Int J Stem Cells.
2015 May;8(1):106-114. 10.15283/ijsc.2015.8.1.106.
Direct Differentiation of Adult Ocular Progenitors into Striatal Dopaminergic Neurons
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE, United States. iahmad@unmc.edu
- 2Department of Genetics, Cell Biology and Anatomy, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE, United States.
- 3Department of Pharmacy Practice, Creighton University, Omaha, NE, United States.
- KMID: 2380804
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc.2015.8.1.106
Abstract
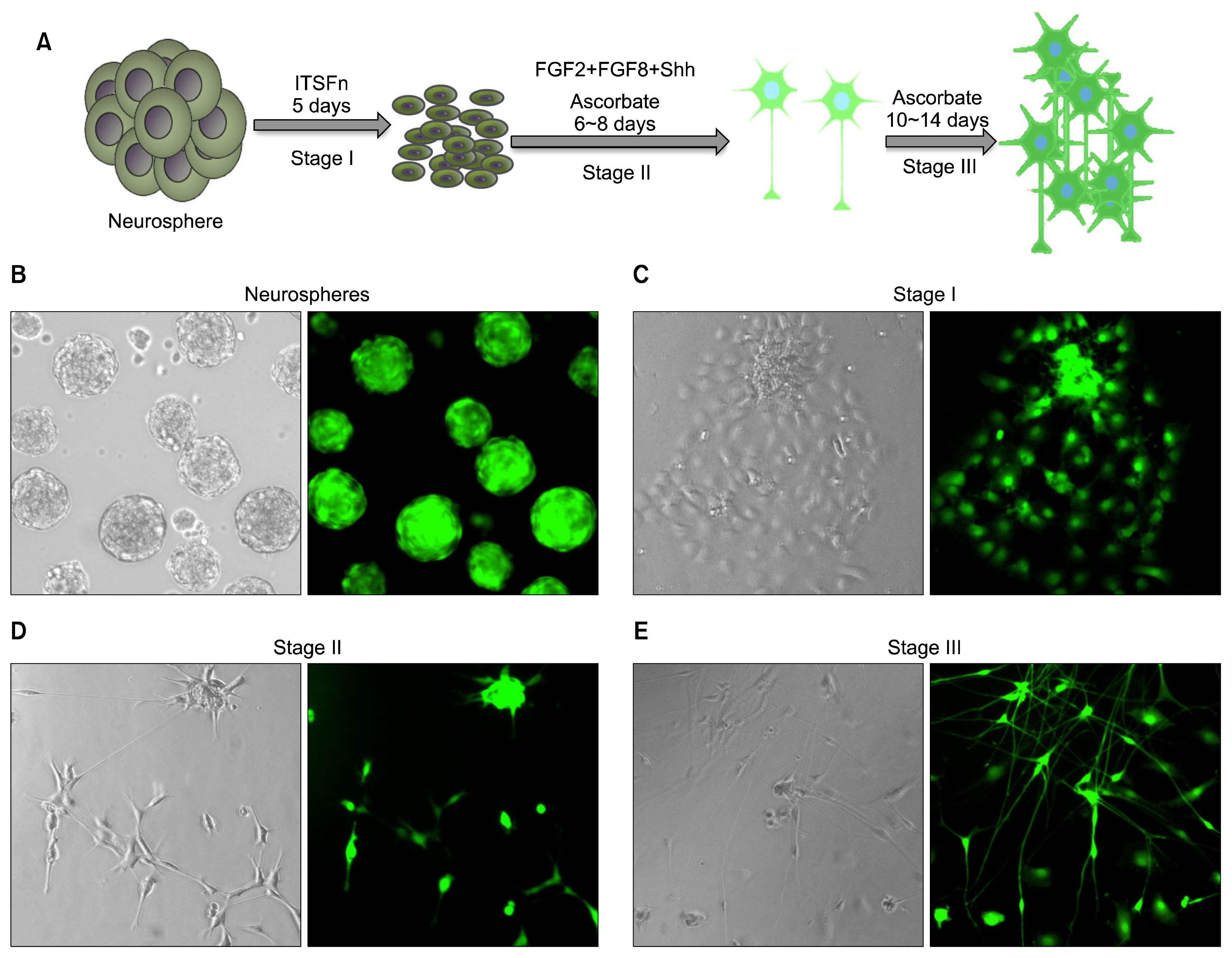
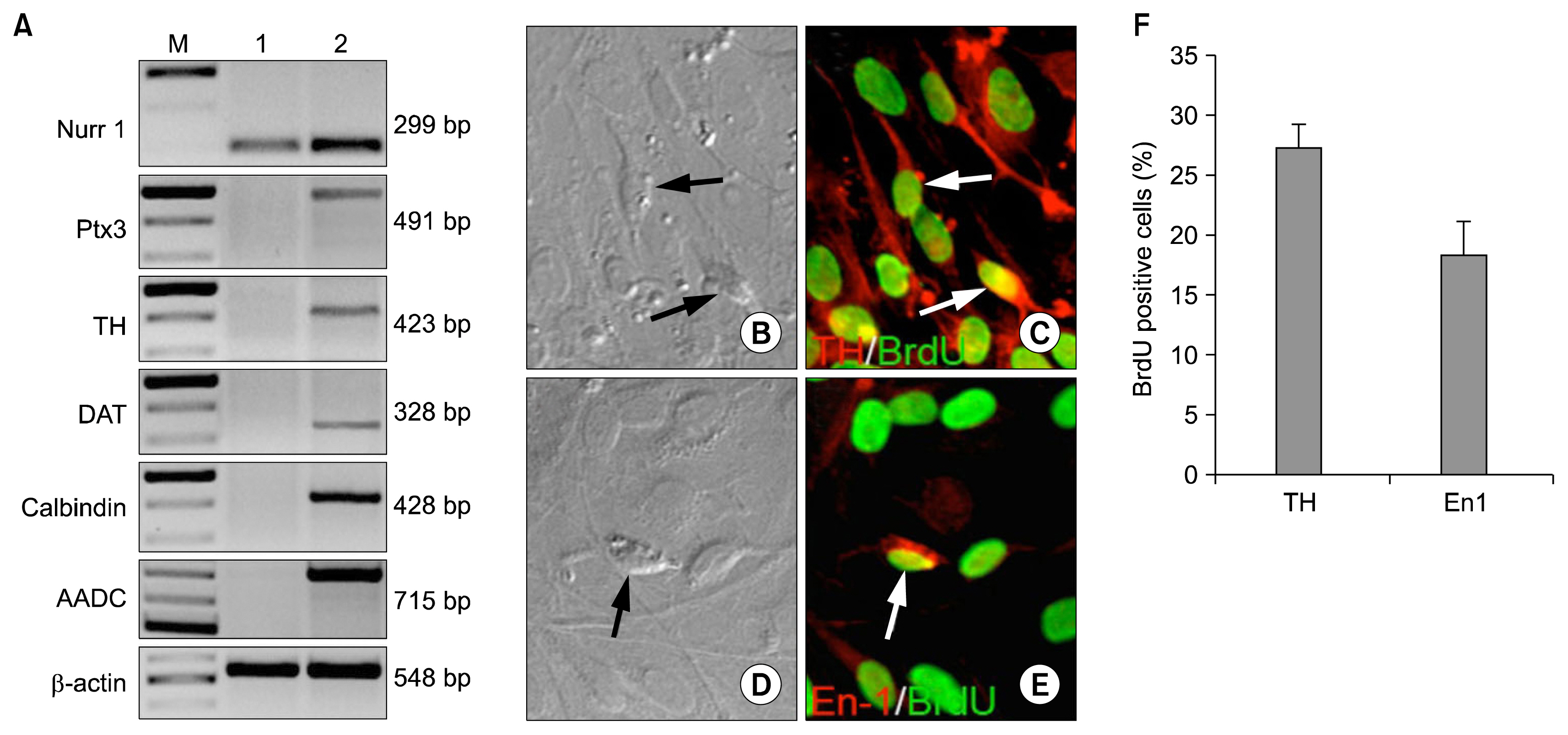
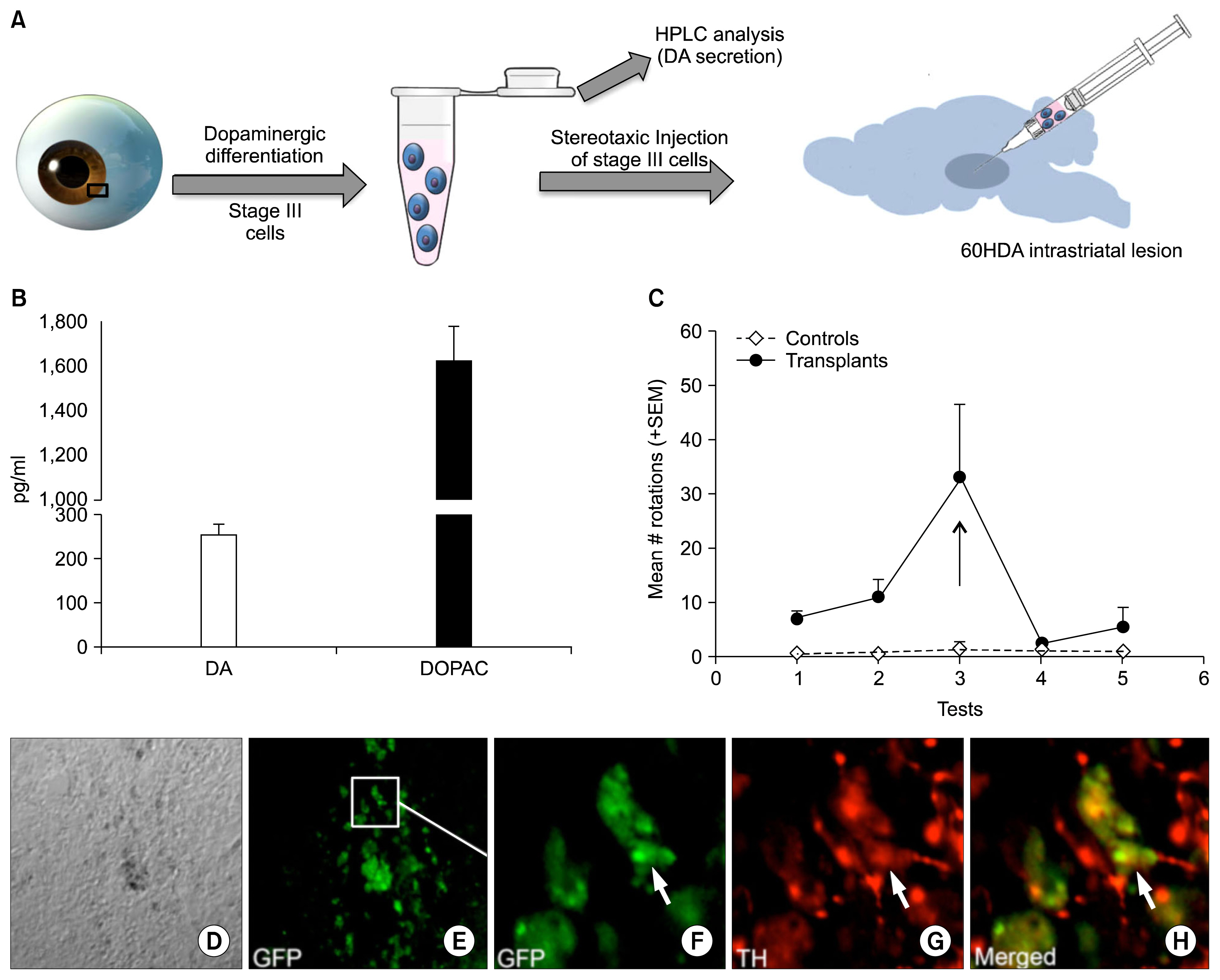
- Parkinson's disease, characterized by motor dysfunction due to the loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons, is one of the most prevalent age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Given there is no current cure, the stem cell approach has emerged as a viable therapeutic option to replace the dopaminergic neurons that are progressively lost to the disease. The success of the approach is likely to depend upon accessible, renewable, immune compatible, and non-tumorigenic sources of neural progenitors from which stable dopaminergic neurons can be generated efficaciously. Here, we demonstrate that neural progenitors derived from limbus, a regenerative and accessible ocular tissue, represent a safe source of dopaminergic neurons. When the limbus-derived neural progenitors were subjected to a well-established protocol of directed differentiation under the influence of Shh and FGF8, they acquired the biochemical and functional phenotype of dopaminergic neurons that included the ability to synthesize dopamine. Their intrastriatal transplantation in the rat model of hemi-Parkinsonism was associated with a reduction in the amphetamine-induced rotation. No tumor formation was observed 6 weeks post-transplantation. Together, these observations posit limbus-derived neural progenitors as an accessible and safe source of dopaminergic neurons for a potential autologous ex-vivo stem cell approach to Parkinson's disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Dyson SC, Barker RA. Cell-based therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011; 11:831–844. PMID: 21651331.
Article2. Kim JH, Auerbach JM, Rodríguez-Gómez JA, Velasco I, Gavin D, Lumelsky N, Lee SH, Nguyen J, Sánchez-Pernaute R, Bankiewicz K, McKay R. Dopamine neurons derived from embryonic stem cells function in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature. 2002; 418:50–56. DOI: 10.1038/nature00900. PMID: 12077607.
Article3. Sundberg M, Isacson O. Advances in stem-cell--generated transplantation therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014; 14:437–453. PMID: 24437368.
Article4. Parameswaran S, Balasubramanian S, Rao MS, Ahmad I. Concise review: non-cell autonomous reprogramming: a nucleic acid-free approach to induction of pluripotency. Stem Cells. 2011; 29:1013–1020. DOI: 10.1002/stem.655. PMID: 21544901.
Article5. Kitada M, Dezawa M. Parkinson’s disease and mesenchymal stem cells: potential for cell-based therapy. Parkinsons Dis. 2012; 2012:873706.
Article6. Dezawa M, Kanno H, Hoshino M, Cho H, Matsumoto N, Itokazu Y, Tajima N, Yamada H, Sawada H, Ishikawa H, Mimura T, Kitada M, Suzuki Y, Ide C. Specific induction of neuronal cells from bone marrow stromal cells and application for autologous transplantation. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:1701–1710. PMID: 15199405. PMCID: 420509.
Article7. Lavker RM, Tseng SC, Sun TT. Corneal epithelial stem cells at the limbus: looking at some old problems from a new angle. Exp Eye Res. 2004; 78:433–446. PMID: 15106923.
Article8. Rama P, Matuska S, Paganoni G, Spinelli A, De Luca M, Pellegrini G. Limbal stem-cell therapy and long-term corneal regeneration. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:147–155. PMID: 20573916.
Article9. Zhao X, Das AV, Thoreson WB, James J, Wattnem TE, Rodriguez-Sierra J, Ahmad I. Adult corneal limbal epithelium: a model for studying neural potential of non-neural stem cells/progenitors. Dev Biol. 2002; 250:317–331. PMID: 12376106.
Article10. Zhao X, Das AV, Bhattacharya S, Thoreson WB, Sierra JR, Mallya KB, Ahmad I. Derivation of neurons with functional properties from adult limbal epithelium: implications in autologous cell therapy for photoreceptor degeneration. Stem Cells. 2008; 26:939–949. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0727. PMID: 18203675.
Article11. Zetterström RH, Solomin L, Jansson L, Hoffer BJ, Olson L, Perlmann T. Dopamine neuron agenesis in Nurr1-deficient mice. Science. 1997; 276:248–250. DOI: 10.1126/science.276.5310.248. PMID: 9092472.
Article12. Liberatore GT, Jackson-Lewis V, Vukosavic S, Mandir AS, Vila M, McAuliffe WG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Przedborski S. Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease. Nat Med. 1999; 5:1403–1409. DOI: 10.1038/70978. PMID: 10581083.
Article13. Lee SH, Lumelsky N, Studer L, Auerbach JM, McKay RD. Efficient generation of midbrain and hindbrain neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2000; 18:675–679. DOI: 10.1038/76536. PMID: 10835609.
Article14. Smidt MP, Asbreuk CH, Cox JJ, Chen H, Johnson RL, Burbach JP. A second independent pathway for development of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons requires Lmx1b. Nat Neurosci. 2000; 3:337–341. DOI: 10.1038/73902. PMID: 10725922.
Article15. Burbach JPH, Smits S, Smidt MP. Transcription factors in the development of midbrain dopamine neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003; 991:61–68. DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07463.x. PMID: 12846974.
Article16. Cadet JL, Zhu SM. The intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine model of hemiparkinsonism: quantitative receptor autoradiographic evidence of correlation between circling behavior and presynaptic as well as postsynaptic nigrostriatal markers in the rat. Brain Res. 1992; 595:316–326. DOI: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91066-N. PMID: 1467973.
Article17. Parameswaran S, Balasubramanian S, Babai N, DelDebbio CB, Harms DW, Gurumurthy CB, Rao MS, Sharp JG, Ahmad I. Nucleic acid and non-nucleic acid-based reprogramming of adult limbal progenitors to pluripotency. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e46734. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046734. PMID: 23056428. PMCID: 3466310.
Article18. Kim TE, Lee HS, Lee YB, Hong SH, Lee YS, Ichinose H, Kim SU, Lee MA. Sonic hedgehog and FGF8 collaborate to induce dopaminergic phenotypes in the Nurr1- overexpressing neural stem cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003; 305:1040–1048. DOI: 10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00879-9. PMID: 12767935.
Article19. Alves dos Santos MT, Smidt MP. En1 and Wnt signaling in midbrain dopaminergic neuronal development. Neural Dev. 2011; 6:23. DOI: 10.1186/1749-8104-6-23. PMID: 21569278. PMCID: 3104484.
Article20. Nelson EL, Liang CL, Sinton CM, German DC. Midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the mouse: computer-assisted mapping. J Comp Neurol. 1996; 369:361–371. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960603)369:3<361::AID-CNE3>3.0.CO;2-3. PMID: 8743418.
Article21. González-Hernández T, Rodríguez M. Compartmental organization and chemical profile of dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2000; 421:107–135. PMID: 10813775.
Article22. Capaccione KM, Pine SR. The Notch signaling pathway as a mediator of tumor survival. Carcinogenesis. 2013; 34:1420–1430. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgt127. PMID: 23585460. PMCID: 3697894.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neural Network Model of Basal Ganglia: Preliminary Study
- Changes of Dopaminergic Neurons in Parkinson's Rat Model after Fetal Striatal Transplantation
- FGF8 is Essential for Functionality of Induced Neural Precursor Cell-derived Dopaminergic Neurons
- Distribution of the Mouse Striatal Cholinergic Neurons in Their Early Postnatal Period
- Neurogenesis and neuronal migration of dopaminergic neurons during mesencephalon development in mice