Korean J Schizophr Res.
2017 Oct;20(2):61-68. 10.16946/kjsr.2017.20.2.61.
Comparison of Hematologic Variability between Clozapine Monotherapy and Augmentation Therapy with Atypical Antipsychotics for Schizophrenia: Results from a 6-Month Retrospective Follow-Up Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea. damiankim@gmail.com
- 2National Center for Mental Health, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2395441
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16946/kjsr.2017.20.2.61
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Clozapine is an antipsychotic agent commonly prescribed in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia. A drawback of using clozapine is risk of hematologic side effects ranging from mild neutropenia to fatal agranulocytosis. In clinical settings, other atypical antipsychotic agents are frequently combined with clozapine because some treatment-resistant patients would not respond to clozapine alone. Unfortunately, other atypical antipsychotics may also cause hematologic side effects, and the combination therapy might aggravate the possible neutropenic side effects. The purpose of this study was to investigate the difference in the incidence of hematologic side effects between clozapine monotherapy and augmentation therapy.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 114 patients who were diagnosed with schizophrenia and being prescribed with clozapine in a single university hospital. White blood cell count (WBC) and absolute neutrophil count (ANC) were identified every 1 month in clozapine monotherapy group and clozapine-atypical antipsychotics augmentation therapy group.
RESULTS
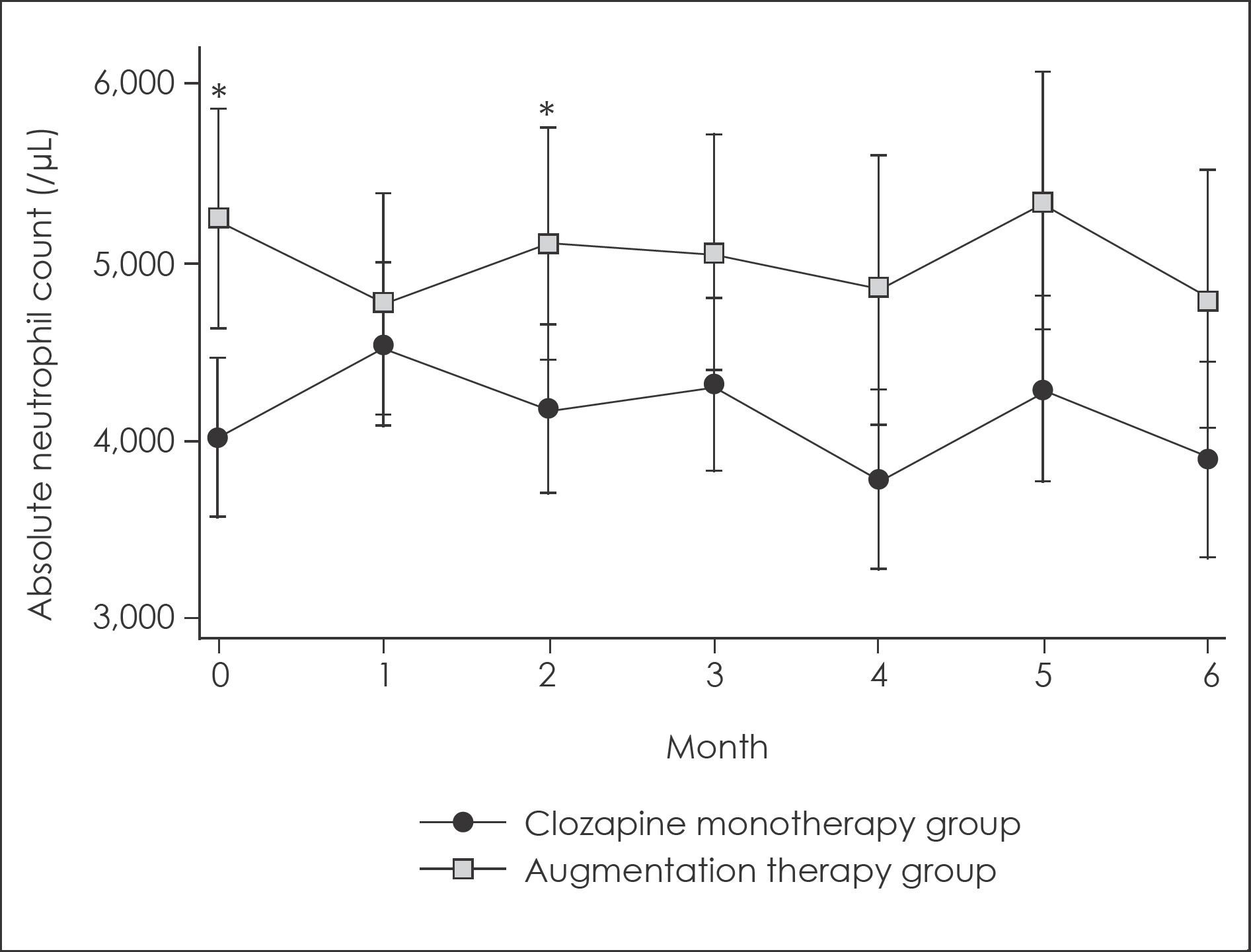
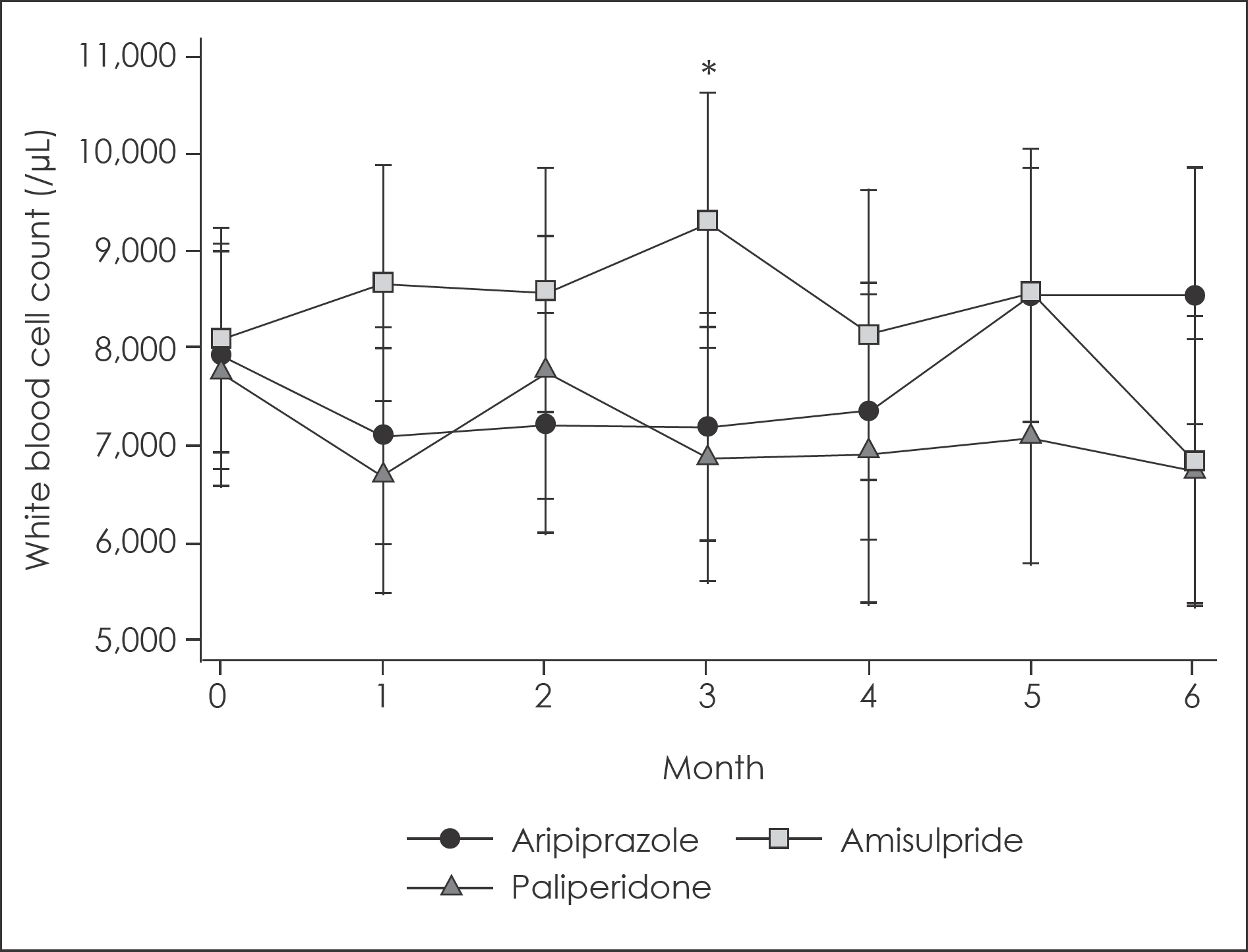
Compared with clozapine monotherapy group, augmentation therapy group showed no significant differences in WBC and ANC for the first 6 months of combination. Amisulpride augmentation showed temporary increases in WBC and ANC, especially compared with paliperidone augmentation.
CONCLUSION
Augmentation of amisulpride to clozapine might be associated with temporary increases in WBC and ANC during the first 3 months of combination. Further investigations should be carried out to clarify the clinical significance of our findings.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lehman AF, Lieberman JA, Dixon LB, McGlashan TH, Miller AL, Perkins DO, et al. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia, second edition. Am J Psychiatry. 2004; 161:1–56.2. Suzuki T, Remington G, Mulsant BH, Uchida H, Rajji TK, Graff-Guerrero A, et al. Defining treatment-resistant schizophrenia and response to antipsychotics: a review and recommendation. Psychiatry Res. 2012; 197:1–6.
Article3. Stroup TS, Gerhard T, Crystal S, Huang C, Olfson M. Comparative Effectiveness of Clozapine and Standard Antipsychotic Treatment in Adults With Schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2016; 173:166–173.
Article4. Lally J, MacCabe JH. Antipsychotic medication in schizophrenia: a review. Br Med Bull. 2015; 114:169–179.
Article5. Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988; 45:789–796.6. Lieberman JA, Kane JM, Johns CA. Clozapine: guidelines for clinical management. J Clin Psychiatry. 1989; 50:329–338.7. Fitzsimons J, Berk M, Lambert T, Bourin M, Dodd S. A review of clozapine safety. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2005; 4:731–744.
Article8. Stubner S, Grohmann R, Engel R, Bandelow B, Ludwig WD, Wagner G, et al. Blood dyscrasias induced by psychotropic drugs. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2004; 37(Suppl 1):S70–78.
Article9. Etain B, Roubaud L, Le Heuzey MF, Mouren Simeoni MC. [A case of leukopenia in treatment with risperidone in an adolescent]. En-cephale. 2000; 26:81–84.10. Godleski LS, Sernyak MJ. Agranulocytosis after addition of risperidone to clozapine treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1996; 153:735–736.11. Ruhe HG, Becker HE, Jessurun P, Marees CH, Heeringa M, Vermeulen HD. Agranulocytosis and granulocytopenia associated with quetiapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2001; 104:311–313. ; discussion 313–314.12. Chakos M, Lieberman J, Hoffman E, Bradford D, Sheitman B. Effectiveness of second-generation antipsychotics in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a review and metaanalysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2001; 158:518–526.
Article13. Cipriani A, Boso M, Barbui C. Clozapine combined with different antipsychotic drugs for treatment resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. CD006324.
Article14. Freudenreich O, Goff DC. Antipsychotic combination therapy in schizophrenia. A review of efficacy and risks of current combinations. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2002; 106:323–330.
Article15. Nielsen J, Dahm M, Lublin H, Taylor D. Psychiatrists'attitude towards and knowledge of clozapine treatment. J Psychopharmacol. 2010; 24:965–971.16. Pani L, Villagran JM, Kontaxakis VP, Alptekin K. Practical issues with amisulpride in the management of patients with schizophrenia. Clin Drug Investig. 2008; 28:465–477.17. Galling B, Roldan A, Hagi K, Rietschel L, Walyzada F, Zheng W, et al. Antipsychotic augmentation vs. monotherapy in schizophrenia: systematic review, metaanalysis and meta-regression analysis. World Psychiatry. 2017; 16:7789.
Article18. Suzuki T, Uchida H, Watanabe K, Nakajima S, Nomura K, Takeuchi H, et al. Effectiveness of antipsychotic polypharmacy for patients with treatment refractory schizophrenia: an open-label trial of olanzapine plus risperidone for those who failed to respond to a sequential treatment with olanzapine, quetiapine and risperidone. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2008; 23:455463.
Article19. Anil Yagcioglu AE, Kivircik Akdede BB, Turgut TI, Tumuklu M, Yazici MK, Alptekin K, et al. A double-blind controlled study of adjunctive treatment with risperidone in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to clozapine: efficacy and safety. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005; 66:63–72.20. Honer WG, Thornton AE, Chen EY, Chan RC, Wong JO, Bergmann A, et al. Clozapine alone versus clozapine and risperidone with refractory schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:472–482.
Article21. Milton J, Lawton J, Smith M, Buckley A. Hidden high-dose antipsychotic prescribing: effects of p.r.n. doses. Psychiatric Bulletin. 1998; 22:675–677.
Article22. Harrington M, Lelliott P, Paton C, Okocha C, Duffett R, Sensky T. The results of a multi-centre audit of the prescribing of antipsychotic drugs for inpatients in the UK. Psychiatric Bulletin. 2002; 26:414–418.
Article23. Paton C, Barnes TR, Cavanagh MR, Taylor D, Lelliott P. High-dose and combination antipsychotic prescribing in acute adult wards in the UK: the challenges posed by p.r.n. prescribing. Br J Psychiatry. 2008; 192:435–439.
Article24. Norvatis. Clozaril Product Information. Available at:. https://www.novartis.co.kr/sites/www.novartis.co.kr/files/clozaril.pdf. Accessed Aug-. 25–2017.25. Fabrazzo M, Prisco V, Sampogna G, Perris F, Catapano F, Montele-one AM, et al. Clozapine versus other antipsychotics during the first 18 weeks of treatment: A retrospective study on risk factor increase of blood dyscrasias. Psychiatry Res. 2017; 256:275–282.
Article26. Hummer M, Kurz M, Barnas C, Saria A, Fleischhacker WW. Clozapine-induced transient white blood count disorders. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994; 55:429–432.27. Lambertenghi Deliliers G. Blood dyscrasias in clozapine-treated patients in Italy. Haematologica. 2000; 85:233–237.28. Ingimarsson O, MacCabe JH, Haraldsson M, Jonsdottir H, Sigurdsson E. Neutropenia and agranulocytosis during treatment of schizophrenia with clozapine versus other antipsychotics: an observational study in Iceland. BMC Psychiatry. 2016; 16:441.
Article29. Rettenbacher MA, Hofer A, Kemmler G, Fleischhacker WW. Neutropenia induced by second generation antipsychotics: a prospective investigation. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2010; 43:41–44.
Article30. Girardin FR, Poncet A, Blondon M, Rollason V, Vernaz N, Cha-landon Y, et al. Monitoring white blood cell count in adult patients with schizophrenia who are taking clozapine: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2014; 1:55–62.
Article31. Alvir JM, Lieberman JA, Safferman AZ, Schwimmer JL, Schaaf JA. Clozapine-induced agranulocytosis. Incidence and risk factors in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:162–167.32. Hotham JE, Simpson PJ, Brooman-White RS, Basu A, Ross CC, Humphreys SA, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with amisulpride: an effective therapeutic strategy for violent treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients in a UK high-security hospital. CNS Spectr. 2014; 19:403–410.
Article33. Zink M, Knopf U, Henn FA, Thome J. Combination of clozapine and amisulpride in treatment-resistant schizophrenia–case reports and review of the literature. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2004; 37:26–31.34. Kampf P, Agelink MW, Naber D. Augmentation of clozapine with amisulpride: a promising therapeutic approach to refractory schizophrenic symptoms. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2005; 38:39–40.
Article35. Genc Y, Taner E, Candansayar S. Comparison of clozapine-amisulpride and clozapine-quetiapine combinations for patients with schizophrenia who are partially responsive to clozapine: a single-blind randomized study. Adv Ther. 2007; 24:1–13.36. Kreinin A, Novitski D, Weizman A. Amisulpride treatment of clozapine-induced hypersalivation in schizophrenia patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled crossover study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006; 21:99–103.
Article37. Blier P, Slater S, Measham T, Koch M, Wiviott G. Lithium and clozapine-induced neutropenia/agranulocytosis. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1998; 13:137–140.
Article38. Small JG, Klapper MH, Malloy FW, Steadman TM. Tolerability and efficacy of clozapine combined with lithium in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2003; 23:223–228.
Article39. Esposito D, Rouillon F, Limosin F. Continuing clozapine treatment despite neutropenia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005; 60:759–764.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of Prescribing Pattern after Clozapine Discontinuation: A Retrospective Chart Review
- Cariprazine — an Alternative Treatment for Clozapine-resistant Schizophrenia?
- Current Status of Clozapine for Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia
- Efficacy of Asenapine in Schizophrenia Resistant to Clozapine Combined with Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Case Report
- The Rationale and Effect of Antipsychotics Combination Therapy