Ewha Med J.
2013 Mar;36(1):58-61. 10.12771/emj.2013.36.1.58.
Angiogenic Inhibitor Induced Complicated Reflux Esophagitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. junghk@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2284016
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2013.36.1.58
Abstract
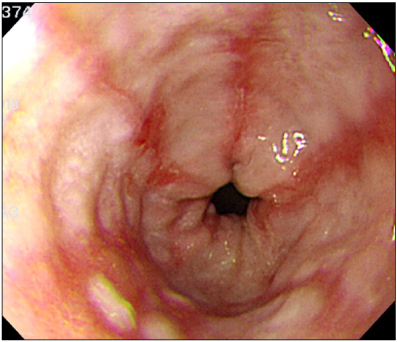
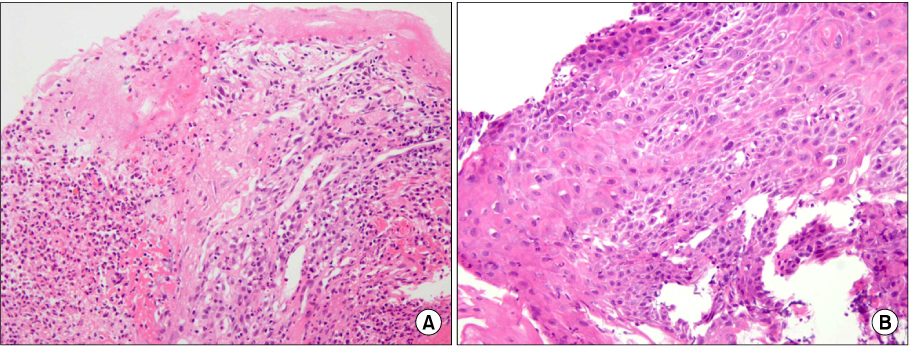
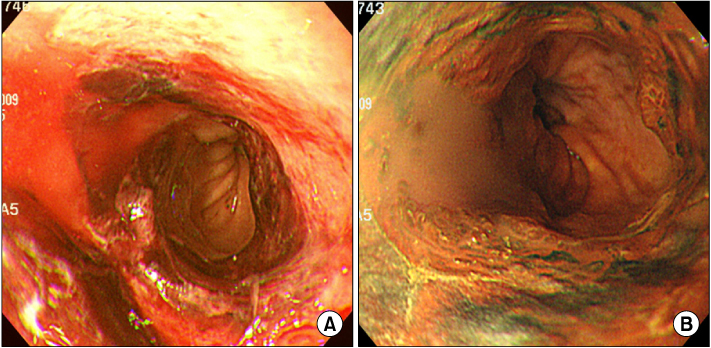
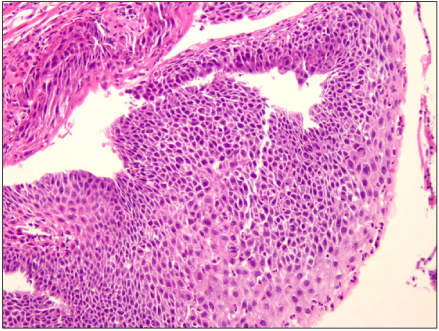
- Sunitinib an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, is highly effective against renal cell carcinoma and is now widely used in patients with metastatic disease. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is rarely reported as a side effect of sunitinib. We report two cases of GERD with upper gastrointestinal bleeding related to sunitinib administration. Both cases responded well to conservative management. Microscopic findings in both cases showed cellular atypia such as hyperchromasia, increases in nuclear size, and multinucleation. The cellular atypia of the squamous mucosa appears to be associated with reparative processes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chow LQ, Eckhardt SG. Sunitinib: from rational design to clinical efficacy. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:884–896.2. Atkins M, Jones CA, Kirkpatrick P. Sunitinib maleate. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006. 5:279–280.3. Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007. 356:115–124.4. Porta C, Paglino C, Imarisio I, Bonomi L. Uncovering. Clin Exp Med. 2007. 7:127–134.5. Di Lorenzo G, Buonerba C, Biglietto M, Scognamiglio F, Chiurazzi B, Riccardi F, et al. The therapy of kidney cancer with biomolecular drugs. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010. 36:Suppl 3. S16–S20.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiologic studies on gastroesophageal reflux
- Minimal Change Esophagitis
- Incidence of Esophagitis in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin-3-O-beta-D-Glucuronopyranoside on Gastritis and Reflux Esophagitis in Rats
- The Role of Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Reflux Esophagitis