J Vet Sci.
2017 Dec;18(4):479-485. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.479.
Differential and correlated expressions of p16/p21/p27/p38 in mammary gland tumors of aged dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Pathology, Small Animal Tumor Diagnostic Center, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 05029, Korea. jsur@konkuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2398507
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.479
Abstract
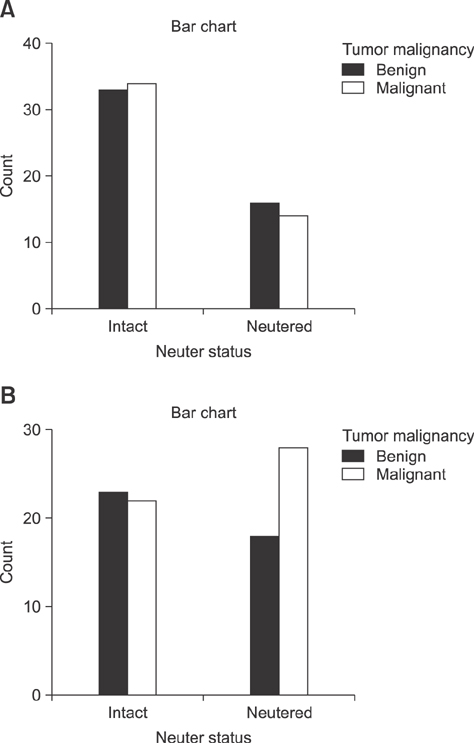
- The inhibitory effect of neutering on mammary gland tumor development in dogs has been well described. However, we observed that the effect of neutering on tumor malignancy may be altered by aging. Therefore, we characterized mammary tumors in aged dogs by analyzing the expression of cellular senescence markers. Expressions of p16, p38, p21, and p27 antibodies, which are senescence-associated markers, were assessed in canine mammary tumors of aged dogs via immunohistochemical analysis. In addition, correlations between those expressions were analyzed. Expression of p16 was negatively associated with strong nuclear p27 expression. Expression of p38 was observed in most of the mammary tumors examined, and negative p38 expression was related to positive p21 expression. Moreover, p21 expression was associated with p27 expression; negative p21 expression was associated with negative p27 expression, while positive p21 expression was associated with positive p27 expression. The results confirm that the p21- and p27-encoding genes have similar expression patterns in the mammary tumors of aged dogs. In the present study, we characterized the expression of cellular senescence markers in these tumors and elucidated the relationships among their expression patterns.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bohn OL, Fuertes-Camilo M, Navarro L, Saldivar J, Sanchez-Sosa S. p16INK4a expression in basal-like breast carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2010; 3:600–607.2. Campisi J. Aging, cellular senescence, and cancer. Annu Rev Physiol. 2013; 75:685–705.
Article3. Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S, Deming SL, Geradts J, Cheang MCU, Nielsen TO, Moorman PG, Earp HS, Millikan RC. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006; 295:2492–2502.
Article4. Catzavelos C, Bhattacharya N, Ung YC, Wilson JA, Roncari L, Sandhu C, Shaw P, Yeger H, Morava-Protzner I, Kapusta L, Franssen E, Pritchard KI, Slingerland JM. Decreased levels of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 protein: prognostic implications in primary breast cancer. Nat Med. 1997; 3:227–230.
Article5. Chlebowski RT, Chen Z, Anderson GL, Rohan T, Aragaki A, Lane D, Dolan NC, Paskett ED, McTiernan A, Hubbell FA, Adams-Campbell LL, Prentice R. Ethnicity and breast cancer: factors influencing differences in incidence and outcome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005; 97:439–448.
Article6. Collado M, Blasco MA, Serrano M. Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell. 2007; 130:223–233.
Article7. Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G, Jarrard DF. Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010; 102:1536–1546.
Article8. Frizelle SP, Grim J, Zhou J, Gupta P, Curiel DT, Geradts J, Kratzke RA. Re-expression of p16INK4a in mesothelioma cells results in cell cycle arrest, cell death, tumor suppression and tumor regression. Oncogene. 1998; 16:3087–3095.
Article9. Fujiwara-Igarashi A, Goto-Koshino Y, Mochizuki H, Sato M, Fujino Y, Ohno K, Tsujimoto H. Inhibition of p16 tumor suppressor gene expression via promoter hypermethylation in canine lymphoid tumor cells. Res Vet Sci. 2014; 97:60–63.
Article10. Gama A, Alves A, Schmitt F. Identification of molecular phenotypes in canine mammary carcinomas with clinical implications: application of the human classification. Virchows Arch. 2008; 453:123–132.
Article11. Jung MS, Jin DH, Chae HD, Kang S, Kim SC, Bang YJ, Choi TS, Choi K, Shin DY. Bcl-xL and E1B-19K proteins inhibit p53-induced irreversible growth arrest and senescence by preventing reactive oxygen species-dependent p38 activation. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:17765–17771.
Article12. Kim HW, Lim HY, Shin JI, Seung BJ, Ju JH, Sur JH. Breed-and age-related differences in canine mammary tumors. Can J Vet Res. 2016; 80:146–155.13. Kim NH, Lim HY, Im KS, Kim JH, Sur JH. Identification of triple-negative and basal-like canine mammary carcinomas using four basal markers. J Comp Pathol. 2013; 148:298–306.
Article14. Klopfleisch R, Gruber AD. Differential expression of cell cycle regulators p21, p27 and p53 in metastasizing canine mammary adenocarcinomas versus normal mammary glands. Res Vet Sci. 2009; 87:91–96.
Article15. Koenig A, Bianco S, Fosmire S, Wojcieszyn J, Modiano JF. Expression and significance of p53, Rb, p21/waf-1, p16/ink-4a, and PTEN tumor suppressors in canine melanoma. Vet Pathol. 2002; 39:458–472.
Article16. Kotake Y, Naemura M, Murasaki C, Inoue Y, Okamoto H. Transcriptional regulation of the p16 tumor suppressor gene. Anticancer Res. 2015; 35:4397–4401.17. Krishnamurthy J, Torrice C, Ramsey MR, Kovalev GI, Al-Regaiey K, Su L, Sharpless NE. Ink4a/Arf expression is a biomarker of aging. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:1299–1307.18. López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013; 153:1194–1217.
Article19. Lee JC, Young PR. Role of CSB/p38/RK stress response kinase in LPS and cytokine signaling mechanisms. J Leukoc Biol. 1996; 59:152–157.
Article20. Milde-Langosch K, Bamberger AM, Rieck G, Kelp B, Löning T. Overexpression of the p16 cell cycle inhibitor in breast cancer is associated with a more malignant phenotype. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2001; 67:61–70.
Article21. Pérez-Mancera PA, Young ARJ, Narita M. Inside and out: the activities of senescence in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014; 14:547–558.
Article22. Queiroga FL, Raposo T, Carvalho MI, Prada J, Pires I. Canine mammary tumours as a model to study human breast cancer: most recent findings. In Vivo. 2011; 25:455–465.23. Serrano M. The tumor suppressor protein p16INK4a. Exp Cell Res. 1997; 237:7–13.24. Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995; 9:1149–1163.25. Sorenmo KU, Shofer FS, Goldschmidt MH. Effect of spaying and timing of spaying on survival of dogs with mammary carcinoma. J Vet Intern Med. 2000; 14:266–270.
Article26. Tsihlias J, Kapusta L, Slingerland J. The prognostic significance of altered cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in human cancer. Annu Rev Med. 1999; 50:401–423.
Article27. van Deursen JM. The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature. 2014; 509:439–446.
Article28. Wang W, Chen JX, Liao R, Deng Q, Zhou JJ, Huang S, Sun P. Sequential activation of the MEK-extracellular signalregulated kinase and MKK3/6-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediates oncogenic ras-induced premature senescence. Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 22:3389–3403.
Article29. Wong SCC, Chan JKC, Lee KC, Hsiao WLW. Differential expression of p16/p21/p27 and cyclin D1/D3, and their relationships to cell proliferation, apoptosis, and tumour progression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. J Pathol. 2001; 194:35–42.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mammary gland tumors in three male dogs
- Assessment of prognostic factors in dogs with mammary gland tumors: 60 cases (2014-2020)
- Plasma free amino acid profiles of canine mammary gland tumors
- Expression of p34(cdc2), p27(Kip1), p21(WAF1/Cip1) and p53 in Human Breast Cancers
- Immunohistochemical Detection of p16,p21,and TGF-β in Cutaneous Epithelial Tumors