Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2016 Jul;20(4):387-397. 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.4.387.
Sequestration of sorcin by aberrant forms of tau results in the defective calcium homeostasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea. wchun@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2School of Pharmacy, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea.
- KMID: 2371056
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.4.387
Abstract
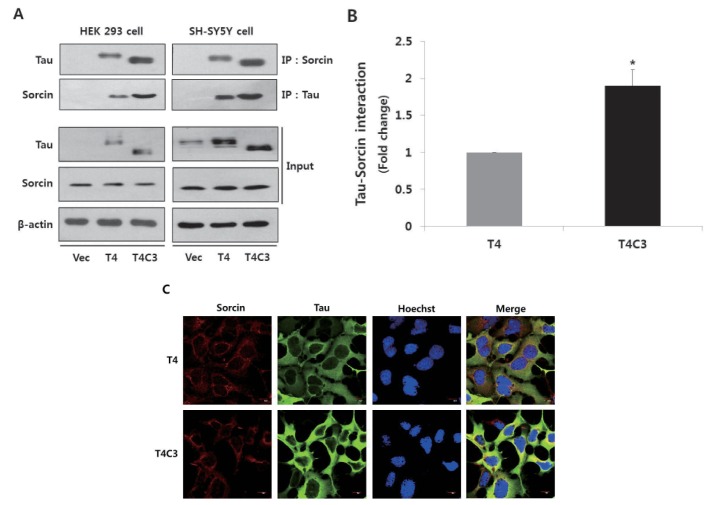
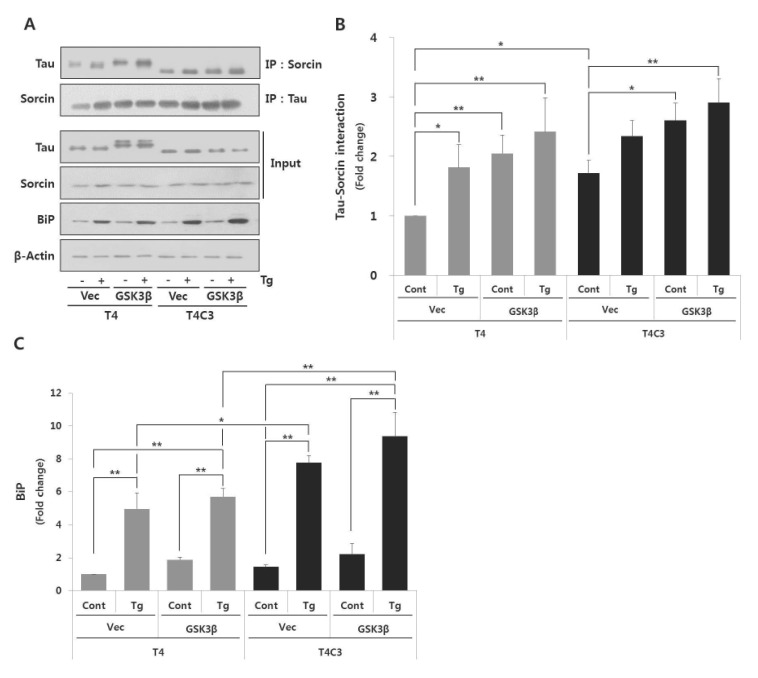
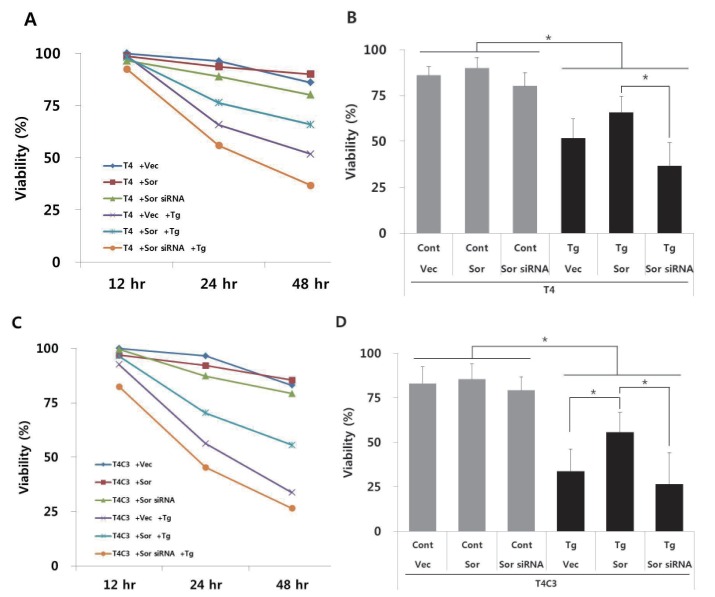
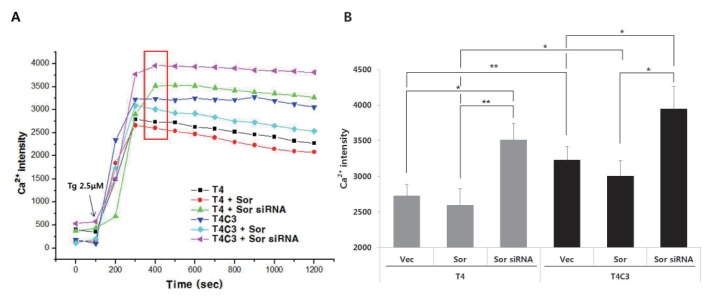
- Neurofi brillary tangles (NFTs) of microtubule-associated protein tau are a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been known to be involved in the pathogenesis of AD. However, the exact role of ER stress in tau pathology has not yet been clearly elucidated. In present study, the possible relationship between tau pathology and ER stress was examined in terms of sorcin, which is a calcium binding protein and plays an important role in calcium homeostasis. Our previous yeast two hybrid study showed that sorcin is a novel tau interacting protein. Caspase-3-cleaved tau (T4C3) showed significantly increased tau-sorcin interaction compared to wild type tau (T4). Thapsigargin-induced ER stress and co-expression of constitutively active GSK3β (GSK3β-S9A) also exhibited significantly increased tau-sorcin interactions. T4C3-expressing cells showed potentiated thapsigargin-induced apoptosis and disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis compared to T4-expressing cells. Overexpression of sorcin signifi cantly attenuated thapsigargin-induced apoptosis and disruption of calcium homeostasis. In contrary, siRNA-mediated knock-down of sorcin showed significantly increased thapsigargin-induced apoptosis and disruption of calcium homeostasis. These data strongly suggest that sequestration of sorcin by aberrant forms of tau compromises the function of sorcin, such as calcium homeostasis and cellular resistance by ER stress, which may consequently result in the contribution to the progression of AD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986; 83:4913–4917. PMID: 3088567.
Article2. Bré MH, Karsenti E. Effects of brain microtubule-associated proteins on microtubule dynamics and the nucleating activity of centrosomes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990; 15:88–98. PMID: 2107033.
Article3. Shahani N, Brandt R. Functions and malfunctions of the tau proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002; 59:1668–1680. PMID: 12475178.
Article4. Stoothoff WH, Johnson GV. Tau phosphorylation: physiological and pathological consequences. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005; 1739:280–297. PMID: 15615646.
Article5. Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Potier MC, Ulrich J, Crowther RA. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989; 8:393–399. PMID: 2498079.
Article6. Morishima-Kawashima M, Hasegawa M, Takio K, Suzuki M, Yoshida H, Titani K, Ihara Y. Proline-directed and non-proline-directed phosphorylation of PHF-tau. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270:823–829. PMID: 7822317.
Article7. Gamblin TC, Chen F, Zambrano A, Abraha A, Lagalwar S, Guillozet AL, Lu M, Fu Y, Garcia-Sierra F, LaPointe N, Miller R, Berry RW, Binder LI, Cryns VL. Caspase cleavage of tau: linking amyloid and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100:10032–10037. PMID: 12888622.
Article8. Kim SI, Lee WK, Kang SS, Lee SY, Jeong MJ, Lee HJ, Kim SS, Johnson GV, Chun W. Suppression of autophagy and activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta facilitate the aggregate formation of tau. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011; 15:107–114. PMID: 21660151.
Article9. LaFerla FM. Calcium dyshomeostasis and intracellular signalling in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002; 3:862–872. PMID: 12415294.
Article10. Katayama T, Imaizumi K, Manabe T, Hitomi J, Kudo T, Tohyama M. Induction of neuronal death by ER stress in Alzheimer's disease. J Chem Neuroanat. 2004; 28:67–78. PMID: 15363492.
Article11. Bezprozvanny I. Calcium signaling and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol Med. 2009; 15:89–100. PMID: 19230774.
Article12. Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Reed JC. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:2656–2664. PMID: 16200199.
Article13. Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC. Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7:1013–1030. PMID: 19043451.
Article14. Kapoor A, Sanyal AJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response. Clin Liver Dis. 2009; 13:581–590. PMID: 19818306.
Article15. Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L. ER stress and neurodege-nerative diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2006; 13:385–392. PMID: 16397584.
Article16. Ho YS, Yang X, Lau JC, Hung CH, Wuwongse S, Zhang Q, Wang J, Baum L, So KF, Chang RC. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces tau pathology and forms a vicious cycle: implication in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012; 28:839–854. PMID: 22101233.
Article17. Maki M, Kitaura Y, Satoh H, Ohkouchi S, Shibata H. Structures, functions and molecular evolution of the penta-EF-hand Ca2+-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002; 1600:51–60. PMID: 12445459.18. Colotti G, Poser E, Fiorillo A, Genovese I, Chiarini V, Ilari A. Sorcin, a calcium binding protein involved in the multidrug resistance mechanisms in cancer cells. Molecules. 2014; 19:13976–13989. PMID: 25197934.
Article19. Sohn JH. Identification of novel protein-protein interactions of wild type and caspase-3-truncated tau using yeast two hybrid assay [Thesis]. Kangwon: Kangwon National University;2012.20. Lalioti VS, Ilari A, O'Connell DJ, Poser E, Sandoval IV, Colotti G. Sorcin links calcium signaling to vesicle trafficking, regulates Polo-like kinase 1 and is necessary for mitosis. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e85438. PMID: 24427308.
Article21. Rissman RA, Poon WW, Blurton-Jones M, Oddo S, Torp R, Vitek MP, LaFerla FM, Rohn TT, Cotman CW. Caspase-cleavage of tau is an early event in Alzheimer disease tangle pathology. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:121–130. PMID: 15232619.
Article22. Kaufmann T, Schlipf S, Sanz J, Neubert K, Stein R, Borner C. Characterization of the signal that directs Bcl-x(L), but not Bcl-2, to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biol. 2003; 160:53–64. PMID: 12515824.
Article23. Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V, Stoica BA, Wang G, Iyer S, Smulson M. Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis. Caspase 3-resistant PARP mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:22932–22940. PMID: 10438458.24. Hetz C, Russelakis-Carneiro M, Maundrell K, Castilla J, Soto C. Caspase-12 and endoplasmic reticulum stress mediate neurotoxicity of pathological prion protein. EMBO J. 2003; 22:5435–5445. PMID: 14532116.
Article25. Quintanilla RA, Jin YN, Fuenzalida K, Bronfman M, Johnson GV. Rosiglitazone treatment prevents mitochondrial dysfunction in mutant huntingtin-expressing cells: possible role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) in the pathogenesis of Huntington disease. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:25628–25637. PMID: 18640979.26. Yu T, Robotham JL, Yoon Y. Increased production of reactive oxygen species in hyperglycemic conditions requires dynamic change of mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:2653–2658. PMID: 16477035.
Article27. Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ. Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986; 83:4044–4048. PMID: 2424016.
Article28. Cotman CW, Poon WW, Rissman RA, Blurton-Jones M. The role of caspase cleavage of tau in Alzheimer disease neuropathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005; 64:104–112. PMID: 15751224.
Article29. Kang HJ, Yoon WJ, Moon GJ, Kim DY, Sohn S, Kwon HJ, Gwag BJ. Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of PHF-1 tau during apoptosis irrespective of excitotoxicity and oxidative stress: an implication to Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2005; 18:450–458. PMID: 15755671.
Article30. Chan SL, Griffin WS, Mattson MP. Evidence for caspase-mediated cleavage of AMPA receptor subunits in neuronal apoptosis and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci Res. 1999; 57:315–323. PMID: 10412022.
Article31. Zilkova M, Zilka N, Kovac A, Kovacech B, Skrabana R, Skrabanova M, Novak M. Hyperphosphorylated truncated protein tau induces caspase-3 independent apoptosis-like pathway in the Alzheimer's disease cellular model. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011; 23:161–169. PMID: 20966551.
Article32. Fasulo L, Ugolini G, Visintin M, Bradbury A, Brancolini C, Verzillo V, Novak M, Cattaneo A. The neuronal microtubule-associated protein tau is a substrate for caspase-3 and an effector of apoptosis. J Neurochem. 2000; 75:624–633. PMID: 10899937.
Article33. Cho JH, Johnson GV. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta induces caspase-cleaved tau aggregation in situ. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:54716–54723. PMID: 15494420.34. Mella M, Colotti G, Zamparelli C, Verzili D, Ilari A, Chiancone E. Information transfer in the penta-EF-hand protein sorcin does not operate via the canonical structural/functional pairing. A study with site-specific mutants. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:24921–24928. PMID: 12711611.35. Zamparelli C, Ilari A, Verzili D, Giangiacomo L, Colotti G, Pascarella S, Chiancone E. Structure-function relationships in sorcin, a member of the penta EF-hand family. Interaction of sorcin fragments with the ryanodine receptor and an Escherichia coli model system. Biochemistry. 2000; 39:658–666. PMID: 10651630.
Article36. Zamparelli C, Macquaide N, Colotti G, Verzili D, Seidler T, Smith GL, Chiancone E. Activation of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger by sorcin via the interaction of the respective Ca2+-binding domains. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010; 49:132–141. PMID: 20298697.37. Matsumoto T, Hisamatsu Y, Ohkusa T, Inoue N, Sato T, Suzuki S, Ikeda Y, Matsuzaki M. Sorcin interacts with sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and modulates excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005; 100:250–262. PMID: 15754088.38. Seidler T, Miller SL, Loughrey CM, Kania A, Burow A, Kettlewell S, Teucher N, Wagner S, Kögler H, Meyers MB, Hasenfuss G, Smith GL. Effects of adenovirus-mediated sorcin overexpression on excitation-contraction coupling in isolated rabbit cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2003; 93:132–139. PMID: 12805242.
Article39. Maddalena F, Laudiero G, Piscazzi A, Secondo A, Scorziello A, Lombardi V, Matassa DS, Fersini A, Neri V, Esposito F, Landriscina M. Sorcin induces a drug-resistant phenotype in human colorectal cancer by modulating Ca2+ homeostasis. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:7659–7669. PMID: 22052463.40. Maddalena F, Sisinni L, Lettini G, Condelli V, Matassa DS, Piscazzi A, Amoroso MR, La Torre G, Esposito F, Landriscina M. Resistance to paclitxel in breast carcinoma cells requires a quality control of mitochondrial antiapoptotic proteins by TRAP1. Mol Oncol. 2013; 7:895–906. PMID: 23735188.
Article41. Pack-Chung E, Meyers MB, Pettingell WP, Moir RD, Brownawell AM, Cheng I, Tanzi RE, Kim TW. Presenilin 2 interacts with sorcin, a modulator of the ryanodine receptor. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:14440–14445. PMID: 10748169.
Article42. Woods WS, Boettcher JM, Zhou DH, Kloepper KD, Hartman KL, Ladror DT, Qi Z, Rienstra CM, George JM. Conformation-specific binding of alpha-synuclein to novel protein partners detected by phage display and NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:34555–34567. PMID: 17893145.43. Tanzi RE, Kovacs DM, Kim TW, Moir RD, Guenette SY, Wasco W. The gene defects responsible for familial Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 1996; 3:159–168. PMID: 8980016.44. Yokota O, Terada S, Ishizu H, Ujike H, Ishihara T, Nakashima H, Yasuda M, Kitamura Y, Uéda K, Checler F, Kuroda S. NACP/alpha-synuclein, NAC, and beta-amyloid pathology of familial Alzheimer's disease with the E184D presenilin-1 mutation: a clinicopathological study of two autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol. 2002; 104:637–648. PMID: 12410385.45. Jensen PH, Hager H, Nielsen MS, Hojrup P, Gliemann J, Jakes R. alpha-synuclein binds to Tau and stimulates the protein kinase A-catalyzed tau phosphorylation of serine residues 262 and 356. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:25481–25489. PMID: 10464279.