Nat Prod Sci.
2017 Mar;23(1):61-68. 10.20307/nps.2017.23.1.61.
Anti-obesity Effect of Steamed Soybean and Fermented Steamed Soybean in High-fat Diet-induced Obese ICR Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. ejcho@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Food Science, Gyeongnam National University of Science and Technology, Jinju 52725, Korea. hykim@gntech.ac.kr
- KMID: 2376501
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2017.23.1.61
Abstract
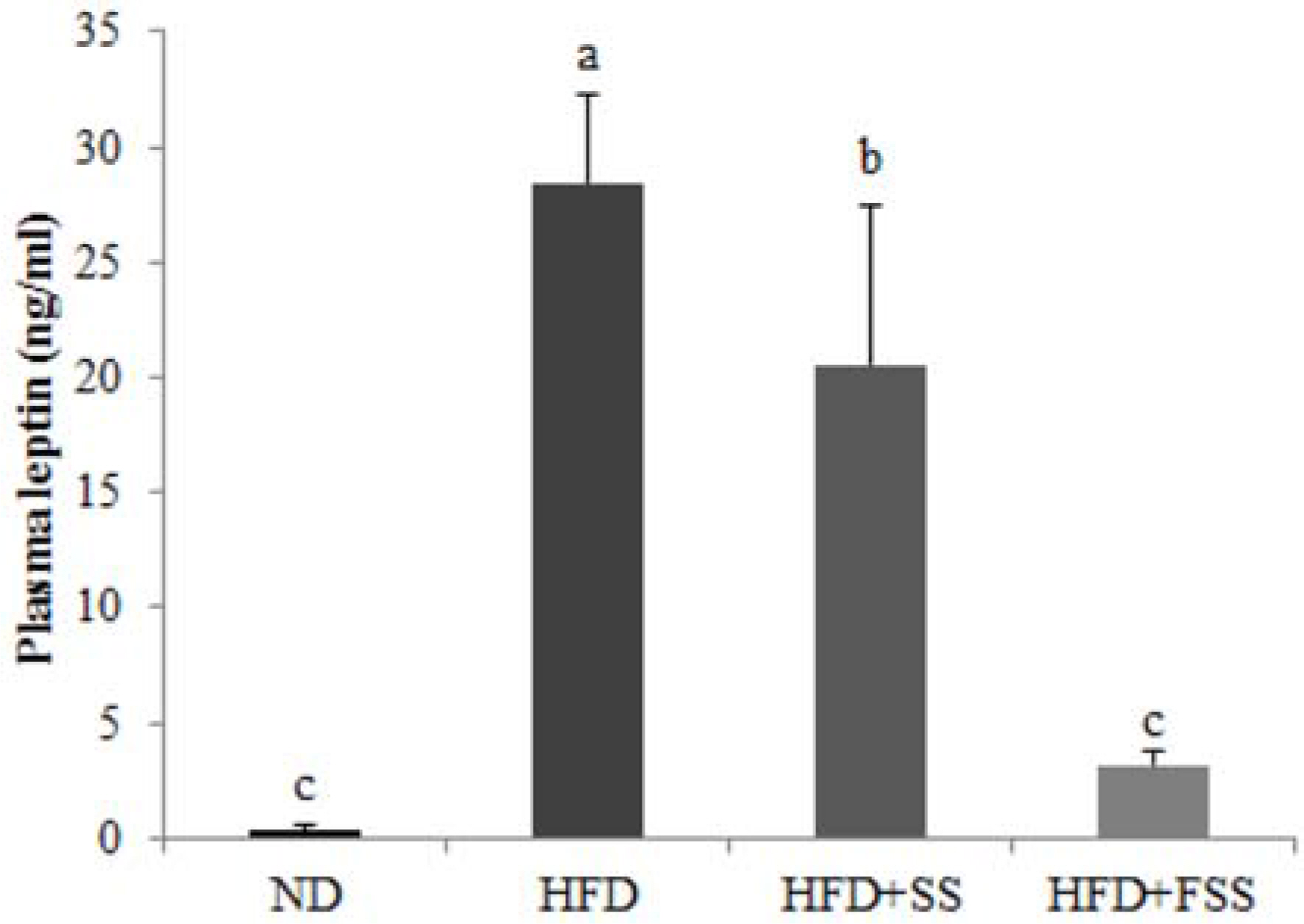
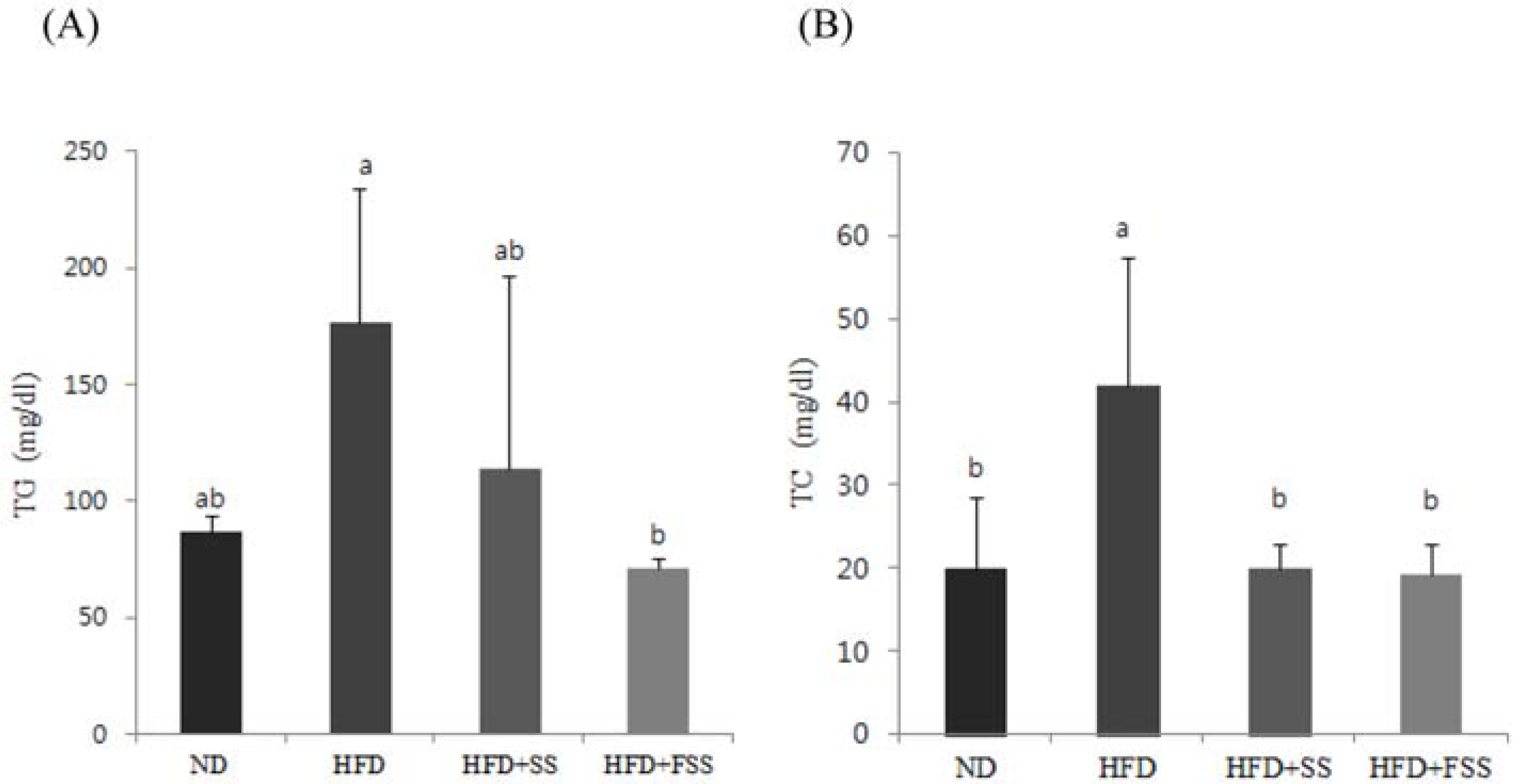
- This study was performed to investigate the ameliorating effects of steamed soybeans (SS) and fermented SS (FSS) on lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. ICR mice were divided into four groups and given the following different diets: normal diet (ND), high-fat diet (HFD), HFD with 1% SS (HFD + SS), and HFD with 1% FSS (HFD + FSS). After 14 weeks, the body weight gain was higher in the HFD group compared with the ND group but lower in the HFD + FSS group compared with the HFD group. Plasma levels of triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein-cholesterol, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were significantly higher in the HFD group compared to the ND group, but lower in the HFD + SS and HFD + FSS groups compared with the HFD group. In addition, leptin concentration in plasma was lower in the groups fed HFD + SS and HFD + FSS compared with the HFD group. The accumulation of hepatic TG and TC was significantly inhibited in the HFD + SS and HFD + FSS groups. Furthermore, SS and FSS attenuated lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide formation in the liver induced by the high-fat diet. These results suggest that soybeans, especially FSS, may be useful in preventing obesity-induced abnormalities in lipid metabolism.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alanine Transaminase
Animals
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Body Weight
Cholesterol
Diet
Diet, High-Fat
Leptin
Lipid Metabolism
Lipid Peroxidation
Liver
Mice
Mice, Inbred ICR*
Mice, Obese
Nitric Oxide
Obesity
Oxidative Stress
Plasma
Soybeans*
Steam*
Triglycerides
Alanine Transaminase
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Cholesterol
Leptin
Nitric Oxide
Steam
Figure
Reference
-
References
(1). Bae C. R.., Kwon D. Y.., Cha Y. S. J.Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014. 54:45–50.(2). de Almeida M. M.., de Souza Y. O.., Dutra Luquetti S. C.., Sabarense C. M.., do Amaral Corrêa J. O.., da Conceição E. P.., Lisboa P. C.., de Moura E. G.., Andrade Soares S. M.., Moura Gualberto A. C.., Gameiro J.., da Gama M. A.., Ferraz Lopes F. C.., González Garcia R. M. J.Oleo. Sci. 2015. 64:539–551.(3). Larsson B.., Björntorp P.., Tibblin G.Int. J. Obes. 1981. 5:97–116.(4). Amo K.., Arai H.., Uebanso T.., Fukaya M.., Koganei M.., Sasaki H.., Yamamoto H.., Taketani Y.., Takeda E. J.Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011. 49:1–7.(5). Reaven G. M.Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2000. 2:503–507.(6). Lei F.., Zhang X. N.., Wang W.., Xing D. M.., Xie W. D.., Su H.., Du L. J.Int. J. Obes. 2007. 31:1023–1029.(7). Ikeuchi M.., Koyama T.., Takahashi J.., Yazawa K.Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007. 71:893–899.(8). Lee Y. S.., Choi B. K.., Lee H. J.., Lee D. R.., Cheng J.., Lee W. K.., Yang S. H.., Suh J. W.AsianPac. J. Trop. Med. 2015. 8:276–282.(9). Mateos-Aparicio I.., Redondo-Cuenca A.., Villanueva-Suárez M. J.., Zapata-Revilla M. A.Nutr. Hosp. 2008. 23:305–312.(10). Liu K. S.In Soybeans: Chemistry, Technology and Utilization; Chapman and Hall, New York,. 1997. 442–447.(11). Craig W. J. J.Am. Diet. Assoc. 1997. 97:S199–S204.(12). Kwon D. Y.., Daily J. W. 3rd.., Kim H. J.., Park S.Nutr. Res. 2010. 30:1–13.(13). Cha Y. S.., Kim S. R.., Yang J. A.., Back H. I.., Kim M. G.., Jung S. J.., Song W. O.., Chae S. W.Nutr. Metab. 2013. 10:24.(14). Yoo K. M.Korean J. Food Nutr. 2011. 24:451–457.(15). Choi M.., Cho K.., Nam S. J.Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014. 43:243–249.(16). Folch J.., Lees M.., Stanley Stanley G. H. J.Biol. Chem. 1957. 226:497–509.(17). Uchiyama M.., Mihara M.Anal. Biochem. 1978. 86:271–278.(18). Sun J.., Zhang X.., Broderick M.., Fein H.Sensors. 2003. 3:276–284.(19). Elmarakby A. A.., Sullivan J. C.Cardiovasc. Ther. 2012. 30:49–59.
Article(20). Bondia-Pons I.., Ryan L.., Martinez J. A. J.Physiol. Biochem. 2012. 4:701–711.(21). Hill J. O.., Catenacci V.., Wyatt H. R.Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 2005. 28:1–23.(22). American Medical Association 2013. American Medical Association: AMA adopt new policies on second day of voting at Annual Meeting (obesity as a disease); Marketwired:. 2013.(23). Kim B.., Lee B. W.., Hwang C. E.., Lee Y. Y.., Lee C.., Kim B. J.., Park J. Y.., Sim E. Y.., Haque M. A.., Lee D. H.., Lee J. H.., Ahn, M J.., Lee H. Y.., Ko J. M.., Kim H. T.., Cho K. M.Kor. J. Microbiol. 2015. 51:231–240.(24). Abete N.American Journal of Medicine. 1999. 107:125–135.(25). Rader D. J.., Hovingh G. K.Lancet. 2014. 384:618–625.(26). Siebel A. L.., Heywood S. E.., Kingwell B. A.Front. Pharmacol. 2015. 6:258.(27). Kahn B. B.., Flier J. S. J.Clin. Invest. 2000. 106:473–481.(28). Lin S.., Thomas T. C.., Storlien L. H.., Huang X. F.Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000. 24:639–646.(29). Cano P. G.., Santacruz A.., Trejo F. M.., Sanz Y.Obesity. 2013. 21:2310–2321.(30). Xu Y.., Zhang M.., Wu T.., Dai S.., Xu J.., Zhou Z.Food Funct. 2015. 6:297–304.(31). Unger R. H.., Zhou Y. T.., Orci L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S.A. 1999. 96:2327–2332.(32). Van Steenbergen W.., Lanckmans S.Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1995. 19:S27–S36.
Article(33). Cohen B.., Novick D.., Rubinstein M.Science. 1996. 274:1185–1188.(34). Chitturi S.., Farrell G.., Frost L.., Kriketos A.., Lin R.., Fung C.., Liddle C.., Samarasinghe D.., George J.Hepatology. 2002. 36:403–409.(35). Sallie R.., Tredger J. M.., William R.Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1991. 12:251–259.(36). Yu X. X.., Murray S. F.., Pandey S. K.., Booten S. L.., Bao D.., Song X. Z.., Kelly S.., Chen S.., McKay R.., Monia B. P.., Bhanot S.Hepatology. 2005. 42:362–371.(37). Fernández-Sánchez A.., Madrigal-Santillán E.., Bautista M.., Esquivel-Soto J.., Morales-González Á.., Esquivel-Chirino C.., Durante-Montiel I.., Sánchez-Rivera G.., Valadez-Vega C.., Morales-González J. A.Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011. 12:3117–3132.(38). Furukawa S.., Fujita T.., Shimabukuro M.., Iwaki M.., Yamada Y.., Nakajima Y.., Makishima M.., Matsuda M.., Shimomura I. J.Clin. Invest. 2004. 114:1752–1761.(39). Milagro F. I.., Campión J.., Martínez J. A.Obesity. 2006. 14:1118–1123.(40). Oliveira C. P.., Coelho A. M.., Barbeiro H. V.., Lima V. M.., Soriano F.., Ribeiro C.., Molan N. A.., Alves V. A.., Souza H. P.., Machado M. C.., Carrilho F. J.Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2006. 39:189–194.(41). Vincent H. K.., Taylor A. G.Int. J. Obes. 2006. 30:400–418.(42). Katsube T.., Tamasaki M.., Shiwaku K.., Ishijima T.., Matsumoto I.., Abe K.., Yamasaki Y. J.Sci. Food Agric. 2010. 90:2386–2392.(43). Jung C. H.., Cho I.., Ahn J.., Jeon T. I.., Ha T. Y.Phytother. Res. 2013. 27:139–143.(44). Rege S. D.., Kumar S.., Wilson D. N.., Tamura L.., Geetha T.., Mathews S. T.., Huggins K. W.., Broderick T. L.., Babu J. R.Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013. 2013:1–7.(45). Ha S. K.., Chae C.Exp. Anim. 2010. 59:595–604.(46). Suzuki Y.., Kosaka M.., Shindo K.., Kawasumi T.., Kimoto-Nira H.., Suzuki C.Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013. 77:1299–1302.(47). Hwang C. E.., An M. J.., Lee H. Y.., Lee B. W.., Kim H. Y.., Ko J. M.., Baek I. Y.., Seo W. T.., Cho K. M.Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014. 46:556–565.(48). Izumi T.., Piskula M. K.., Osawa S.., Obata A.., Tobe K.., Saito M.., Kataoka S.., Kikuchi M. J.Nutr. 2000. 130:1695–1699.(49). Choi I.., Kim Y.., Park Y.., Seog H.., Choi H.Bio Factors. 2007. 29:105–112.(50). Terpstra A. H.., Javadi M.., Beynen A. C.., Kocsis S.., Lankhorst A. E.., Lemmens A. G.., Mohede I. C. J.Nutr. 2003. 133:3181–3186.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inhibitory effects of Doenjang, Korean traditional fermented soybean paste, on oxidative stress and inflammation in adipose tissue of mice fed a high-fat diet
- Cytotoxicity on Human Cancer Cells and Antitumorigenesis of Chungkookjang, a Fermented Soybean Product, in DMBA-Treated Rats
- Effect of fermented soybean curd residue (FSCR; SCR-meju) by aspergillus oryzae on the anti-obesity and lipids improvement
- The protective effects of steamed ginger on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and adiposity in diet-induced obese mice
- Effects of Resistance Exercise and Fermented Soybean Consumption on Glucose Tolerance and Expressions of Immune Senescence-Related Myokines in Middle-Aged Obese Rats