J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Sep;32(9):1451-1459. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1451.
ABCG2 Polymorphism Is Associated with Hyperuricemia in a Study of a Community-Based Korean Cohort
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine and Institute for Medical Science, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea. junjb@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2385951
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1451
Abstract
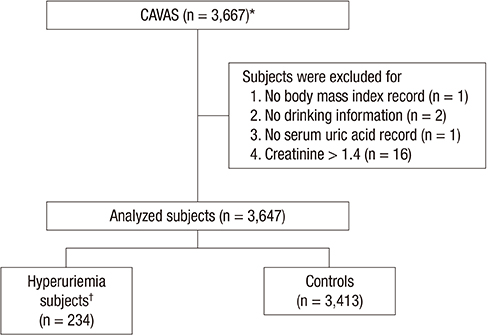
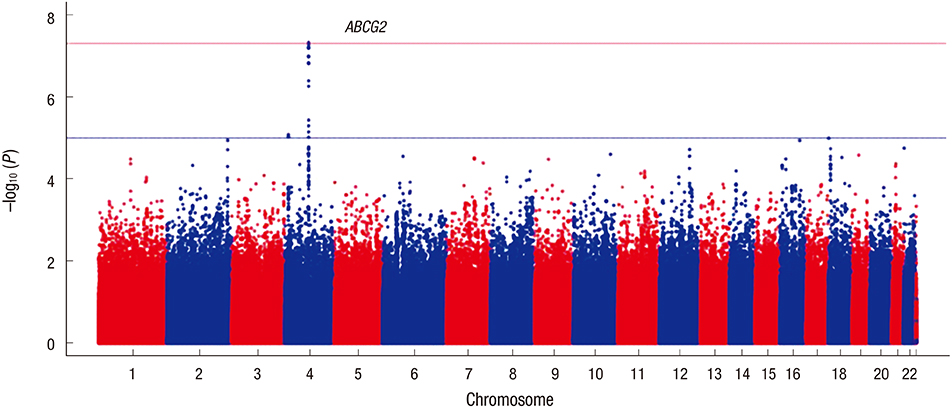
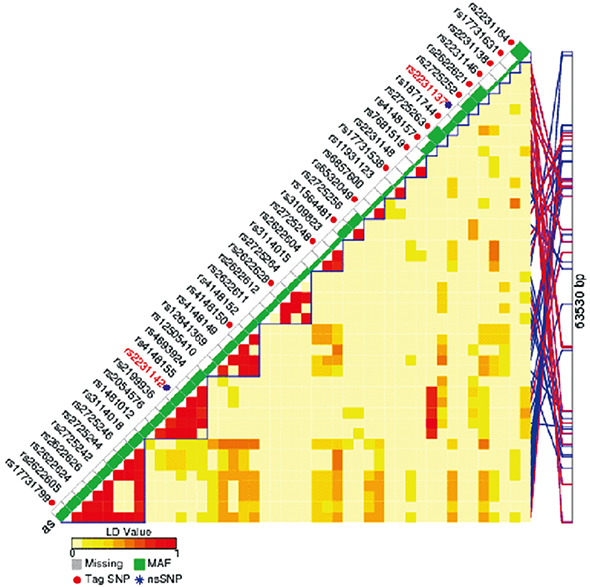
- The purpose of the present study was to find novel loci associated with hyperuricemia using data from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) conducted on healthy Koreans. We conducted a GWAS using data from a community-based cohort study where 3,647 subjects aged 40-89 were recruited by the Korea National Institute of Health (KNIH). The community-based cohort consisted of subjects who did not suffer from any of 6 major diseases (hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, heart diseases, brain diseases, and cancers). Epidemiologic information includes 249 traits such as epidemiological surveys, physical examinations, and laboratory tests. A total of 3,647 participants, including 234 hyperuricemia cases (serum uric acid [SUA] level was 7 mg/dL or higher) and 3,413 controls, were genotyped by Illumina HumanOmni1-Quad BeadChip GWAS array at KNIH. In the multivariate regression analysis of clinical variables, significant variables associated with hyperuricemia were male gender (odds ratio [OR], 5.526; P = 3.2 × 10⻹â°), old age (OR, 1.017; P = 0.040), high body mass index (BMI) (OR, 1.147; P = 5.4 × 10â»â·), current alcohol intake (OR, 2.413; P = 4.7 × 10â»â·), and high creatinine (OR, 1.647; P = 1.6 × 10⻹³). We identified a hyperuricemia susceptible loci (rs2054576 in ABCG2, OR, 1.883; P = 4.7 × 10â»â¸) that passed a genome-wide significance threshold, adjusted by clinical variables (male, age, BMI, current alcohol, and creatinine). It was first identified that rs2054576 in ABCG2 is associated with hyperuricemia. Our results should be validated through replication studies among other Korean subjects or various ethnic groups.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. So A, Thorens B. Uric acid transport and disease. J Clin Invest. 2010; 120:1791–1799.2. Anzai N, Jutabha P, Amonpatumrat-Takahashi S, Sakurai H. Recent advances in renal urate transport: characterization of candidate transporters indicated by genome-wide association studies. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012; 16:89–95.3. Köttgen A, Albrecht E, Teumer A, Vitart V, Krumsiek J, Hundertmark C, Pistis G, Ruggiero D, O'Seaghdha CM, Haller T, et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 18 new loci associated with serum urate concentrations. Nat Genet. 2013; 45:145–154.4. Kolz M, Johnson T, Sanna S, Teumer A, Vitart V, Perola M, Mangino M, Albrecht E, Wallace C, Farrall M, et al. Meta-analysis of 28,141 individuals identifies common variants within five new loci that influence uric acid concentrations. PLoS Genet. 2009; 5:e1000504.5. Lee YH, Song GG. Pathway analysis of genome-wide association studies on uric acid concentrations. Hum Immunol. 2012; 73:805–810.6. Takeuchi F, Yamamoto K, Isono M, Katsuya T, Akiyama K, Ohnaka K, Rakugi H, Yamori Y, Ogihara T, Takayanagi R, et al. Genetic impact on uric acid concentration and hyperuricemia in the Japanese population. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013; 20:351–367.7. Yang B, Mo Z, Wu C, Yang H, Yang X, He Y, Gui L, Zhou L, Guo H, Zhang X, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies common variants influencing serum uric acid concentrations in a Chinese population. BMC Med Genomics. 2014; 7:10.8. Shin J, Kim Y, Kong M, Lee C. Genetic architecture for susceptibility to gout in the KARE cohort study. J Hum Genet. 2012; 57:379–384.9. Hong KW, Lyu J, Lee SH, Choi BY, Kim SS, Kim Y. A nonsynonymous SNP in BANK1 is associated with serum LDL cholesterol levels in three Korean populations. J Hum Genet. 2015; 60:113–118.10. Bae J, Park PS, Chun BY, Choi BY, Kim MK, Shin MH, Lee YH, Shin DH, Kim SK. The effect of coffee, tea, and caffeine consumption on serum uric acid and the risk of hyperuricemia in Korean Multi-Rural Communities Cohort. Rheumatol Int. 2015; 35:327–336.11. Jin LH, Chang SJ, Koh SB, Kim KS, Lee TY, Ryu SY, Song JS, Park JK. Association between alcohol consumption and bone strength in Korean adults: the Korean Genomic Rural Cohort Study. Metabolism. 2011; 60:351–358.12. Yamanaka H. Japanese Society of Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism. Japanese guideline for the management of hyperuricemia and gout: second edition. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2011; 30:1018–1029.13. Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007; 81:559–575.14. Pe’er I, Yelensky R, Altshuler D, Daly MJ. Estimation of the multiple testing burden for genomewide association studies of nearly all common variants. Genet Epidemiol. 2008; 32(9):–. 381–385.15. Ge D, Zhang K, Need AC, Martin O, Fellay J, Urban TJ, Telenti A, Goldstein DB. WGAViewer: software for genomic annotation of whole genome association studies. Genome Res. 2008; 18:640–643.16. Pruim RJ, Welch RP, Sanna S, Teslovich TM, Chines PS, Gliedt TP, Boehnke M, Abecasis GR, Willer CJ. LocusZoom: regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics. 2010; 26:2336–2337.17. Dehghan A, Köttgen A, Yang Q, Hwang SJ, Kao WL, Rivadeneira F, Boerwinkle E, Levy D, Hofman A, Astor BC, et al. Association of three genetic loci with uric acid concentration and risk of gout: a genome-wide association study. Lancet. 2008; 372:1953–1961.18. Yamagishi K, Tanigawa T, Kitamura A, Köttgen A, Folsom AR, Iso H. CIRCS Investigators. The rs2231142 variant of the ABCG2 gene is associated with uric acid levels and gout among Japanese people. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:1461–1465.19. Matsuo H, Takada T, Ichida K, Nakamura T, Nakayama A, Ikebuchi Y, Ito K, Kusanagi Y, Chiba T, Tadokoro S, et al. Common defects of ABCG2, a high-capacity urate exporter, cause gout: a function-based genetic analysis in a Japanese population. Sci Transl Med. 2009; 1:5ra11.20. Wang B, Miao Z, Liu S, Wang J, Zhou S, Han L, Meng D, Wang Y, Li C, Ma X. Genetic analysis of ABCG2 gene C421A polymorphism with gout disease in Chinese Han male population. Hum Genet. 2010; 127:245–246.21. Tin A, Woodward OM, Kao WH, Liu CT, Lu X, Nalls MA, Shriner D, Semmo M, Akylbekova EL, Wyatt SB, et al. Genome-wide association study for serum urate concentrations and gout among African Americans identifies genomic risk loci and a novel URAT1 loss-of-function allele. Hum Mol Genet. 2011; 20:4056–4068.22. Zhang L, Spencer KL, Voruganti VS, Jorgensen NW, Fornage M, Best LG, Brown-Gentry KD, Cole SA, Crawford DC, Deelman E, et al. Association of functional polymorphism rs2231142 (Q141K) in the ABCG2 gene with serum uric acid and gout in 4 US populations: the PAGE Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2013; 177:923–932.23. Woodward OM, Köttgen A, Coresh J, Boerwinkle E, Guggino WB, Köttgen M. Identification of a urate transporter, ABCG2, with a common functional polymorphism causing gout. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009; 106:10338–10342.24. Sulem P, Gudbjartsson DF, Walters GB, Helgadottir HT, Helgason A, Gudjonsson SA, Zanon C, Besenbacher S, Bjornsdottir G, Magnusson OT, et al. Identification of low-frequency variants associated with gout and serum uric acid levels. Nat Genet. 2011; 43:1127–1130.25. Stark K, Reinhard W, Grassl M, Erdmann J, Schunkert H, Illig T, Hengstenberg C. Common polymorphisms influencing serum uric acid levels contribute to susceptibility to gout, but not to coronary artery disease. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e7729.26. Phipps-Green AJ, Hollis-Moffatt JE, Dalbeth N, Merriman ME, Topless R, Gow PJ, Harrison AA, Highton J, Jones PB, Stamp LK, et al. A strong role for the ABCG2 gene in susceptibility to gout in New Zealand Pacific Island and Caucasian, but not Māori, case and control sample sets. Hum Mol Genet. 2010; 19:4813–4819.27. Dong Z, Guo S, Yang Y, Wu J, Guan M, Zou H, Jin L, Wang J. Association between ABCG2 Q141K polymorphism and gout risk affected by ethnicity and gender: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015; 18:382–391.28. Lv X, Zhang Y, Zeng F, Yin A, Ye N, Ouyang H, Feng D, Li D, Ling W, Zhang X. The association between the polymorphism rs2231142 in the ABCG2 gene and gout risk: a meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2014; 33:1801–1805.29. Qiu Y, Liu H, Qing Y, Yang M, Tan X, Zhao M, Lin M, Zhou J. The ABCG2 gene Q141K polymorphism contributes to an increased risk of gout: a meta-analysis of 2185 cases. Mod Rheumatol. 2014; 24:829–834.30. Okada Y, Sim X, Go MJ, Wu JY, Gu D, Takeuchi F, Takahashi A, Maeda S, Tsunoda T, Chen P, et al. Meta-analysis identifies multiple loci associated with kidney function-related traits in east Asian populations. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:904–909.31. Sull JW, Yang SJ, Kim S, Jee SH. The ABCG2 polymorphism rs2725220 is associated with hyperuricemia in the Korean population. Genomics Inform. 2014; 12:231–235.32. Kamatani Y, Matsuda K, Okada Y, Kubo M, Hosono N, Daigo Y, Nakamura Y, Kamatani N. Genome-wide association study of hematological and biochemical traits in a Japanese population. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:210–215.33. Karns R, Zhang G, Sun G, Rao Indugula S, Cheng H, Havas-Augustin D, Novokmet N, Rudan D, Durakovic Z, Missoni S, et al. Genome-wide association of serum uric acid concentration: replication of sequence variants in an island population of the Adriatic coast of Croatia. Ann Hum Genet. 2012; 76:121–127.34. Reginato AM, Mount DB, Yang I, Choi HK. The genetics of hyperuricaemia and gout. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012; 8:610–621.35. Li WD, Jiao H, Wang K, Zhang CK, Glessner JT, Grant SF, Zhao H, Hakonarson H, Arlen Price R. A genome wide association study of plasma uric acid levels in obese cases and never-overweight controls. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013; 21:E490–E494.36. Sakurai H. Urate transporters in the genomic era. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013; 22:545–550.37. Stacy AE, Jansson PJ, Richardson DR. Molecular pharmacology of ABCG2 and its role in chemoresistance. Mol Pharmacol. 2013; 84:655–669.38. Matsuo H, Yamamoto K, Nakaoka H, Nakayama A, Sakiyama M, Chiba T, Takahashi A, Nakamura T, Nakashima H, Takada Y, et al. Genome-wide association study of clinically defined gout identifies multiple risk loci and its association with clinical subtypes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016; 75:652–659.39. Yano H, Tamura Y, Kobayashi K, Tanemoto M, Uchida S. Uric acid transporter ABCG2 is increased in the intestine of the 5/6 nephrectomy rat model of chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2014; 18:50–55.40. Son CN, Bang SY, Cho SK, Sung YK, Kim TH, Bae SC, Jun JB. The frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms and their association with uric acid concentration based on data from genome-wide association studies in the Korean population. Rheumatol Int. 2014; 34:777–783.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The ABCG2 Polymorphism rs2725220 Is Associated with Hyperuricemia in the Korean Population
- ABCG2 C421A Polymorphism and Imatinib Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Hyper-homocysteinemia Inducing Hyperuricemia: What are the Mechanisms?
- Urate Transporters in the Kidney: What Clinicians Need to Know
- Silencing of ABCG2 by MicroRNA-3163 Inhibits Multidrug Resistance in Retinoblastoma Cancer Stem Cells