Tuberc Respir Dis.
2017 Jan;80(1):60-68. 10.4046/trd.2017.80.1.60.
Mometasone Furoate Suppresses PMA-Induced MUC-5AC and MUC-2 Production in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University (Rangsit Center), Pathum Thani, Thailand. orapanpoachanukoon@yahoo.com
- 2Oral Biology Laboratory, Faculty of Dentistry, Thammasat University (Rangsit Center), Pathum Thani, Thailand.
- KMID: 2396342
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.80.1.60
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Mucus hypersecretion from airway epithelium is a characteristic feature of airway inflammatory diseases. Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) regulates mucin synthesis. Glucocorticoids including mometasone fuorate (MF) have been used to attenuate airway inflammation. However, effects of MF on mucin production have not been reported.
METHODS
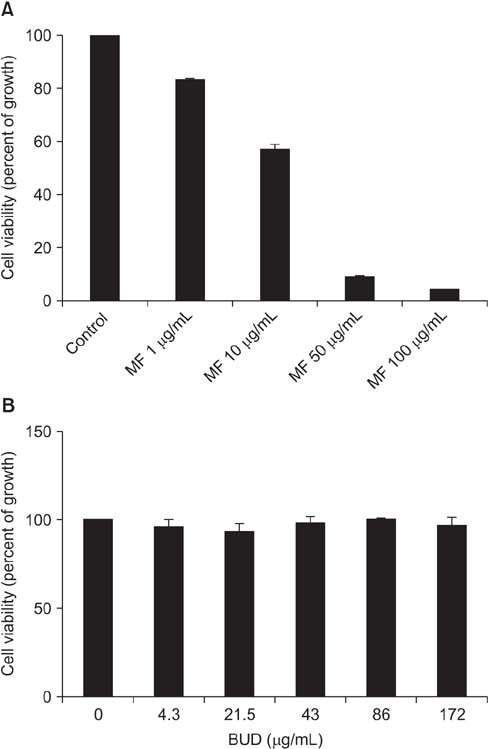
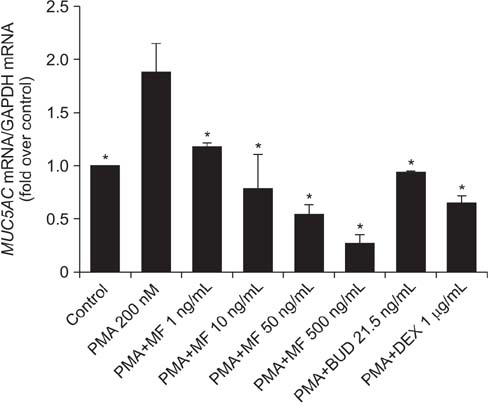
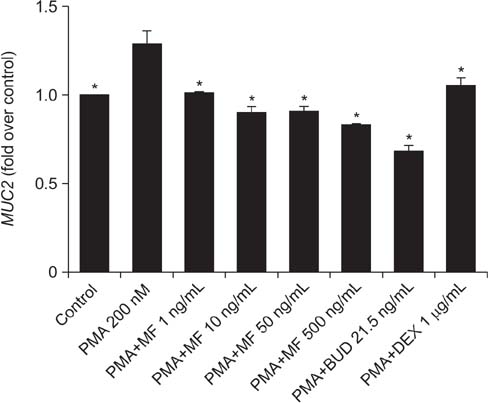
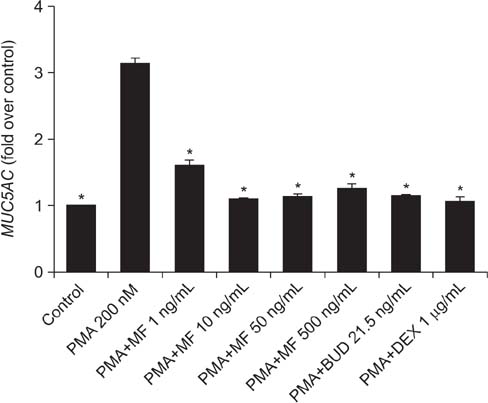
Effects of MF and budesonide (BUD) on the phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)-induction of mucin and TNF-α in human airway epithelial cells (NCI-H292) were investigated in the present study. Confluent NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with PMA (200 nM) for 2 hours. Subsequently, the cells were stimulated with MF (1-500 ng/mL) or BUD (21.5 ng/mL) for 8 hours. Dexamethasone (1 µg/mL) was used as the positive control. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to determine MUC2 and MUC5AC mRNA levels. The level of total mucin, MUC2, MUC5AC, and TNF-α in culture supernatants were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
RESULTS
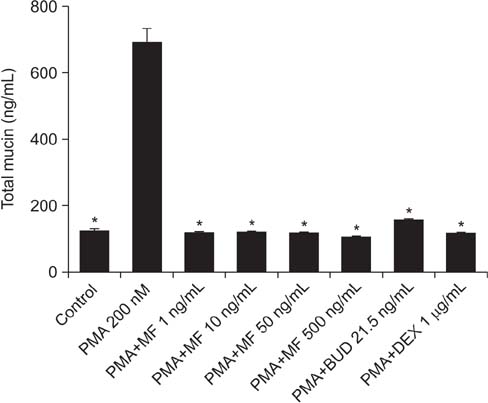
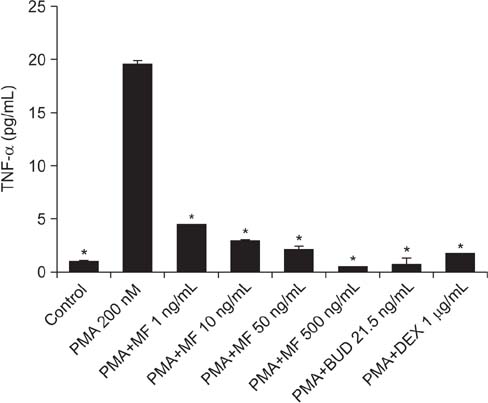
MF and BUD significantly suppressed MUC2 and MUC5AC gene expression in PMA-stimulated NCI-H292 cells. The inhibitory effects of the two steroid drugs were also observed in the production of total mucin, MUC2 and MUC5AC proteins, and TNF-α.
CONCLUSION
Our findings demonstrated that MF and BUD attenuated mucin and TNF-α production in PMA-induced human airway epithelial cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Budesonide
Dexamethasone
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Epithelial Cells*
Epithelium
Gene Expression
Glucocorticoids
Humans*
Inflammation
Mometasone Furoate*
Mucins
Mucus
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Budesonide
Dexamethasone
Glucocorticoids
Mometasone Furoate
Mucins
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang X, Morrison-Carpenter T, Holt JB, Callahan DB. Trends in adult current asthma prevalence and contributing risk factors in the United States by state: 2000-2009. BMC Public Health. 2013; 13:1156.2. Sedaghat AR, Phipatanakul W, Cunningham MJ. Prevalence of and associations with allergic rhinitis in children with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 78:343–347.3. Mello JF Jr, Mion Ode G, Andrade NA, Anselmo-Lima WT, Stamm AE, Almeida WL, et al. Brazilian Academy of Rhinology position paper on topical intranasal therapy. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 79:391–400.4. Yang D, Wang J, Bunjhoo H, Xiong W, Xu Y, Zhao J. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of mometasone furoate to other inhaled steroids for asthma: a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2013; 31:26–35.5. Martinez-Anton A, Debolos C, Garrido M, Roca-Ferrer J, Barranco C, Alobid I, et al. Mucin genes have different expression patterns in healthy and diseased upper airway mucosa. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006; 36:448–457.6. Kim DH, Chu HS, Lee JY, Hwang SJ, Lee SH, Lee HM. Up-regulation of MUC5AC and MUC5B mucin genes in chronic rhinosinusitis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 130:747–752.7. Morcillo EJ, Cortijo J. Mucus and MUC in asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006; 12:1–6.8. Kim YD, Kwon EJ, Park DW, Song SY, Yoon SK, Baek SH. Interleukin-1beta induces MUC2 and MUC5AC synthesis through cyclooxygenase-2 in NCI-H292 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2002; 62:1112–1118.9. Takami S, Mizuno T, Oyanagi T, Tadaki H, Suzuki T, Muramatsu K, et al. Glucocorticoids inhibit MUC5AC production induced by transforming growth factor-alpha in human respiratory cells. Allergol Int. 2012; 61:451–459.10. Burgel PR, Cardell LO, Ueki IF, Nadel JA. Intranasal steroids decrease eosinophils but not mucin expression in nasal polyps. Eur Respir J. 2004; 24:594–600.11. Westergaard CG, Porsbjerg C, Backer V. A review of mometasone furoate/formoterol in the treatment of asthma. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013; 14:339–346.12. Park SJ, Kim TH, Jun YJ, Lee SH, Ryu HY, Jung KJ, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps and without polyps is associated with increased expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling 1 and 3. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:772–780.13. Brightling C, Berry M, Amrani Y. Targeting TNF-alpha: a novel therapeutic approach for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:5–10.14. Rudiger JJ, Gencay M, Yang JQ, Bihl M, Tamm M, Roth M. Fast beneficial systemic anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide and formoterol on circulating lymphocytes in asthma. Respirology. 2013; 18:840–847.15. Ciprandi G, Tosca MA, Passalacqua G, Canonica GW. Intranasal mometasone furoate reduces late-phase inflammation after allergen challenge. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001; 86:433–438.16. Inoue D, Yamaya M, Kubo H, Sasaki T, Hosoda M, Numasaki M, et al. Mechanisms of mucin production by rhinovirus infection in cultured human airway epithelial cells. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006; 154:484–499.17. Li R, Meng Z. Effects of SO2 derivatives on expressions of MUC5AC and IL-13 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol. 2007; 81:867–874.18. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001; 25:402–408.19. Bamrungphon W, Prempracha N, Bunchu N, Rangdaeng S, Sandhu T, Srisukho S, et al. A new mucin antibody/enzyme-linked lectin-sandwich assay of serum MUC5AC mucin for the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2007; 247:301–308.20. Hewson CA, Edbrooke MR, Johnston SL. PMA induces the MUC5AC respiratory mucin in human bronchial epithelial cells, via PKC, EGF/TGF-alpha, Ras/Raf, MEK, ERK and Sp1-dependent mechanisms. J Mol Biol. 2004; 344:683–695.21. Davies DE, Polosa R, Puddicombe SM, Richter A, Holgate ST. The epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligand family: their potential role in repair and remodelling in asthma. Allergy. 1999; 54:771–783.22. Shao MX, Nadel JA. Dual oxidase 1-dependent MUC5AC mucin expression in cultured human airway epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:767–772.23. Ishinaga H, Takeuchi K, Kishioka C, Suzuki S, Basbaum C, Majima Y. Pranlukast inhibits NF-kappaB activation and MUC2 gene expression in cultured human epithelial cells. Pharmacology. 2005; 73:89–96.24. Bernstein DI, Berkowitz RB, Chervinsky P, Dvorin DJ, Finn AF, Gross GN, et al. Dose-ranging study of a new steroid for asthma: mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler. Respir Med. 1999; 93:603–612.25. Affrime MB, Cuss F, Padhi D, Wirth M, Pai S, Clement RP, et al. Bioavailability and metabolism of mometasone furoate following administration by metered-dose and dry-powder inhalers in healthy human volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2000; 40:1227–1236.26. Smith CL, Kreutner W. In vitro glucocorticoid receptor binding and transcriptional activation by topically active glucocorticoids. Arzneimittelforschung. 1998; 48:956–960.27. Valotis A, Hogger P. Significant receptor affinities of metabolites and a degradation product of mometasone furoate. Respir Res. 2004; 5:7.28. Papi A, Papadopoulos NG, Degitz K, Holgate ST, Johnston SL. Corticosteroids inhibit rhinovirus-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 up-regulation and promoter activation on respiratory epithelial cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 105(2 Pt 1):318–326.29. Sabatini F, Silvestri M, Sale R, Serpero L, Giuliani M, Scarso L, et al. Concentration-dependent effects of mometasone furoate and dexamethasone on foetal lung fibroblast functions involved in airway inflammation and remodeling. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 16:287–297.30. Kim YD, Kwon EJ, Kwon TK, Baek SH, Song SY, Suh JS. Regulation of IL-1beta-mediated MUC2 gene in NCI-H292 human airway epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 274:112–116.31. Feinstein MB, Schleimer RP. Regulation of the action of hydrocortisone in airway epithelial cells by 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999; 21:403–408.32. Chen Y, Nickola TJ, DiFronzo NL, Colberg-Poley AM, Rose MC. Dexamethasone-mediated repression of MUC5AC gene expression in human lung epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006; 34:338–347.33. Barton BE, Jakway JP, Smith SR, Siegel MI. Cytokine inhibition by a novel steroid, mometasone furoate. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 1991; 13:251–261.34. Ek A, Larsson K, Siljerud S, Palmberg L. Fluticasone and budesonide inhibit cytokine release in human lung epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages. Allergy. 1999; 54:691–699.35. Joyce DA, Kloda A, Steer JH. Dexamethasone suppresses release of soluble TNF receptors by human monocytes concurrently with TNF-alpha suppression. Immunol Cell Biol. 1997; 75:345–350.36. Nakamura Y, Murai T, Ogawa Y. Effect of in vitro and in vivo administration of dexamethasone on rat macrophage functions: comparison between alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Eur Respir J. 1996; 9:301–306.37. Levine SJ, Larivee P, Logun C, Angus CW, Ognibene FP, Shelhamer JH. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces mucin hypersecretion and MUC-2 gene expression by human airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995; 12:196–204.38. Ryu J, Lee HJ, Park SH, Sikder MA, Kim JO, Hong JH, et al. Effect of Prunetin on TNF-alpha-induced MUC5AC mucin gene expression, production, degradation of IkappaB and translocation of NF-kappaB p65 in human airway epithelial cells. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2013; 75:205–209.39. Shimizu T, Shimizu S, Hattori R, Gabazza EC, Majima Y. In vivo and in vitro effects of macrolide antibiotics on mucus secretion in airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 168:581–587.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Galangin Regulates Mucin 5AC Gene Expression via the Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor α/Nuclear Factor-κB p65 Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Effects of Curcumin and Genistein on Phorbol Ester or Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha-Induced Mucin Production from Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- The Effect of Topical Steroid Nasal Instillation in Induced Anosmic Mice
- Rhinovirus-Induced Mucin Gene Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells
- Synergistic Effect of Dermatophagoides farinae and Lipopolysaccharides in Human Middle ear Epithelial Cells