Ann Dermatol.
2014 Jun;26(3):363-373.
The Effect of Imiquimod on Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in Malignant Melanoma Cell Invasion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Yeouido Oracle Dermatology and Cosmetic Dermatosurgery Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Severance Hospital, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kychung@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Dermatology, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
A number of reports have been published regarding the use of imiquimod for the treatment of melanoma in situ and metastatic melanoma. Essential steps in the process of melanoma invasion and metastasis include degradation of basement membranes and remodeling of the extracellular matrix by proteolytic enzymes, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs).
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the antiinvasive effect of imiquimod in human malignant melanoma cell lines, SK-MEL-2 and SK-MEL-24, in vitro, and to investigate imiquimod-induced changes in the expression of MMPs and TIMPs.
METHODS
Invasiveness of melanoma cell lines following imiquimod treatment was evaluated by invasion assays. In order to investigate the mechanism of the anti-invasive effect of imiquimod, mRNA and protein levels of MMP-2, -9, membrane type 1 (MT1)-MMP, TIMP-1, and -2 were assessed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, gelatin zymography, and western blotting.
RESULTS
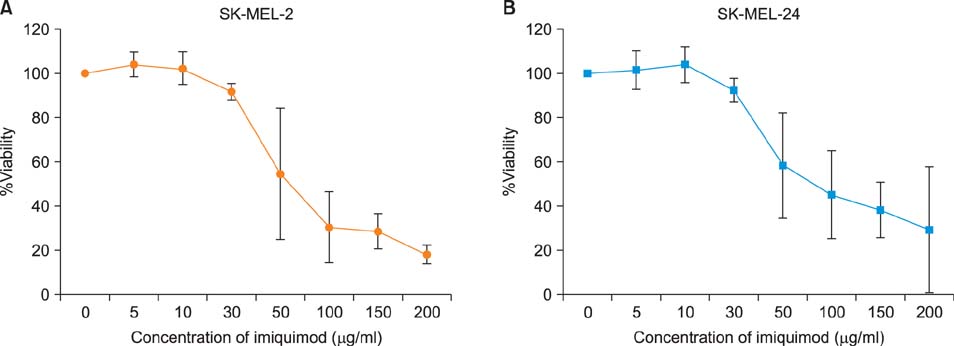
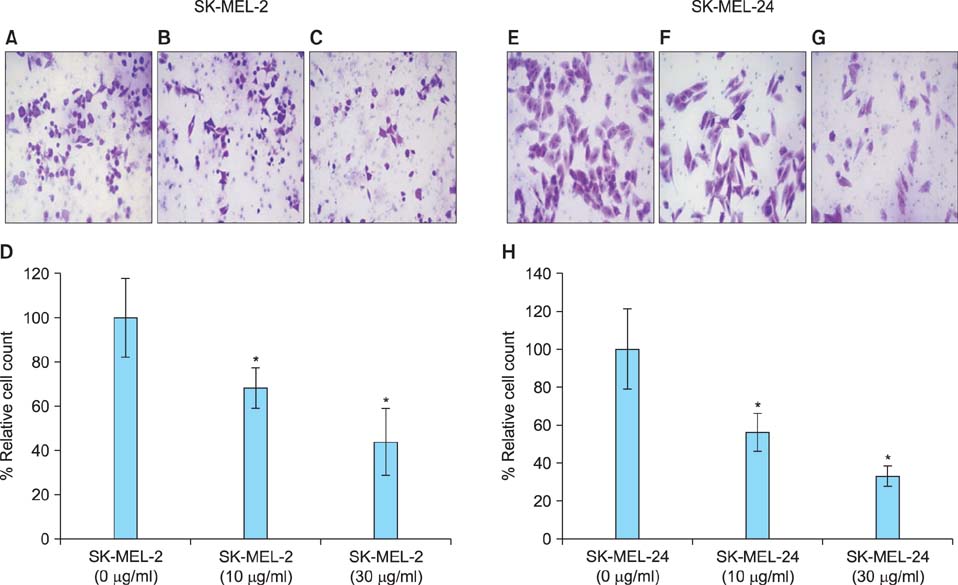
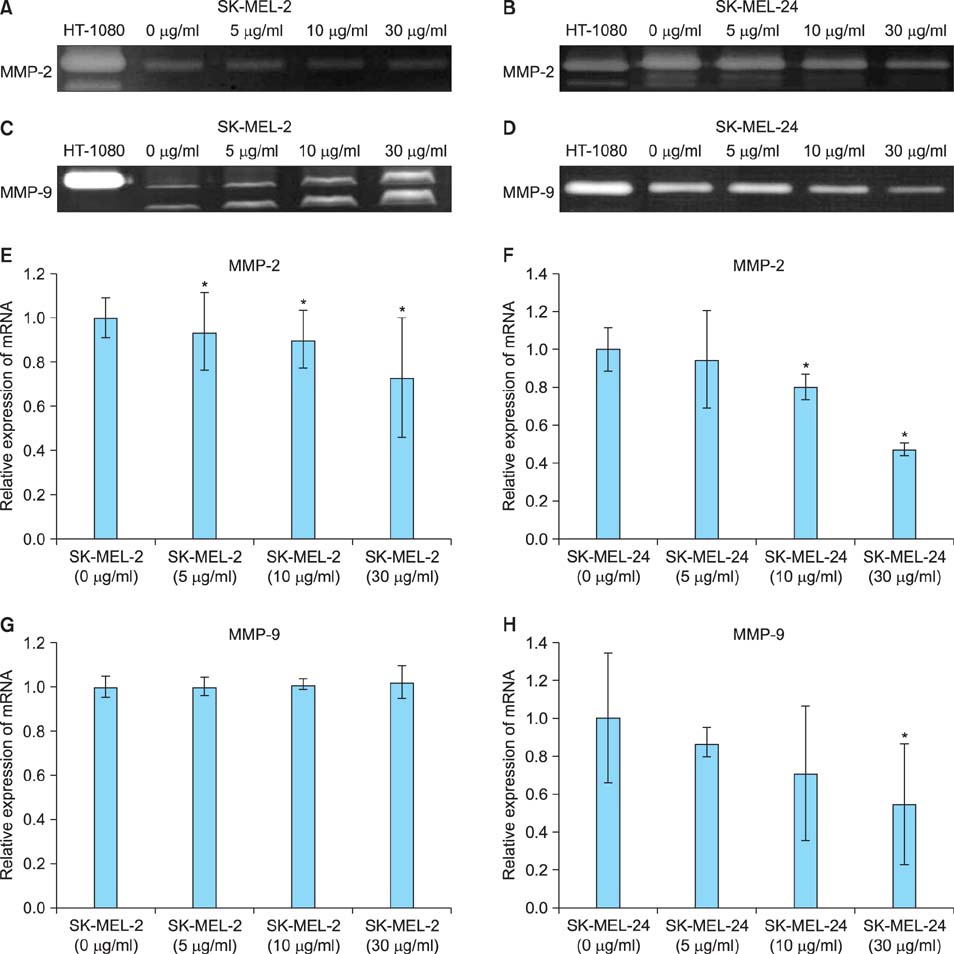
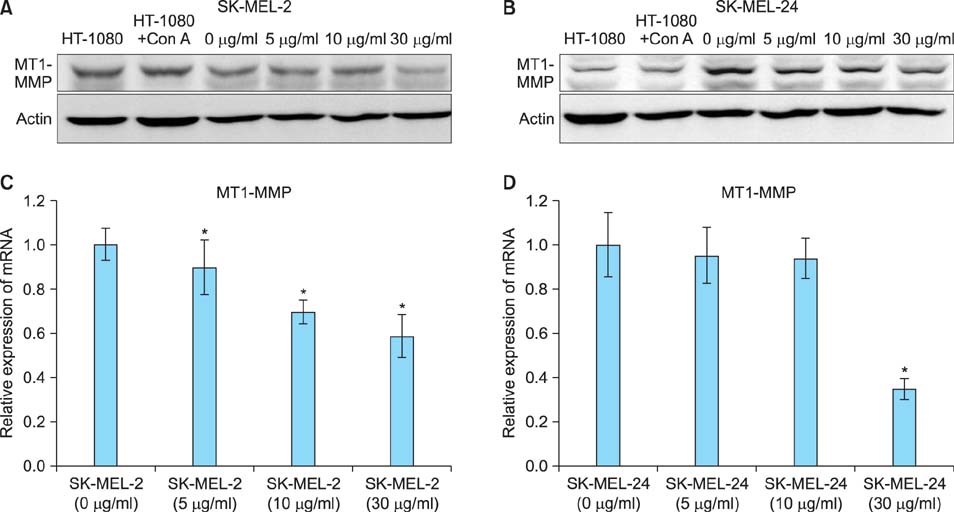
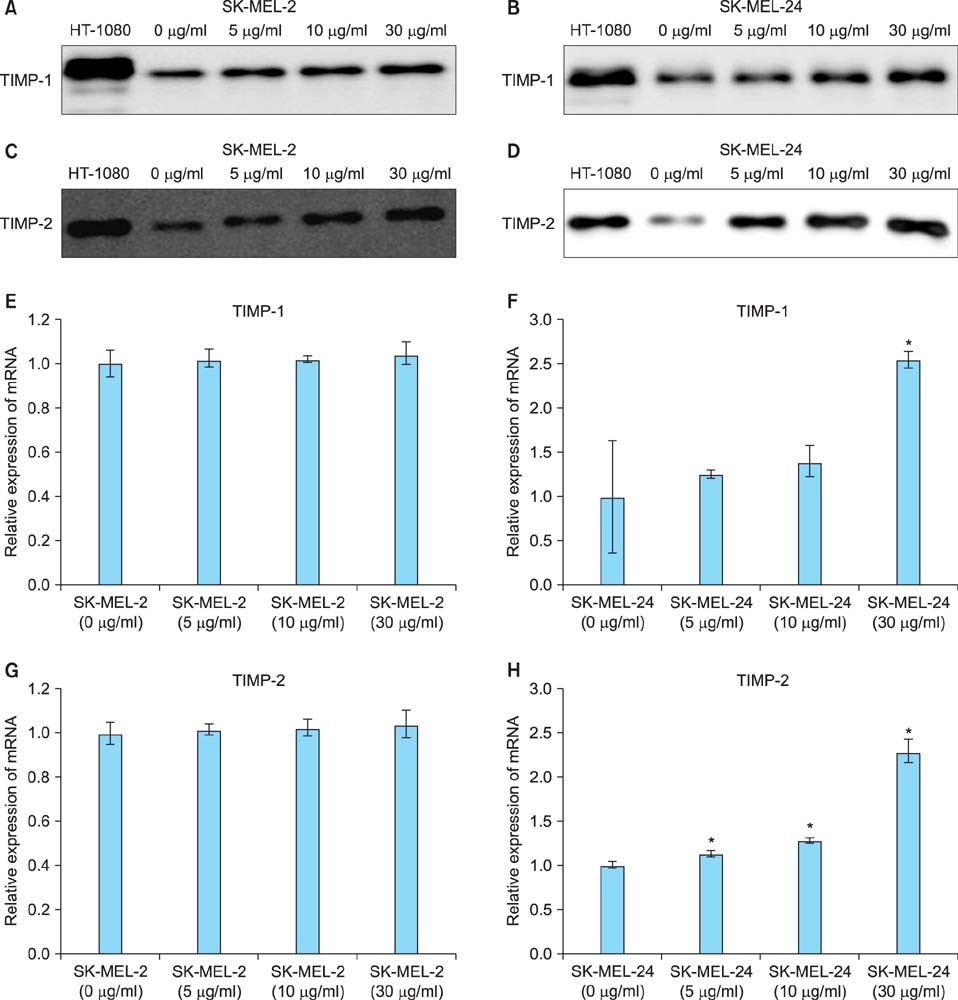
Imiquimod treatment decreased in vitro viability of melanoma cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Imiquimod also elicited a concentration-dependent suppression of invasion in both melanoma cell lines. A concentration-dependent decrease in MMP-2 and MT1-MMP protein levels and a concentration-dependent increase in TIMP-1 and -2 protein levels by imiquimod was observed in both melanoma cell lines. However, expression of MMP-9 protein was increased in SK-MEL-2 but decreased in SK-MEL-24 with increasing imiquimod concentrations. Imiquimod elicited alterations in MMPs and TIMPs mRNA levels that parallel the observed changes in protein levels.
CONCLUSION
Imiquimod may elicit an anti-invasive effect on human melanoma cells by regulating MMPs and TIMPs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Basement Membrane
Blotting, Western
Cell Line
Extracellular Matrix
Gelatin
Humans
Matrix Metalloproteinase 14
Matrix Metalloproteinases*
Melanoma*
Membranes
Metalloproteases*
Neoplasm Metastasis
Peptide Hydrolases
RNA, Messenger
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1
Gelatin
Matrix Metalloproteinase 14
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Metalloproteases
Peptide Hydrolases
RNA, Messenger
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1
Figure
Reference
-
1. van Meurs T, van Doorn R, Kirtschig G. Recurrence of lentigo maligna after initial complete response to treatment with 5% imiquimod cream. Dermatol Surg. 2007; 33:623–626.
Article2. Wolf IH, Cerroni L, Kodama K, Kerl H. Treatment of lentigo maligna (melanoma in situ) with the immune response modifier imiquimod. Arch Dermatol. 2005; 141:510–514.
Article3. Naylor MF, Crowson N, Kuwahara R, Teague K, Garcia C, Mackinnis C, et al. Treatment of lentigo maligna with topical imiquimod. Br J Dermatol. 2003; 149:Suppl 66. 66–70.
Article4. Cotter MA, McKenna JK, Bowen GM. Treatment of lentigo maligna with imiquimod before staged excision. Dermatol Surg. 2008; 34:147–151.
Article5. Woodmansee CS, McCall MW. Recurrence of lentigo maligna and development of invasive melanoma after treatment of lentigo maligna with imiquimod. Dermatol Surg. 2009; 35:1286–1289.
Article6. Hofmann UB, Westphal JR, Van Muijen GN, Ruiter DJ. Matrix metalloproteinases in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2000; 115:337–344.
Article7. Hesling C, DIncan M, Mansard S, Franck F, Corbin-Duval A, Chèvenet C, et al. In vivo and in situ modulation of the expression of genes involved in metastasis and angiogenesis in a patient treated with topical imiquimod for melanoma skin metastases. Br J Dermatol. 2004; 150:761–767.
Article8. Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Sanjo H, Hoshino K, et al. Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol. 2002; 3:196–200.
Article9. Schön M, Bong AB, Drewniok C, Herz J, Geilen CC, Reifenberger J, et al. Tumor-selective induction of apoptosis and the small-molecule immune response modifier imiquimod. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003; 95:1138–1149.
Article10. Stockfleth E, Trefzer U, Garcia-Bartels C, Wegner T, Schmook T, Sterry W. The use of Toll-like receptor-7 agonist in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma: an overview. Br J Dermatol. 2003; 149:Suppl 66. 53–56.
Article11. Schön MP, Wienrich BG, Drewniok C, Bong AB, Eberle J, Geilen CC, et al. Death receptor-independent apoptosis in malignant melanoma induced by the small-molecule immune response modifier imiquimod. J Invest Dermatol. 2004; 122:1266–1276.
Article12. Felding-Habermann B. Integrin adhesion receptors in tumor metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003; 20:203–213.13. Liotta LA, Rao CN, Wewer UM. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986; 55:1037–1057.
Article14. Brinckerhoff CE, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases: a tail of a frog that became a prince. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 3:207–214.
Article15. Sun J. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases are essential for the inflammatory response in cancer cells. J Signal Transduct. 2010; 2010:985132.
Article16. Gokaslan ZL, Chintala SK, York JE, Boyapati V, Jasti S, Sawaya R, et al. Expression and role of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human spinal column tumors. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1998; 16:721–728.17. Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. 2010; 141:52–67.
Article18. Visse R, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 2003; 92:827–839.19. Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Yoshiji H, Thorgeirsson UP. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur J Cell Biol. 1997; 74:111–122.20. Brew K, Dinakarpandian D, Nagase H. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: evolution, structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000; 1477:267–283.
Article21. Stetler-Stevenson WG, Seo DW. TIMP-2: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis. Trends Mol Med. 2005; 11:97–103.
Article22. Stetler-Stevenson WG, Liotta LA, Kleiner DE Jr. Extracellular matrix 6: role of matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. FASEB J. 1993; 7:1434–1441.
Article23. Hofmann UB, Houben R, Bröcker EB, Becker JC. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in melanoma cell invasion. Biochimie. 2005; 87:307–314.
Article24. Liotta LA, Tryggvason K, Garbisa S, Hart I, Foltz CM, Shafie S. Metastatic potential correlates with enzymatic degradation of basement membrane collagen. Nature. 1980; 284:67–68.
Article25. Strongin AY, Collier I, Bannikov G, Marmer BL, Grant GA, Goldberg GI. Mechanism of cell surface activation of 72-kDa type IV collagenase. Isolation of the activated form of the membrane metalloprotease. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270:5331–5338.26. Väisänen A, Tuominen H, Kallioinen M, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (72 kD type IV collagenase) expression occurs in the early stage of human melanocytic tumour progression and may have prognostic value. J Pathol. 1996; 180:283–289.
Article27. Väisänen A, Kallioinen M, Taskinen PJ, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T. Prognostic value of MMP-2 immunoreactive protein (72 kD type IV collagenase) in primary skin melanoma. J Pathol. 1998; 186:51–58.
Article28. Pyke C, Ralfkiaer E, Tryggvason K, Danø K. Messenger RNA for two type IV collagenases is located in stromal cells in human colon cancer. Am J Pathol. 1993; 142:359–365.29. Sakata K, Shigemasa K, Nagai N, Ohama K. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP) and their inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in common epithelial tumors of the ovary. Int J Oncol. 2000; 17:673–681.
Article30. van den Oord JJ, Paemen L, Opdenakker G, de Wolf-Peeters C. Expression of gelatinase B and the extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer EMMPRIN in benign and malignant pigment cell lesions of the skin. Am J Pathol. 1997; 151:665–670.31. MacDougall JR, Bani MR, Lin Y, Rak J, Kerbel RS. The 92-kDa gelatinase B is expressed by advanced stage melanoma cells: suppression by somatic cell hybridization with early stage melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:4174–4181.32. Hofmann UB, Eggert AA, Blass K, Bröcker EB, Becker JC. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases in the microenvironment of spontaneous and experimental melanoma metastases reflects the requirements for tumor formation. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:8221–8225.33. d'Ortho MP, Will H, Atkinson S, Butler G, Messent A, Gavrilovic J, et al. Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 2 exhibit broad-spectrum proteolytic capacities comparable to many matrix metalloproteinases. Eur J Biochem. 1997; 250:751–757.34. Deryugina EI, Soroceanu L, Strongin AY. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase stimulates human glioma xenograft growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2002; 62:580–588.35. Hotary K, Allen E, Punturieri A, Yana I, Weiss SJ. Regulation of cell invasion and morphogenesis in a three-dimensional type I collagen matrix by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, and 3. J Cell Biol. 2000; 149:1309–1323.
Article36. Iida J, Wilhelmson KL, Price MA, Wilson CM, Pei D, Furcht LT, et al. Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase promotes human melanoma invasion and growth. J Invest Dermatol. 2004; 122:167–176.
Article37. Butler GS, Butler MJ, Atkinson SJ, Will H, Tamura T, Schade van Westrum S, et al. The TIMP2 membrane type 1 metalloproteinase "receptor" regulates the concentration and efficient activation of progelatinase A. A kinetic study. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:871–880.
Article38. Hofmann UB, Westphal JR, Zendman AJ, Becker JC, Ruiter DJ, van Muijen GN. Expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and its co-localization with membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) correlate with melanoma progression. J Pathol. 2000; 191:245–256.
Article39. Stetler-Stevenson WG. The tumor microenvironment: regulation by MMP-independent effects of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008; 27:57–66.
Article40. Itoh Y, Takamura A, Ito N, Maru Y, Sato H, Suenaga N, et al. Homophilic complex formation of MT1-MMP facilitates pro-MMP-2 activation on the cell surface and promotes tumor cell invasion. EMBO J. 2001; 20:4782–4793.
Article41. Henriet P, Blavier L, Declerck YA. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in invasion and proliferation. APMIS. 1999; 107:111–119.
Article42. Montgomery AM, Mueller BM, Reisfeld RA, Taylor SM, DeClerck YA. Effect of tissue inhibitor of the matrix metalloproteinases-2 expression on the growth and spontaneous metastasis of a human melanoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1994; 54:5467–5473.43. Khokha R. Suppression of the tumorigenic and metastatic abilities of murine B16-F10 melanoma cells in vivo by the overexpression of the tissue inhibitor of the metalloproteinases-1. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994; 86:299–304.
Article44. Finan KM, Hodge G, Reynolds AM, Hodge S, Holmes MD, Baker AH, et al. In vitro susceptibility to the pro-apoptotic effects of TIMP-3 gene delivery translates to greater in vivo efficacy versus gene delivery for TIMPs-1 or -2. Lung Cancer. 2006; 53:273–284.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Its Inhibitor in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
- Clinical Significance of Tissue Levels of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in Gastric Cancer
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase and Tissue Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Malignant Lymphoma
- Immunodetections of Metalloproteinase-2 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2 in the Uterine Endometrium
- The effect of periodontal flap surgery on Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and Tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) levels in gingival crevicular fluids of periodontitis patients