Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2016 May;8(3):276-278. 10.4168/aair.2016.8.3.276.
A Case of Pranlukast-Induced Anaphylactic Shock
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jomlee@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2391048
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2016.8.3.276
Abstract
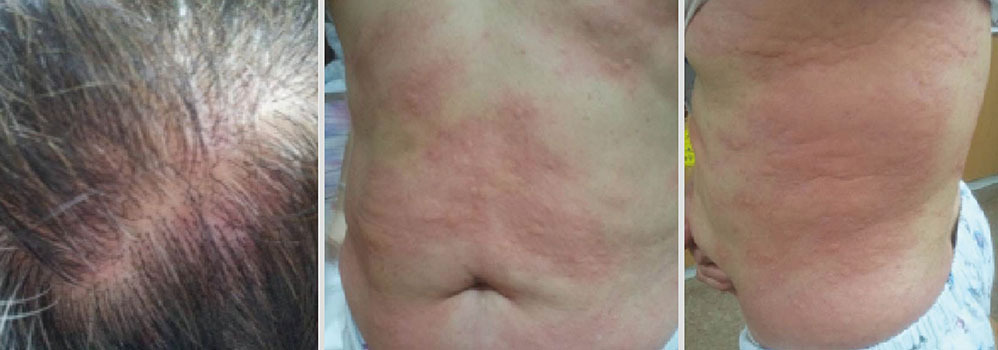
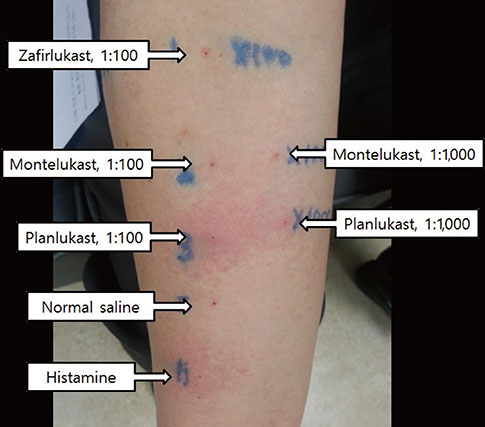
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists, which are generally considered safe with a few adverse drug reactions, are increasingly used in the treatment of various allergic diseases, including asthma and allergic rhinitis. Although a few anaphylactic reactions to montelukast have been reported worldwide, there is still a lack of reports about severe adverse drug reactions associated with pranlukast. Here, we report a case of severe hypersensitivity reaction associated with pranlukast. A 65-year-old woman developed anaphylactic shock that presented as generalized urticaria, angioedema, collapse, and loss of consciousness after receiving pranlukast. A positive response to oral challenge and skin prick testing with pranlukast was observed in the patient. In this case, it was demonstrated that pranlukast can induce anaphylaxis, possibly mediated by the IgE-dependent pathway.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Riccioni G, Bucciarelli T, Mancini B, Di Ilio C, D'Orazio N. Antileukotriene drugs: clinical application, effectiveness and safety. Curr Med Chem. 2007; 14:1966–1977.2. Funk CD. Leukotriene modifiers as potential therapeutics for cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005; 4:664–672.3. Kanaoka Y, Boyce JA. Cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors; emerging concepts. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:288–295.4. García-Marcos L, Schuster A, Pérez-Yarza EG. Benefit-risk assessment of antileukotrienes in the management of asthma. Drug Saf. 2003; 26:483–518.5. Calapai G, Casciaro M, Miroddi M, Calapai F, Navarra M, Gangemi S. Montelukast-induced adverse drug reactions: a review of case reports in the literature. Pharmacology. 2014; 94:60–70.6. Minciullo PL, Saija A, Bonanno D, Ferlazzo E, Gangemi S. Montelukast-induced generalized urticaria. Ann Pharmacother. 2004; 38:999–1001.7. Tayeb MM. Allergy to montelukast sodium treated effectively by protracted oral desensitization: first case report. Glob Adv Res J Med Med Sci. 2013; 2:120–124.8. Gerard A, Harkisoon S. Singulair-induced anaphylaxis? J Fam Pract. 2009; 58:133–134.9. Barnes NC, de Jong B, Miyamoto T. Worldwide clinical experience with the first marketed leukotriene receptor antagonist. Chest. 1997; 111:52S–60S.10. Keam SJ, Lyseng-Williamson KA, Goa KL. Pranlukast: a review of its use in the management of asthma. Drugs. 2003; 63:991–1019.11. The Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association. Japan Pharmaceutical Reference: Onon® Capsules 112.5 mg [Internet]. Tokyo: The Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association;2010. cited 2015 Jun 5. Available from http://www.e-search.ne.jp/~jpr/PDF/ONO04.PDF.12. Ohnishi-Inoue Y, Mitsuya K, Horio T. Aspirin-sensitive urticaria: provocation with a leukotriene receptor antagonist. Br J Dermatol. 1998; 138:483–485.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anaphylactic shock caused by intramuscular injection of midazolam during the perioperative period: a case report
- Simultaneous hypersensitivity reactions to trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole and amoxicillinclavulanate in a dog
- Usefulness of Serum Mast Cell Tryptase Analysis in Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock
- A suspected case of sugammadex-induced anaphylactic shock: A case report
- Factors Associated with Echinococcosis-Induced Perioperative Anaphylactic Shock