AUF1 Induction Contribute to the Suppression of Inflammatory Mediators Expression by Globular Adiponectin via Autophagy Induction in Macrophages
- Oxidation-dependent effects of oxidized LDL: proliferation or cell death
- The Effects of Irisin on the Interaction between Hepatic Stellate Cell and Macrophage in Liver Fibrosis
- Silymarin Inhibits Morphological Changes in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages by Blocking NF-kappaB Pathway