Cancer Res Treat.
2014 Oct;46(4):339-347. 10.4143/crt.2013.154.
Efficacy and Safety of Everolimus in Korean Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Following Treatment Failure with a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jaelyun@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Hematology-Oncology, KEPCO Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Departments of Hematology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2380371
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.154
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to assess the efficacy and safety of everolimus in Korean patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) for whom initial treatment with a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (VEGFr-TKI) has failed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eligible patients with mRCC (any histology) who had progressed on or were intolerant of VEGFr-TKI therapy received oral everolimus (10 mg dose once daily). Tumor response was reassessed according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST).
RESULTS
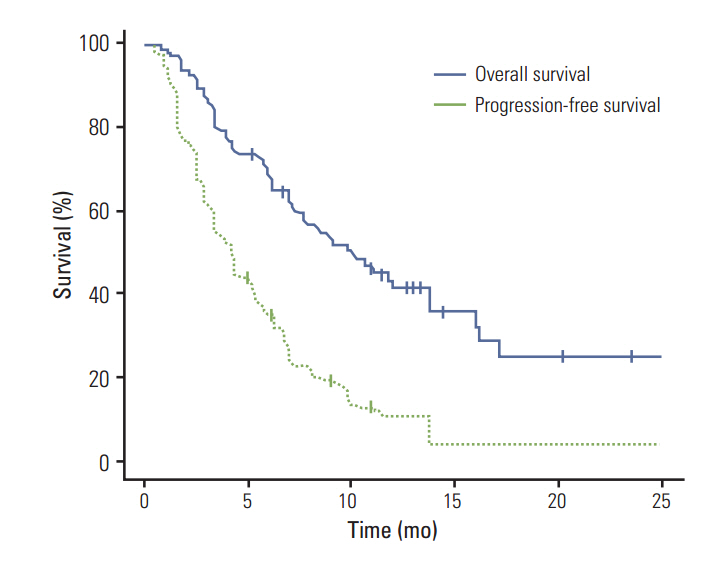
This study included 100 patientswith a median follow-up duration of 10.2 months, a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 4.2 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.4 to 5.0 months), and an overall survival of 10.1 months (95% CI, 6.9 to 13.3 months). The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events (AEs) overall were anemia (13%), pneumonitis (9%), hyperglycemia (8%), and stomatitis (6%). While the incidence of pneumonitis was similar (26 cases, 26%) to the reported incidence in Western patients, the Korean presentations were more severe: 10 patients permanently discontinued everolimus due to pneumonitis, including two deaths on treatment. Statistically significant relationships were established between biologic toxicities, hyperglycemia and anemia, and PFS (hyperglycemia vs. non-hyperglycemia: hazard ratio [HR], 0.61; p=0.055 and anemia vs. non-anemia: HR, 0.51; p=0.021).
CONCLUSION
Everolimus was effective in Korean patients with mRCC who had failed initial VEGFr-TKI therapy. While everolimus was well tolerated in general and the AE incidence of this study was similar to those of previous reports, severe pneumonitis was common. Hyperglycemia and anemia showed significant correlation with PFS and thus may be potentially useful as prognostic indicators.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:125–34.
Article2. Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007; 370:2103–11.
Article3. Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:2271–81.
Article4. Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, et al. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008; 372:449–56.
Article5. Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:115–24.
Article6. Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, Stadler WM, Vaena DA, Ou SS, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB 90206. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:5422–8.
Article7. Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:1061–8.
Article8. Patel PH, Senico PL, Curiel RE, Motzer RJ. Phase I study combining treatment with temsirolimus and sunitinib malate in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2009; 7:24–7.
Article9. Feldman DR, Baum MS, Ginsberg MS, Hassoun H, Flombaum CD, Velasco S, et al. Phase I trial of bevacizumab plus escalated doses of sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:1432–9.
Article10. Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Kaprin A, Szczylik C, Hutson TE, et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus so-rafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011; 378:1931–9.
Article11. Park K, Lee JL, Park I, Park S, Ahn Y, Ahn JH, et al. Comparative efficacy of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor as second-line therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma after the failure of first-line VEGF TKI. Med Oncol. 2012; 29:3291–7.
Article12. Hutson TE, Escudier B, Esteban E, Bjarnason GA, Lim HY, Pittman K, et al. Temsirolimus versus sorafenib as second line therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from the INTORSECT trial. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23(Suppl 9):Absr LBA22.13. Tsukamoto T, Shinohara N, Tsuchiya N, Hamamoto Y, Maruoka M, Fujimoto H, et al. Phase III trial of everolimus in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: subgroup analysis of Japanese patients from RECORD-1. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011; 41:17–24.
Article14. Grunwald V, Karakiewicz PI, Bavbek SE, Miller K, Machiels JP, Lee SH, et al. An international expanded-access programme of everolimus: addressing safety and efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who progress after initial vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2012; 48:324–32.15. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:228–47.
Article16. National Cancer Institute. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE). Version 4.0. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health, US Department of Health and Human Services;2009.17. Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Warren MA, Golshayan AR, Sahi C, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:5794–9.
Article18. Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, et al. Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma : final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer. 2010; 116:4256–65.19. Dabydeen DA, Jagannathan JP, Ramaiya N, Krajewski K, Schutz FA, Cho DC, et al. Pneumonitis associated with mTOR inhibitors therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: incidence, radiographic findings and correlation with clinical outcome. Eur J Cancer. 2012; 48:1519–24.
Article20. Zama IN, Hutson TE, Elson P, Cleary JM, Choueiri TK, Heng DY, et al. Sunitinib rechallenge in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Cancer. 2010; 116:5400–6.
Article21. George S, Reichardt P, Lechner T, Li S, Cohen DP, Demetri GD. Hypertension as a potential biomarker of efficacy in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated with suni-tinib. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:3180–7.
Article22. White DA, Camus P, Endo M, Escudier B, Calvo E, Akaza H, et al. Noninfectious pneumonitis after everolimus therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 182:396–403.
Article23. Rini BI, Cohen DP, Lu DR, Chen I, Hariharan S, Gore ME, et al. Hypertension as a biomarker of efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011; 103:763–73.
Article24. Perez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA, Rowinsky EK, Huberman M, Karp D, et al. Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:3238–47.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Everolimus-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis in a Patient with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: a Case Report
- Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase on Endothelial Cells in an Orthotopic Tumor Model of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinorma
- Concomitant inhibition of epidermal growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Molecular Basis of Drug Resistance: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors
- Angiogenic Inhibitor Induced Complicated Reflux Esophagitis