Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2018 Jan;22(1):71-80. 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.1.71.
Antidepressant drug paroxetine blocks the open pore of Kv3.1 potassium channel
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Institute for Medical Science, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 54097, Korea. bhchoi@jbnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, Institute for Medical Science, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 54097, Korea.
- 3Department of Physiology, Medical Research Center, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- KMID: 2398557
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.1.71
Abstract
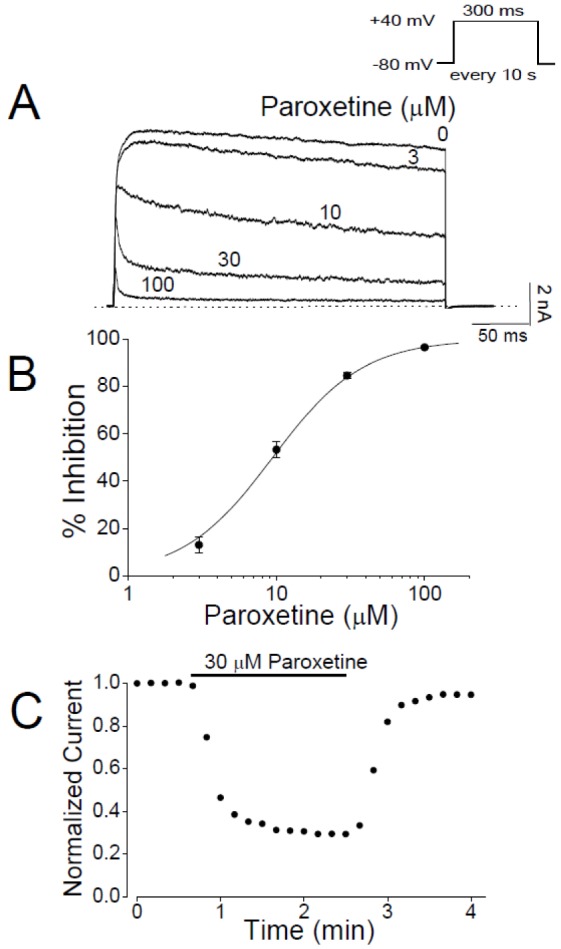
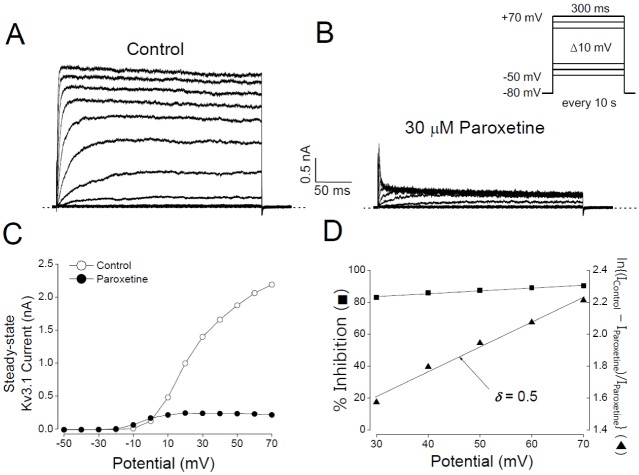
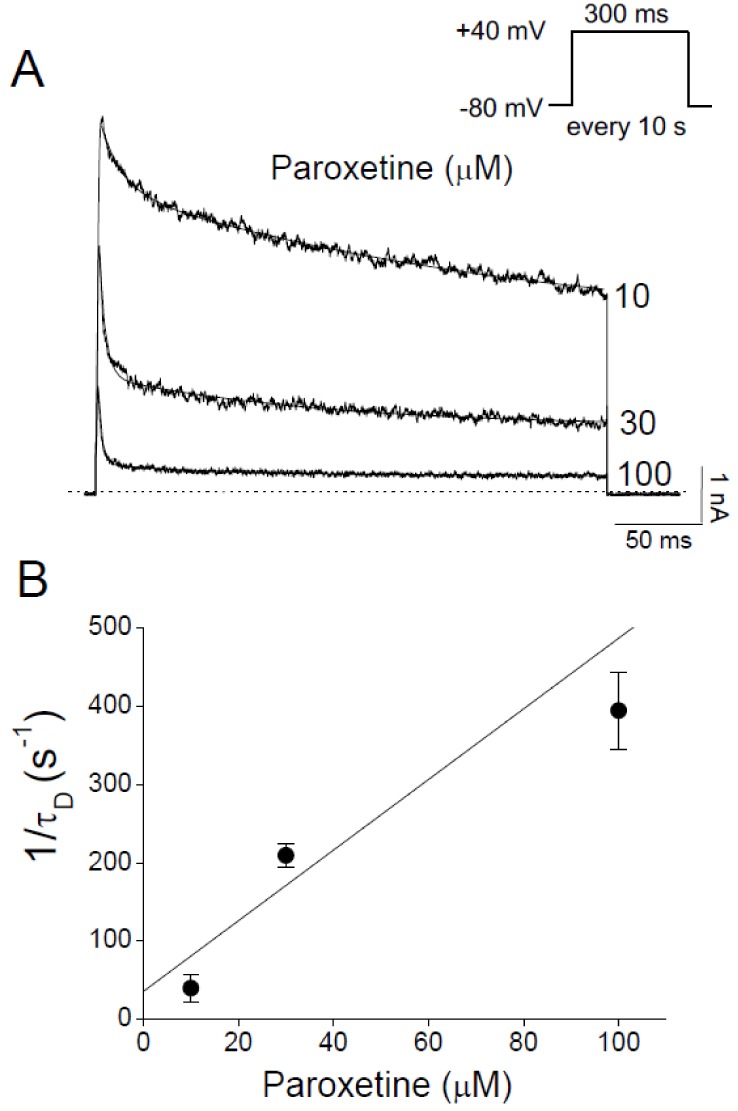
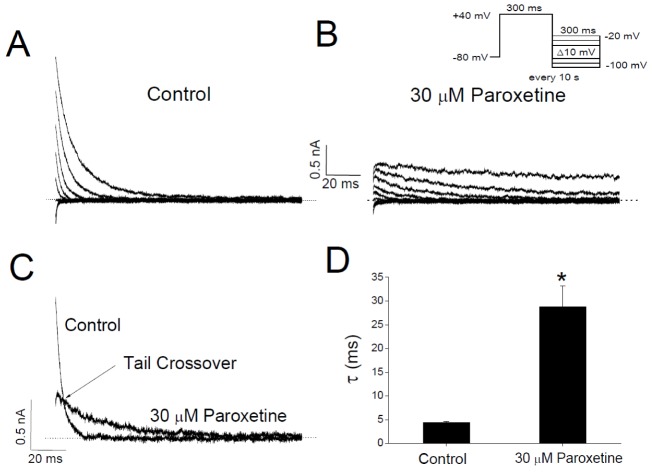
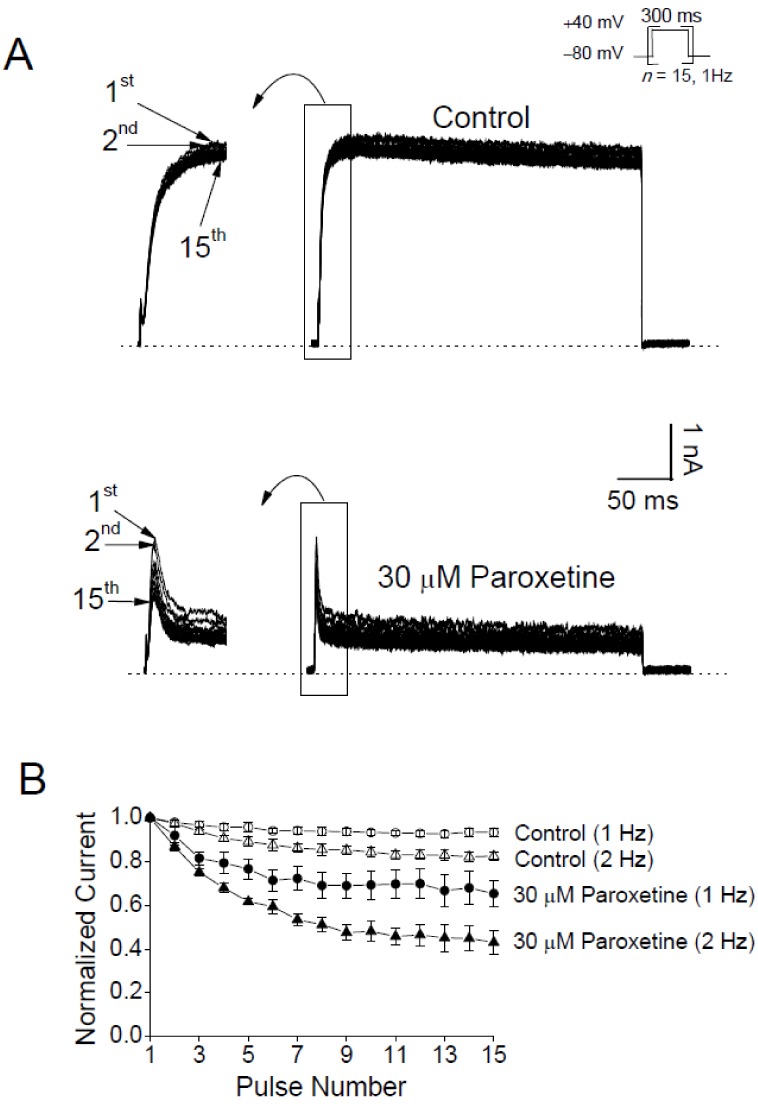
- In patients with epilepsy, depression is a common comorbidity but difficult to be treated because many antidepressants cause pro-convulsive effects. Thus, it is important to identify the risk of seizures associated with antidepressants. To determine whether paroxetine, a very potent selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), interacts with ion channels that modulate neuronal excitability, we examined the effects of paroxetine on Kv3.1 potassium channels, which contribute to highfrequency firing of interneurons, using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. Kv3.1 channels were cloned from rat neurons and expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Paroxetine reversibly reduced the amplitude of Kv3.1 current, with an ICâ‚…â‚€ value of 9.43 µM and a Hill coefficient of 1.43, and also accelerated the decay of Kv3.1 current. The paroxetine-induced inhibition of Kv3.1 channels was voltage-dependent even when the channels were fully open. The binding (kâ‚Šâ‚) and unbinding (kâ‚‹â‚) rate constants for the paroxetine effect were 4.5 µM⻹s⻹ and 35.8 s⻹, respectively, yielding a calculated K(D) value of 7.9 µM. The analyses of Kv3.1 tail current indicated that paroxetine did not affect ion selectivity and slowed its deactivation time course, resulting in a tail crossover phenomenon. Paroxetine inhibited Kv3.1 channels in a usedependent manner. Taken together, these results suggest that paroxetine blocks the open state of Kv3.1 channels. Given the role of Kv3.1 in fast spiking of interneurons, our data imply that the blockade of Kv3.1 by paroxetine might elevate epileptic activity of neural networks by interfering with repetitive firing of inhibitory neurons.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hoppe C, Elger CE. Depression in epilepsy: a critical review from a clinical perspective. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011; 7:462–472. PMID: 21750525.
Article2. Montgomery SA. Antidepressants and seizures: emphasis on newer agents and clinical implications. Int J Clin Pract. 2005; 59:1435–1440. PMID: 16351676.
Article3. Cardamone L, Salzberg MR, O’Brien TJ, Jones NC. Antidepressant therapy in epilepsy: can treating the comorbidities affect the underlying disorder? Br J Pharmacol. 2013; 168:1531–1554. PMID: 23146067.
Article4. Kanner AM. The treatment of depressive disorders in epilepsy: what all neurologists should know. Epilepsia. 2013; 54(Suppl 1):3–12.
Article5. Henry JA, Alexander CA, Sener EK. Relative mortality from overdose of antidepressants. BMJ. 1995; 310:221–224. PMID: 7866123.
Article6. Henry JA. Epidemiology and relative toxicity of antidepressant drugs in overdose. Drug Saf. 1997; 16:374–390. PMID: 9241492.
Article7. Reilly JG, Ayis SA, Ferrier IN, Jones SJ, Thomas SH. QTc-interval abnormalities and psychotropic drug therapy in psychiatric patients. Lancet. 2000; 355:1048–1052. PMID: 10744090.
Article8. Scherer D, von Löwenstern K, Zitron E, Scholz EP, Bloehs R, Kathöfer S, Thomas D, Bauer A, Katus HA, Karle CA, Kiesecker C. Inhibition of cardiac hERG potassium channels by tetracyclic antidepressant mianserin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008; 378:73–83. PMID: 18458880.
Article9. Hamid H, Kanner AM. Should antidepressant drugs of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor family be tested as antiepileptic drugs? Epilepsy Behav. 2013; 26:261–265. PMID: 23395350.
Article10. Favale E, Audenino D, Cocito L, Albano C. The anticonvulsant effect of citalopram as an indirect evidence of serotonergic impairment in human epileptogenesis. Seizure. 2003; 12:316–368. PMID: 12810346.
Article11. Specchio LM, Iudice A, Specchio N, La Neve A, Spinelli A, Galli R, Rocchi R, Ulivelli M, de Tommaso M, Pizzanelli C, Murri L. Citalopram as treatment of depression in patients with epilepsy. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004; 27:133–136. PMID: 15190237.
Article12. Favale E, Rubino V, Mainardi P, Lunardi G, Albano C. Anticonvulsant effect of fluoxetine in humans. Neurology. 1995; 45:1926–1927. PMID: 7477995.
Article13. Hyttel J. Citalopram.pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1982; 6:277–295. PMID: 6128769.14. Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Engleman EA. Prozac (fluoxetine, Lilly 110140), the first selective serotonin uptake inhibitor and an antidepressant drug: twenty years since its first publication. Life Sci. 1995; 57:411–441. PMID: 7623609.
Article15. Anderson IM. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors versus tricyclic antidepressants: a meta-analysis of efficacy and tolerability. J Affect Disord. 2000; 58:19–36. PMID: 10760555.
Article16. Montgomery SA. A meta-analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of paroxetine versus tricyclic antidepressants in the treatment of major depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2001; 16:169–178. PMID: 11354239.
Article17. Curran S. Effect of paroxetine on seizure length during electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1995; 92:239–240. PMID: 7484206.
Article18. Pisani F, Oteri G, Costa C, Di Raimondo G, Di Perri R. Effects of psychotropic drugs on seizure threshold. Drug Saf. 2002; 25:91–110. PMID: 11888352.
Article19. Choi HC, Kim YI, Song HK, Kim JE, Kim DS, Kang TC. Effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on GABAergic inhibition in the hippocampus of normal and pilocarpine induced epileptic rats. Brain Res. 2010; 1357:131–141. PMID: 20707986.
Article20. Boyer WF, Feighner JP. An overview of paroxetine. J Clin Psychiatry. 1992; 53(Suppl):3–6.21. Kamal SM. Combination of valproate and paroxetine in mice exposed to picrotoxin. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012; 7:2583–2589. PMID: 22679369.
Article22. Kobayashi T, Washiyama K, Ikeda K. Inhibition of G protein-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels by the antidepressant paroxetine. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006; 102:278–287. PMID: 17072103.23. Thummler S, Duprat F, Lazdunski M. Antipsychotics inhibit TREK but not TRAAK channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 354:284–289. PMID: 17222806.24. Signorini S, Liao YJ, Duncan SA, Jan LY, Stoffel M. Normal cerebellar development but susceptibility to seizures in mice lacking G protein-coupled, inwardly rectifying K+ channel GIRK2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997; 94:923–927. PMID: 9023358.25. Franks NP, Honore E. The TREK K2P channels and their role in general anaesthesia and neuroprotection. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004; 25:601–608. PMID: 15491783.
Article26. Sekirnjak C, Martone ME, Weiser M, Deerinck T, Bueno E, Rudy B, Ellisman M. Subcellular localization of the K+ channel subunit Kv3.1b in selected rat CNS neurons. Brain Res. 1997; 766:173–187. PMID: 9359601.
Article27. Rudy B, Chow A, Lau D, Amarillo Y, Ozaita A, Saganich M, Moreno H, Nadal MS, Hernandez-Pineda R, Hernandez-Cruz A, Erisir A, Leonard C, Vega-Saenz de Miera E. Contributions of Kv3 channels to neuronal excitability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999; 868:304–343. PMID: 10414303.
Article28. Ozaita A, Martone ME, Ellisman MH, Rudy B. Differential subcellular localization of the two alternatively spliced isoforms of the Kv3.1 potassium channel subunit in brain. J Neurophysiol. 2002; 88:394–408. PMID: 12091563.
Article29. Perney TM, Marshall J, Martin KA, Hockfield S, Kaczmarek LK. Expression of the mRNAs for the Kv3.1 potassium channel gene in the adult and developing rat brain. J Neurophysiol. 1992; 68:756–766. PMID: 1432046.
Article30. Wang LY, Gan L, Forsythe ID, Kaczmarek LK. Contribution of the Kv3.1 potassium channel to high-frequency firing in mouse auditory neurones. J Physiol. 1998; 509:183–194. PMID: 9547392.
Article31. Erisir A, Lau D, Rudy B, Leonard CS. Function of specific K+ channels in sustained high-frequency firing of fast-spiking neocortical interneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1999; 82:2476–2489. PMID: 10561420.32. Kanemasa T, Gan L, Perney TM, Wang LY, Kaczmarek LK. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of a mammalian Shaw channel expressed in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. J Neurophysiol. 1995; 74:207–217. PMID: 7472324.
Article33. Sung MJ, Ahn HS, Hahn SJ, Choi BH. Open channel block of Kv3.1 currents by fluoxetine. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008; 106:38–45. PMID: 18187934.
Article34. Hahn SJ, Wang LY, Kaczmarek LK. Inhibition by nystatin of Kv1.3 channels expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Neuropharmacology. 1996; 35:895–901. PMID: 8938720.
Article35. Luneau CJ, Williams JB, Marshall J, Levitan ES, Oliva C, Smith JS, Antanavage J, Folander K, Stein RB, Swanson R, et al. Alternative splicing contributes to K+ channel diversity in the mammalian central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991; 88:3932–3936. PMID: 2023941.36. Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981; 391:85–100. PMID: 6270629.
Article37. Snyders DJ, Yeola SW. Determinants of antiarrhythmic drug action. Electrostatic and hydrophobic components of block of the human cardiac hKv1.5 channel. Circ Res. 1995; 77:575–583. PMID: 7641327.38. Woodhull AM. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973; 61:687–708. PMID: 4541078.
Article39. Philipson LH, Malayev A, Kuznetsov A, Chang C, Nelson DJ. Functional and biochemical characterization of the human potassium channel Kv1.5 with a transplanted carboxyl-terminal epitope in stable mammalian cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993; 1153:111–121. PMID: 7694656.
Article40. Snyders DJ, Tamkun MM, Bennett PB. A rapidly activating and slowly inactivating potassium channel cloned from human heart. Functional analysis after stable mammalian cell culture expression. J Gen Physiol. 1993; 101:513–543. PMID: 8505626.
Article41. Choi BH, Choi JS, Jeong SW, Hahn SJ, Yoon SH, Jo YH, Kim MS. Direct block by bisindolylmaleimide of rat Kv1.5 expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000; 293:634–640. PMID: 10773038.42. Valenzuela C, Delpon E, Franqueza L, Gay P, Perez O, Tamargo J, Snyders DJ. Class III antiarrhythmic effects of zatebradine. Time-, state-, use-, and voltage-dependent block of hKv1.5 channels. Circulation. 1996; 94:562–570. PMID: 8759103.43. Delpón E, Valenzuela C, Gay P, Franqueza L, Snyders DJ, Tamargo J. Block of human cardiac Kv1.5 channels by loratadine: voltage-, time- and use-dependent block at concentrations above therapeutic levels. Cardiovasc Res. 1997; 35:341–350. PMID: 9349397.
Article44. Franqueza L, Valenzuela C, Delpón E, Longobardo M, Caballero R, Tamargo J. Effects of propafenone and 5-hydroxy-propafenone on hKv1.5 channels. Br J Pharmacol. 1998; 125:969–978. PMID: 9846634.
Article45. Sung MJ, Hahn SJ, Choi BH. Effect of psoralen on the cloned Kv3.1 currents. Arch Pharm Res. 2009; 32:407–412. PMID: 19387585.
Article46. Choi BH, Choi JS, Yoon SH, Rhie DJ, Min DS, Jo YH, Kim MS, Hahn SJ. Effects of norfluoxetine, the major metabolite of fluoxetine, on the cloned neuronal potassium channel Kv3.1. Neuropharmacology. 2001; 41:443–453. PMID: 11543764.
Article47. Choi JS, Hahn SJ, Rhie DJ, Yoon SH, Jo YH, Kim MS. Mechanism of fluoxetine block of cloned voltage-activated potassium channel Kv1.3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999; 291:1–6. PMID: 10490879.48. Vasskog T, Berger U, Samuelsen PJ, Kallenborn R, Jensen E. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in sewage influents and effluents from Tromsø, Norway. J Chromatogr A. 2006; 1115:187–195. PMID: 16574138.
Article49. Tytgat J1, Maertens C, Daenens P. Effect of fluoxetine on a neuronal, voltage-dependent potassium channel (Kv1.1). Br J Pharmacol. 1997; 122:1417–1424. PMID: 9421290.
Article50. Snyders J, Knoth KM, Roberds SL, Tamkun MM. Time-, voltage-, and state-dependent block by quinidine of a cloned human cardiac potassium channel. Mol Pharmacol. 1992; 41:322–330. PMID: 1538710.51. Lee HM, Hahn SJ, Choi BH. Open channel block of Kv1.5 currents by citalopram. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010; 31:429–435. PMID: 20228830.
Article52. Grissmer S, Ghanshani S, Dethlefs B, McPherson JD, Wasmuth JJ, Gutman GA, Cahalan MD, Chandy KG. The Shaw-related potassium channel gene, Kv3.1, on human chromosome 11, encodes the type l K+ channel in T cells. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267:20971–20979. PMID: 1400413.53. Hernández-Pineda R, Chow A, Amarillo Y, Moreno H, Saganich M, Vega-Saenz de Miera EC, Hernández-Cruz A, Rudy B. Kv3.1-Kv3.2 channels underlie a high-voltage-activating component of the delayed rectifier K+ current in projecting neurons from the globus pallidus. J Neurophysiol. 1999; 82:1512–1528. PMID: 10482766.
Article54. Bezaire MJ, Soltesz I. Quantitative assessment of CA1 local circuits: knowledge base for interneuron-pyramidal cell connectivity. Hippocampus. 2013; 23:751–785. PMID: 23674373.
Article55. Wang GK, Mitchell J, Wang SY. Block of persistent late Na+ currents by antidepressant sertraline and paroxetine. J Membr Biol. 2008; 222:79–90. PMID: 18418539.56. Dick IE, Brochu RM, Purohit Y, Kaczorowski GJ, Martin WJ, Priest BT. Sodium channel blockade may contribute to the analgesic efficacy of antidepressants. J Pain. 2007; 8:315–324. PMID: 17175203.
Article