Korean J Leg Med.
2013 May;37(2):73-77. 10.7580/kjlm.2013.37.2.73.
Usefulness of Serum Mast Cell Tryptase Analysis in Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Forensic Medicine, National Forensic Service, Seoul, Korea. giifpap@korea.kr
- 2Department of Forensic Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1433182
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2013.37.2.73
Abstract
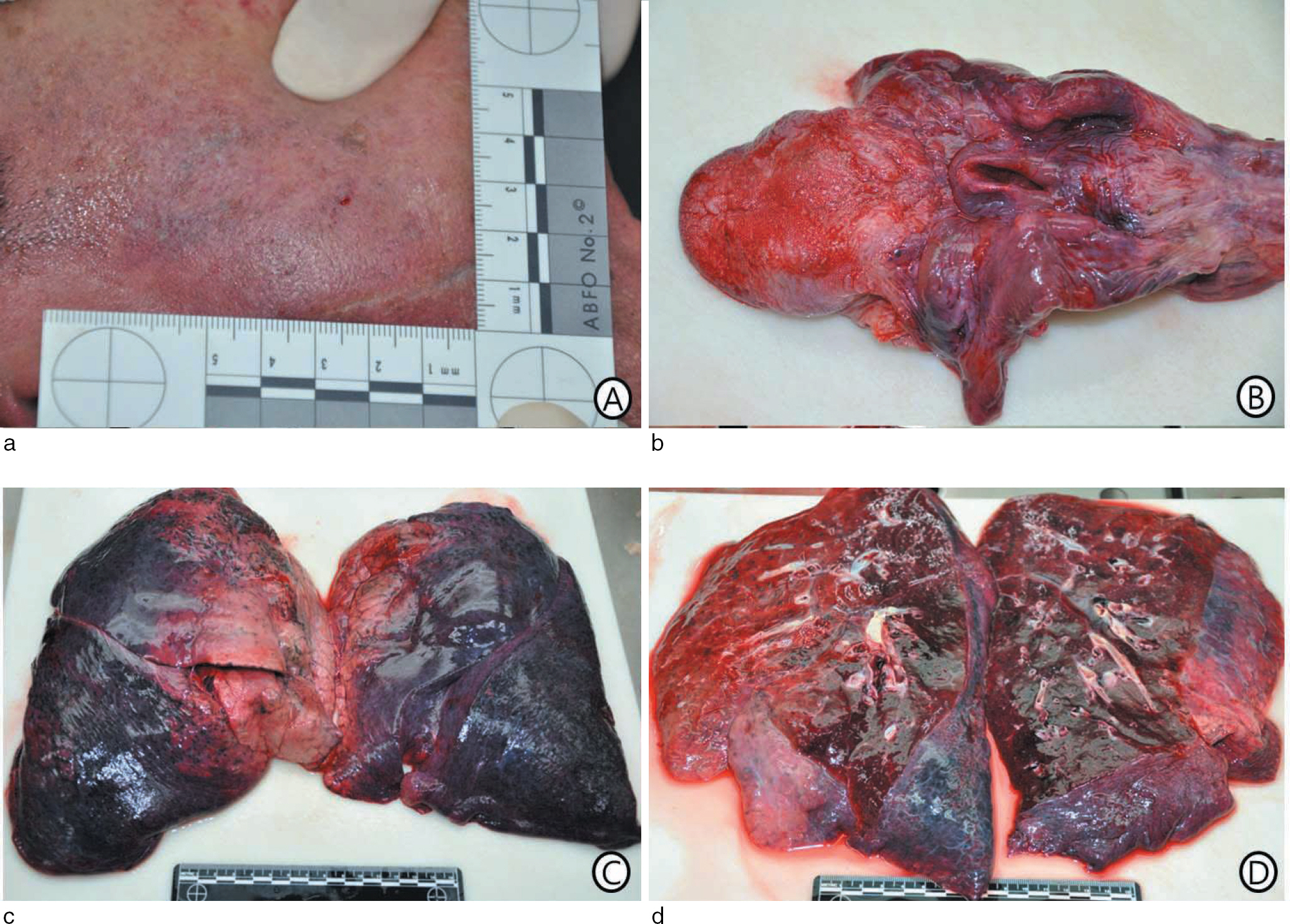
- Anaphylactic deaths are frequently observed at autopsies. Since death associated with medical practice has become social concern, the identification of anaphylactic shock is an important part of forensic medicine. However, autopsy findings of anaphylactic shock are usually non-specific; therefore, the diagnosis of anaphylactic shock must be inferred from collecting data on the past history of the deceased, circumstances of death, and negative autopsy findings. The analysis of serum mast cell tryptase level is a well-known, useful ancillary test for the diagnosis of anaphylactic shock, but is not widely used in daily practice in Korea. We recently encountered 2 autopsy cases of anaphylactic shock and confirmed that analysis of serum mast cell tryptase level was useful for the diagnosis of anaphylactic shock. In this report, we present these 2 autopsy cases of anaphylactic shock, with literature review of the usefulness and limitations of serum mast cell tryptase analysis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Da Broi U, Moreschi C. Postmortem diagnosis of anaphylaxis: a difficult task in forensic medicine. Forensic Sci Int. 2011; 204:1–5.
Article2. Pumphrey RS, Roberts IS. Postmortem findings after fatal anaphylactic reactions. J Clin Pathol. 2000; 53:273–6.
Article3. DiMaio VJ, DiMaio D. Forensic pathology. 2nd ed.Florida: CRC Press;2001. p. 468–9.4. Byard RW. An analysis of possible mechanisms of unexpected death occurring in Hydatid diease (echinococcosis). J Forensic Sci. 2009; 54:919–22.5. Nara A, Aki T, Funakoshi T, et al. Death due to blood transfusion-induced anaphylactic shock: a case report. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2010; 12:148–50.
Article6. Belton AL, Chira T. Fatal anaphylactic reaction to hair dye. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1997; 18:290–2.
Article7. Mayer DE, Krauskopf A, Hemmera W, et al. Usefulness of post mortem determination of serum tryptase, histamine and diamine oxidase in the diagnosis of fatal anaphylaxis. Forensic Sci Int. 2011; 212:96–101.
Article8. Edston E, van Hage-Hamsten M. beta-Tryptase measurements postmortem in anaphylactic deaths and in controls. Forensic Sci Int. 1998; 93:135–42.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of Mast Cell Tryptase Analysis for Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock
- Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock by Histopathological Examination of Mast Cell
- Anaphylactic Shock by Hemocoagulase with Increased Concentration of Mast Cell Tryptase: A case report
- Expression of Mast Cell Tryptase in the Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion
- Serum eosinophil cathionic protein and tryptase concentrations in atopic asthmatic patients after allergen bronchial challenge