J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Sep;32(9):1542-1547. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1542.
Role of the ABCB1 Drug Transporter Polymorphisms in the Pharmacokinetics of Oseltamivir in Humans: a Preliminary Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jonglyul.ghim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2385963
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1542
Abstract
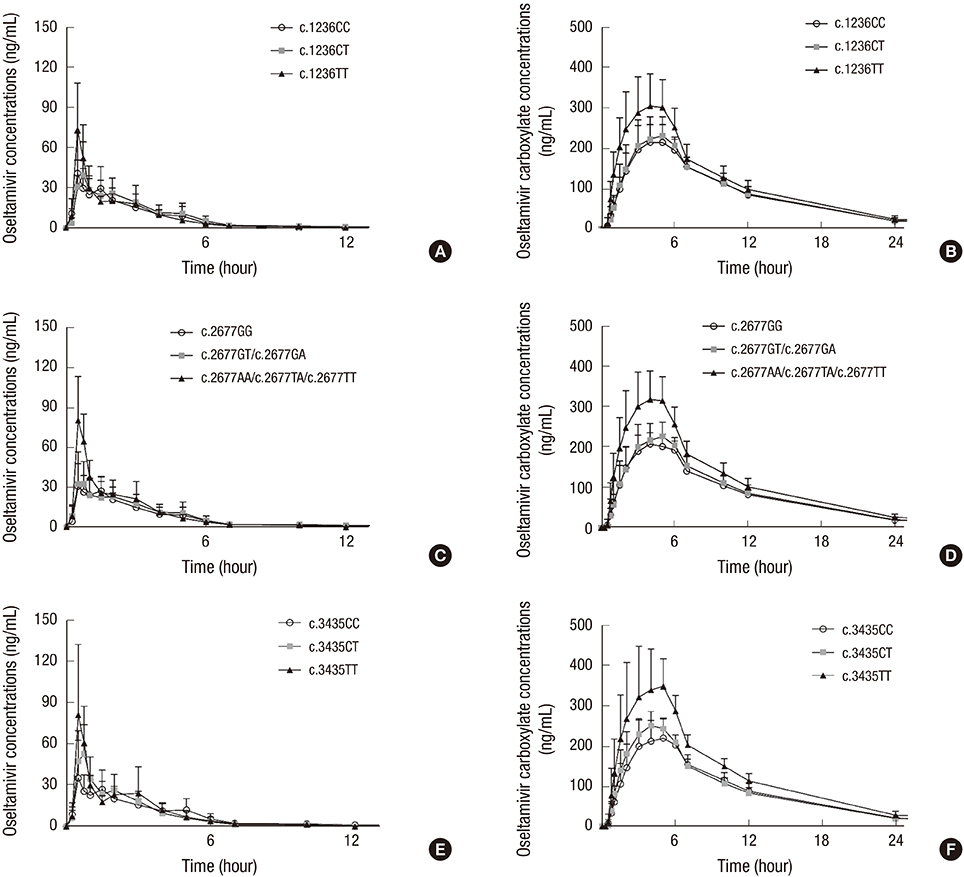
- Oseltamivir is a substrate of P-glycoprotein, an efflux drug transporter encoded by ABCB1. The objective of this study was to assess the role of ABCB1 (c.1236C>T, c.2677G>T/A, and c.3435C>T) polymorphisms in the pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir and its active metabolite, oseltamivir carboxylate in humans. Nineteen healthy male subjects were enrolled, and their ABCB1 polymorphisms were evaluated. After the oral administration of 75 mg oseltamivir, the plasma concentrations of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate were measured. Pharmacokinetic analysis was carried out. Systemic exposure to oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate was higher in the mutant group than in the wild-type and heterozygous groups. We suggest that ABCB1 polymorphisms affect the pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir in humans. Further studies in a large population are necessary to validate the results of this preliminary study (Clinical Trial Registration Information [CRIS] registry: http://cris.nih.go.kr, No. KCT0001903).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ose A, Kusuhara H, Yamatsugu K, Kanai M, Shibasaki M, Fujita T, Yamamoto A, Sugiyama Y. P-glycoprotein restricts the penetration of oseltamivir across the blood-brain barrier. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008; 36:427–434.2. Morimoto K, Nakakariya M, Shirasaka Y, Kakinuma C, Fujita T, Tamai I, Ogihara T. Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) efflux transport at the blood-brain barrier via P-glycoprotein. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008; 36:6–9.3. Davies BE. Pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir: an oral antiviral for the treatment and prophylaxis of influenza in diverse populations. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010; 65:Suppl 2. ii5–ii10.4. He G, Massarella J, Ward P. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the prodrug oseltamivir and its active metabolite Ro 64-0802. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999; 37:471–484.5. Hama R. Oseltamivir’s adverse reactions: fifty sudden deaths may be related to central suppression. BMJ. 2007; 335:59.6. Maxwell SR. Tamiflu and neuropsychiatric disturbance in adolescents. BMJ. 2007; 334:1232–1233.7. Hama R, Bennett CL. The mechanisms of sudden-onset type adverse reactions to oseltamivir. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017; 135:148–160.8. Hoffman KB, Demakas A, Erdman CB, Dimbil M, Doraiswamy PM. Neuropsychiatric adverse effects of oseltamivir in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System, 1999–2012. BMJ. 2013; 347:f4656.9. Brinkmann U, Eichelbaum M. Polymorphisms in the ABC drug transporter gene MDR1. Pharmacogenomics J. 2001; 1:59–64.10. Ieiri I. Functional significance of genetic polymorphisms in P-glycoprotein (MDR1, ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP, ABCG2). Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012; 27:85–105.11. Song P, Lamba JK, Zhang L, Schuetz E, Shukla N, Meibohm B, Yates CR. G2677T and C3435T genotype and haplotype are associated with hepatic ABCB1 (MDR1) expression. J Clin Pharmacol. 2006; 46:373–379.12. Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmöller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, et al. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000; 97:3473–3478.13. Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I. Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001; 69:169–174.14. Hemauer SJ, Nanovskaya TN, Abdel-Rahman SZ, Patrikeeva SL, Hankins GD, Ahmed MS. Modulation of human placental P-glycoprotein expression and activity by MDR1 gene polymorphisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010; 79:921–925.15. Morimoto K, Nagaoka K, Nagai A, Kashii H, Hosokawa M, Takahashi Y, Ogihara T, Kubota M. Analysis of a child who developed abnormal neuropsychiatric symptoms after administration of oseltamivir: a case report. BMC Neurol. 2015; 15:130.16. Nakamura K, Schwartz BS, Lindegårdh N, Keh C, Guglielmo BJ. Possible neuropsychiatric reaction to high-dose oseltamivir during acute 2009 H1N1 influenza A infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2010; 50:e47–e49.17. L'Huillier AG, Ing Lorenzini K, Crisinel PA, Rebsamen MC, Fluss J, Korff CM, Barbe RP, Siegrist CA, Dayer P, Posfay-Barbe KM, et al. ABCB1 polymorphisms and neuropsychiatric adverse events in oseltamivir-treated children during influenza H1N1/09 pandemia. Pharmacogenomics. 2011; 12:1493–1501.18. Wattanagoon Y, Stepniewska K, Lindegårdh N, Pukrittayakamee S, Silachamroon U, Piyaphanee W, Singtoroj T, Hanpithakpong W, Davies G, Tarning J, et al. Pharmacokinetics of high-dose oseltamivir in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:945–952.19. Jhee SS, Yen M, Ereshefsky L, Leibowitz M, Schulte M, Kaeser B, Boak L, Patel A, Hoffmann G, Prinssen EP, et al. Low penetration of oseltamivir and its carboxylate into cerebrospinal fluid in healthy Japanese and Caucasian volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52:3687–3693.20. Massarella JW, He GZ, Dorr A, Nieforth K, Ward P, Brown A. The pharmacokinetics and tolerability of the oral neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir (Ro 64-0796/GS4104) in healthy adult and elderly volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2000; 40:836–843.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Common ABCB1 SNP, C3435T could affect systemic exposure of dapagliflozin in healthy subject
- Association between ABCB1 Polymorphisms and Antidepressant Treatment Response in Taiwanese Major Depressive Patients
- The Impact of ABCB1 Gene Polymorphism on Steroid Responsiveness in Acute Rejection in Kidney Transplantation
- Psychiatric Symptoms in a Patient with Influenza A (H1N1) Treated with Oseltamivir (Tamiflu): A Case Report
- A Case of Bilateral Vestibular Hypofunction Following Oseltamivir Medication