Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2017 Jul;21(4):397-405. 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.4.397.
MDL-12330A potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through CHOP-mediated DR5 upregulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju 61501, Korea.
- 2Division of Premedical Science, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju 61501, Korea. sihan@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2384453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.4.397
Abstract
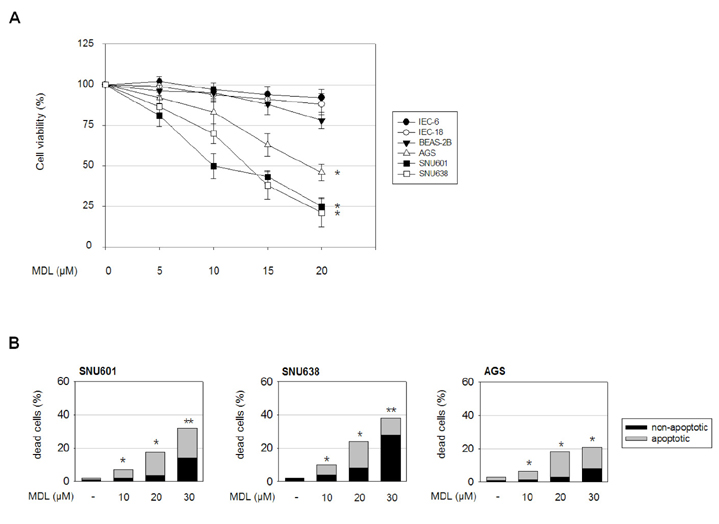
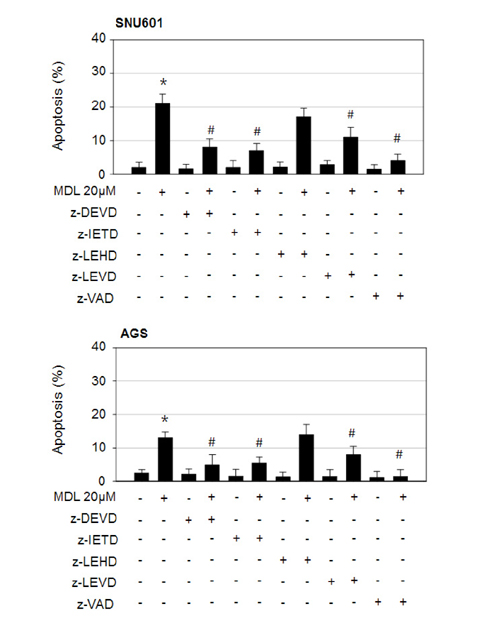
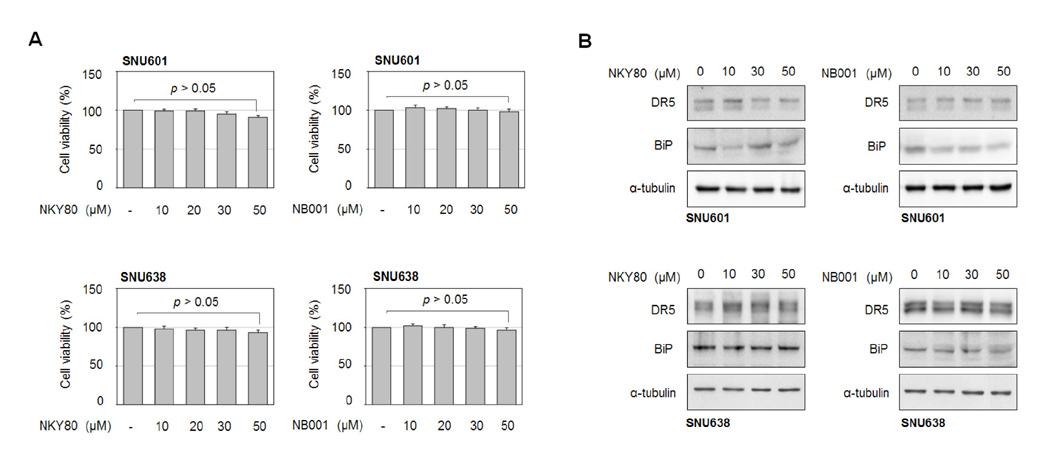
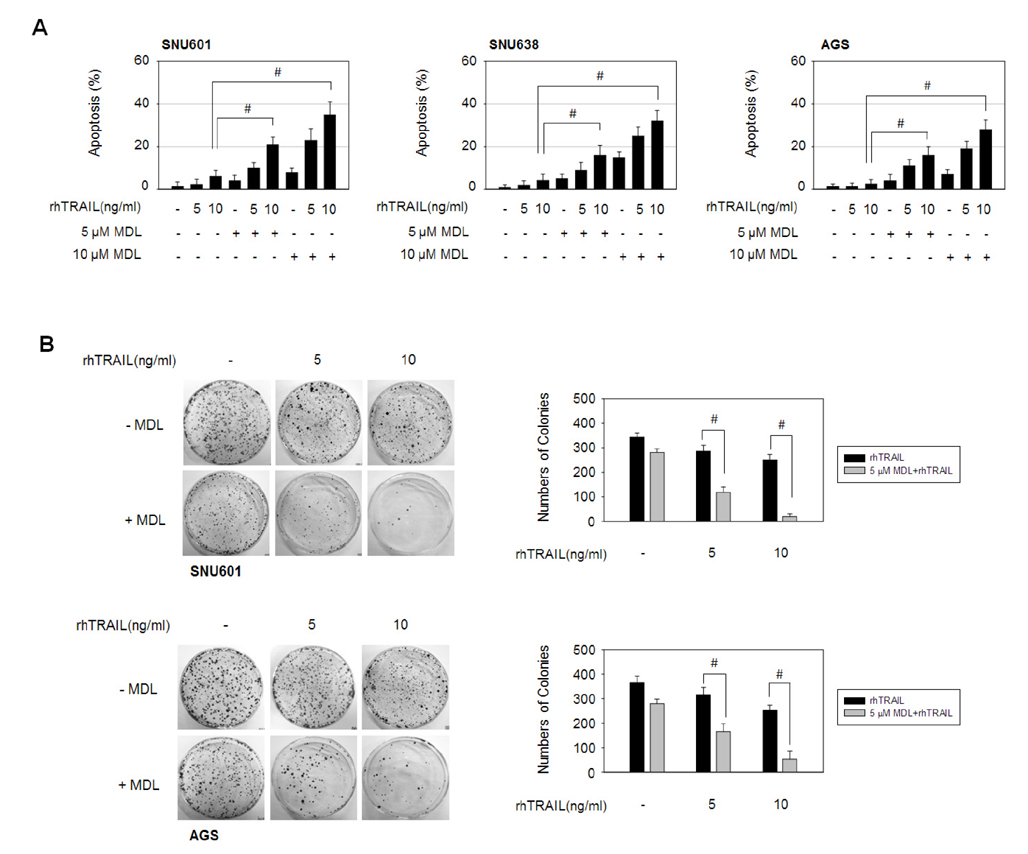
- MDL-12330A is a widely used adenylyl cyclase (AC) inhibitor that blocks AC/cAMP signaling. In this study, we demonstrated a novel antitumor activity of this drug in gastric carcinoma (GC) cell lines. In these GC cells, MDL-12330A reduced cell viability and induced cell death in a concentration-dependent manner. At a moderate concentration (~20 µM), MDL-12330A mainly induced apoptotic death whereas at concentrations greater than 20 µM, it increased non-apoptotic cell death. The induction of apoptosis was at least partially regulated by CHOP-mediated DR5 upregulation, as detected by immunoblotting and gene interference assays. More importantly, low concentrations of MDL-12330A effectively enhanced recombinant human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhTRAIL)-induced apoptosis and clonogenicity in these gastric cancer cells. This study demonstrates a possible role of MDL-12330A as a potential sensitizer to TRAIL, and suggests a novel therapeutic strategy targeting gastric cancer cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer. 1999; 83:18–29.2. Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin. 2001; 51:15–36.3. Roukos DH. Current status and future perspectives in gastric cancer management. Cancer Treat Rev. 2000; 26:243–255.4. Gura T. How TRAIL kills cancer cells, but not normal cells. Science. 1997; 277:768.5. Baker SJ, Reddy EP. Modulation of life and death by the TNF receptor superfamily. Oncogene. 1998; 17:3261–3270.6. Ashkenazi A. Targeting death and decoy receptors of the tumour-necrosis factor superfamily. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002; 2:420–430.7. Srivastava RK. TRAIL/Apo-2L: mechanisms and clinical applications in cancer. Neoplasia. 2001; 3:535–546.8. Prasad S, Yadav VR, Kannappan R, Aggarwal BB. Ursolic acid, a pentacyclin triterpene, potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis through p53-independent up-regulation of death receptors: evidence for the role of reactive oxygen species and JNK. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:5546–5557.9. Siddiqui IA, Malik A, Adhami VM, Asim M, Hafeez BB, Sarfaraz S, Mukhtar H. Green tea polyphenol EGCG sensitizes human prostate carcinoma LNCaP cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis and synergistically inhibits biomarkers associated with angiogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene. 2008; 27:2055–2063.10. Szliszka E, Krol W. The role of dietary polyphenols in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis for cancer chemoprevention. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2011; 20:63–69.11. Seifert R, Lushington GH, Mou TC, Gille A, Sprang SR. Inhibitors of membranous adenylyl cyclases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 33:64–78.12. Li X, Guo Q, Gao J, Yang J, Zhang W, Liang Y, Wu D, Liu Y, Weng J, Li Q, Zhang Y. The adenylyl cyclase inhibitor MDL-12,330A potentiates insulin secretion via blockade of voltage-dependent K(+) channels in pancreatic beta cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e77934.13. Gadea A, López E, López-Colomé AM. The adenylate cyclase inhibitor MDL-12330A has a non-specific effect on glycine transport in Müller cells from the retina. Brain Res. 1999; 838:200–204.14. Shin JN, Park SY, Cha JH, Park JY, Lee BR, Jung SA, Lee ST, Yun CW, Seol DW, Kim TH. Generation of a novel proform of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) protein that can be reactivated by matrix metalloproteinases. Exp Cell Res. 2006; 312:3892–3898.15. Kim CH, Han SI, Lee SY, Youk HS, Moon JY, Duong HQ, Park MJ, Joo YM, Park HG, Kim YJ, Yoo MA, Lim SC, Kang HS. Protein kinase C-ERK1/2 signal pathway switches glucose depletion-induced necrosis to apoptosis by regulating superoxide dismutases and suppressing reactive oxygen species production in A549 lung cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2007; 211:371–385.16. Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2006; 1:2315–2319.17. Kong F, You H, Zhao J, Liu W, Hu L, Luo W, Hu W, Tang R, Zheng K. The enhanced expression of death receptor 5 (DR5) mediated by HBV X protein through NF-kappaB pathway is associated with cell apoptosis induced by (TNF-α related apoptosis inducing ligand) TRAIL in hepatoma cells. Virol J. 2015; 12:192.18. Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald ER 3rd, Jiang W, Meng R, Krantz ID, Kao G, Gan DD, Zhou JY, Muschel R, Hamilton SR, Spinner NB, Markowitz S, Wu G, el-Deiry WS. KILLER/DR5 is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated death receptor gene. Nat Genet. 1997; 17:141–143.19. Pennati M, Sbarra S, De Cesare M, Lopergolo A, Locatelli SL, Campi E, Daidone MG, Carlo-Stella C, Gianni AM, Zaffaroni N. YM155 sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to membrane-bound TRAIL through p38 MAPK- and CHOP-mediated DR5 upregulation. Int J Cancer. 2015; 136:299–309.20. Lim JH, Park JW, Choi KS, Park YB, Kwon TK. Rottlerin induces apoptosis via death receptor 5 (DR5) upregulation through CHOP-dependent and PKC delta-independent mechanism in human malignant tumor cells. Carcinogenesis. 2009; 30:729–736.21. Mérino D, Lalaoui N, Morizot A, Solary E, Micheau O. TRAIL in cancer therapy: present and future challenges. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007; 11:1299–1314.22. Fulda S. Tumor-necrosis-factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014; 818:167–180.23. Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert A, DeForge L, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen H, Shahrokh Z, Schwall RH. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest. 1999; 104:155–162.24. Zhou Y, Tian L, Long L, Quan M, Liu F, Cao J. Casticin potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e58855.25. Kim S, Lee TJ, Leem J, Choi KS, Park JW, Kwon TK. Sanguinarine-induced apoptosis: generation of ROS, down-regulation of Bcl-2, c-FLIP, and synergy with TRAIL. J Cell Biochem. 2008; 104:895–907.26. Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, Nakata S, Horinaka M, Wakada M, Mizutani Y, Miki T, Sakai T. Proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces death receptor 5 through CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:5662–5667.27. Shiraishi T, Yoshida T, Nakata S, Horinaka M, Wakada M, Mizutani Y, Miki T, Sakai T. Tunicamycin enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:6364–6370.28. English AR, Zurek N, Voeltz GK. Peripheral ER structure and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009; 21:596–602.29. Nishitoh H. CHOP is a multifunctional transcription factor in the ER stress response. J Biochem. 2012; 151:217–219.30. Szewczyk A. The intracellular potassium and chloride channels: properties, pharmacology and function (review). Mol Membr Biol. 1998; 15:49–58.31. Kuum M, Veksler V, Kaasik A. Potassium fluxes across the endoplasmic reticulum and their role in endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis. Cell Calcium. 2015; 58:79–85.32. Liu H, Jiang CC, Lavis CJ, Croft A, Dong L, Tseng HY, Yang F, Tay KH, Hersey P, Zhang XD. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells through XBP-1-mediated up-regulation of TRAIL-R2. Mol Cancer. 2009; 8:122.33. Moon DO, Park SY, Choi YH, Ahn JS, Kim GY. Guggulsterone sensitizes hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the induction of CHOP-dependent DR5: involvement of ROS-dependent ER-stress. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011; 82:1641–1650.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Paxilline enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of glioma cells via modulation of c-FLIP, survivin and DR5
- Cytotoxic Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand (TRAIL)and its Molecular Mechanism in Human Gastric Cancer Cells
- Vanillin oxime inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and activates apoptosis through JNK/ERK-CHOP pathway
- Extracellular acidity enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis via DR5 in gastric cancer cells
- Troglitazone Increases the Susceptibility to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines