J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Apr;31(4):525-534. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.525.
Type 2 Diabetes Induces Prolonged P-wave Duration without Left Atrial Enlargement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Shenjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China. shengjinglxd@126.com
- KMID: 2363690
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.525
Abstract
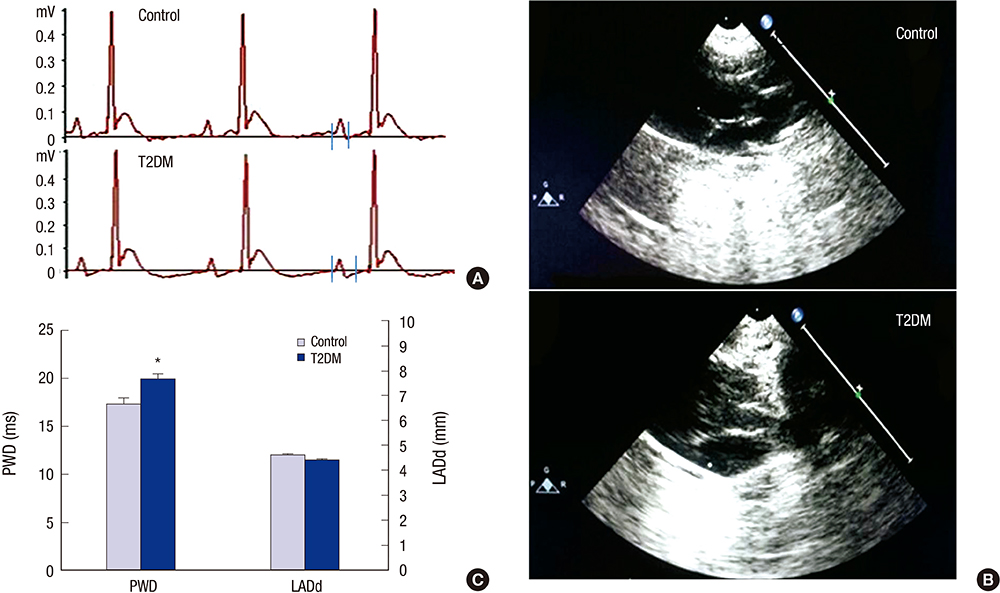
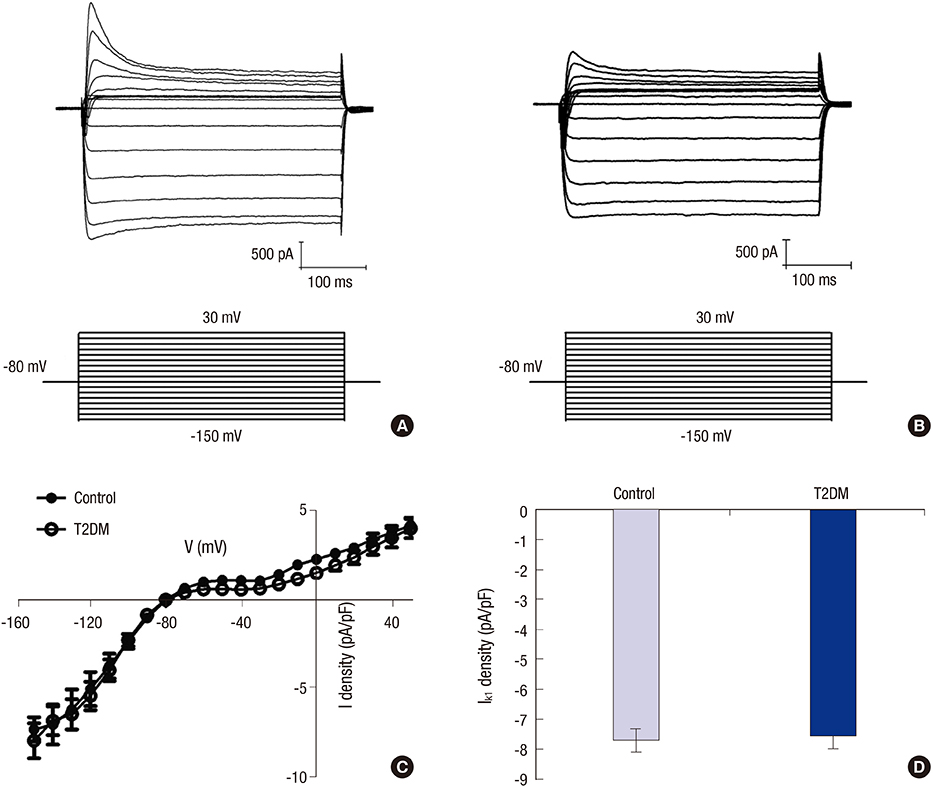
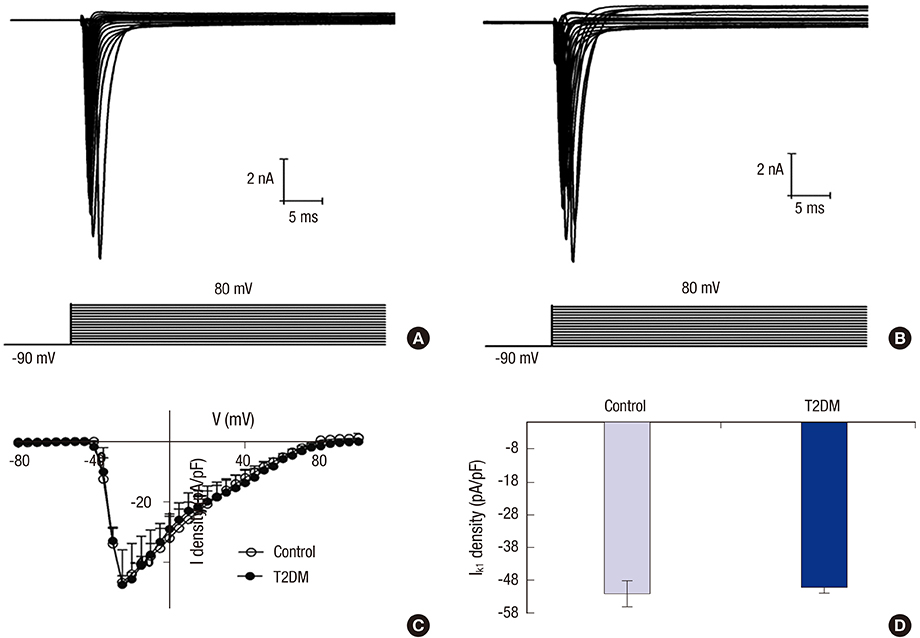
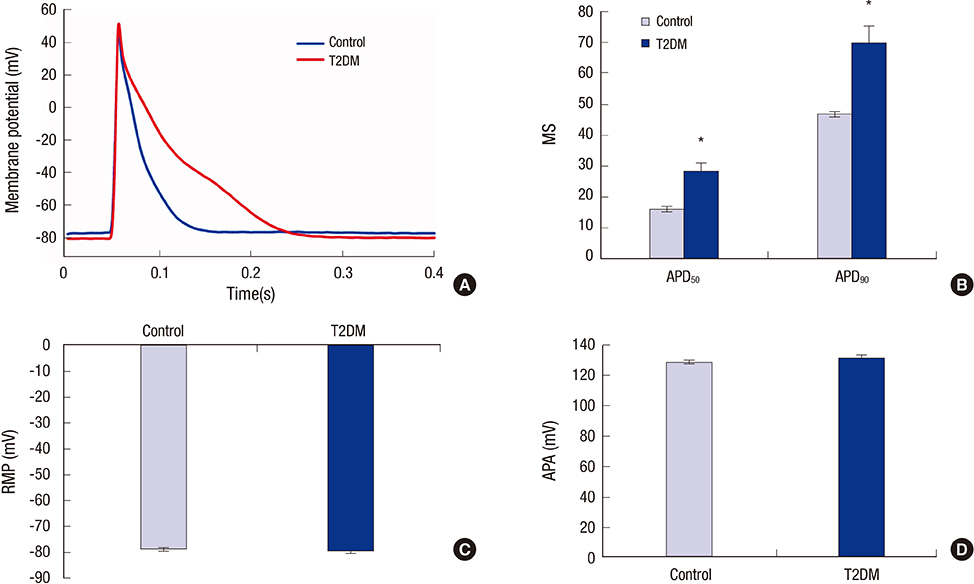
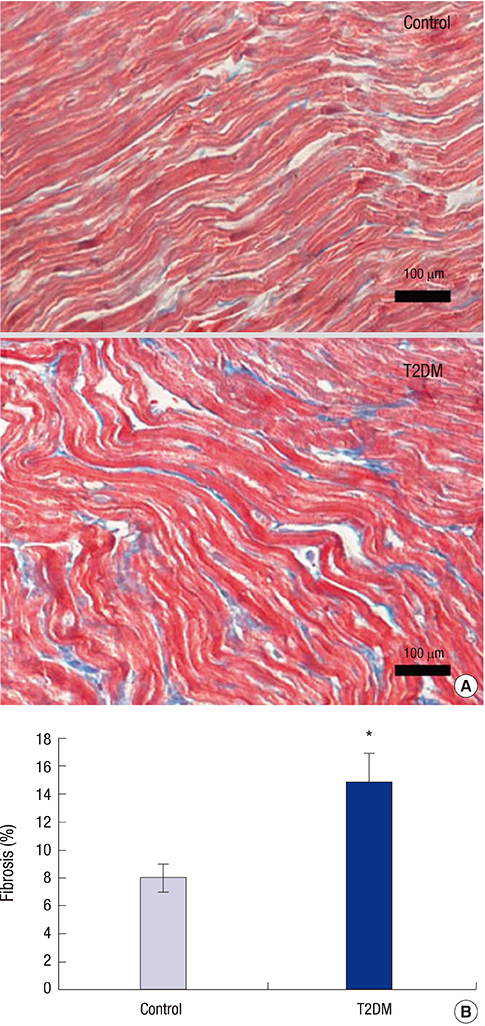
- Prolonged P-wave duration has been observed in diabetes. However, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The aim of this study was to elucidate the possible mechanisms. A rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) was used. P-wave durations were obtained using surface electrocardiography and sizes of the left atrium were determined using echocardiography. Cardiac inward rectifier K+ currents (I(k1)), Na+ currents (I(Na)), and action potentials were recorded from isolated left atrial myocytes using patch clamp techniques. Left atrial tissue specimens were analyzed for total connexin-40 (Cx40) and connexin-43 (Cx43) expression levels on western-blots. Specimens were also analyzed for Cx40 and Cx43 distribution and interstitial fibrosis by immunofluorescent and Masson trichrome staining, respectively. The mean P-wave duration was longer in T2DM rats than in controls; however, the mean left atrial sizes of each group of rats were similar. The densities of I(k1) and I(Na) were unchanged in T2DM rats compared to controls. The action potential duration was longer in T2DM rats, but there was no significant difference in resting membrane potential or action potential amplitude compared to controls. The expression level of Cx40 protein was significantly lower, but Cx43 was unaltered in T2DM rats. However, immunofluorescent labeling of Cx43 showed a significantly enhanced lateralization. Staining showed interstitial fibrosis was greater in T2DM atrial tissue. Prolonged P-wave duration is not dependent on the left atrial size in rats with T2DM. Dysregulation of Cx40 and Cx43 protein expression, as well as fibrosis, might partly account for the prolongation of P-wave duration in T2DM.
MeSH Terms
-
Action Potentials
Animals
Blotting, Western
Connexin 43/metabolism
Connexins/metabolism
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/*physiopathology
Disease Models, Animal
Echocardiography
Electrocardiography
Fibrosis/pathology
Heart Atria/*diagnostic imaging/physiopathology
In Vitro Techniques
Male
Membrane Potentials
Microscopy, Fluorescence
Patch-Clamp Techniques
Potassium Channels/metabolism
Rats
Rats, Wistar
Connexin 43
Connexins
Potassium Channels
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huxley RR, Filion KB, Konety S, Alonso A. Meta-analysis of cohort and case-control studies of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2011; 108:56–62.2. Yazici M, Ozdemir K, Altunkeser BB, Kayrak M, Duzenli MA, Vatankulu MA, Soylu A, Ulgen MS. The effect of diabetes mellitus on the P-wave dispersion. Circ J. 2007; 71:880–883.3. Ariyarajah V, Mercado K, Apiyasawat S, Puri P, Spodick DH. Correlation of left atrial size with p-wave duration in interatrial block. Chest. 2005; 128:2615–2618.4. Dagli N, Karaca I, Yavuzkir M, Balin M, Arslan N. Are maximum P wave duration and P wave dispersion a marker of target organ damage in the hypertensive population? Clin Res Cardiol. 2008; 97:98–104.5. Goyal SB, Spodick DH. Electromechanical dysfunction of the left atrium associated with interatrial block. Am Heart J. 2001; 142:823–827.6. Soliman EZ, Prineas RJ, Case LD, Zhang ZM, Goff DC Jr. Ethnic distribution of ECG predictors of atrial fibrillation and its impact on understanding the ethnic distribution of ischemic stroke in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Stroke. 2009; 40:1204–1211.7. Magnani JW, Johnson VM, Sullivan LM, Gorodeski EZ, Schnabel RB, Lubitz SA, Levy D, Ellinor PT, Benjamin EJ. P wave duration and risk of longitudinal atrial fibrillation in persons ≥ 60 years old (from the Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 2011; 107:917–921.8. Watanabe M, Yokoshiki H, Mitsuyama H, Mizukami K, Ono T, Tsutsui H. Conduction and refractory disorders in the diabetic atrium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012; 303:H86–95.9. Shimoni Y, Firek L, Severson D, Giles W. Short-term diabetes alters K+ currents in rat ventricular myocytes. Circ Res. 1994; 74:620–628.10. Pacher P, Ungvári Z, Nánási PP, Kecskeméti V. Electrophysiological changes in rat ventricular and atrial myocardium at different stages of experimental diabetes. Acta Physiol Scand. 1999; 166:7–13.11. Chen J, Li Q, Dong R, Gao H, Peng H, Wu Y. The effect of the Ras homolog gene family (Rho), member A/Rho associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase pathway in atrial fibrosis of type 2 diabetes in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 8:836–840.12. Wang L, Sun L, Zhang Y, Wu H, Li C, Pan Z, Lu Y, Yang B. Ionic mechanisms underlying action potential prolongation by focal cerebral ischemia in rat ventricular myocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2009; 23:305–316.13. Spodick DH. Unappreciated prevalence of interatrial block and associated consequences: a poorly perceived pandemic. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004; 79:668–670.14. Maeno K, Kasai T, Kasagi S, Kawana F, Ishiwata S, Ohno M, Yamaguchi T, Narui K. Relationship between atrial conduction delay and obstructive sleep apnea. Heart Vessels. 2013; 28:639–645.15. Yoon N, Cho JG, Kim KH, Park KH, Sim DS, Yoon HJ, Hong YJ, Park HW, Kim JH, Ahn Y, et al. Beneficial effects of an angiotensin-II receptor blocker on structural atrial reverse-remodeling in a rat model of ischemic heart failure. Exp Ther Med. 2013; 5:1009–1016.16. Bond RC, Choisy SC, Bryant SM, Hancox JC, James AF. Inhibition of a TREK-like K+ channel current by noradrenaline requires both beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptors in rat atrial myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2014; 104:206–215.17. Saffitz JE, Douglas P. Zipes Lecture. Biology and pathobiology of cardiac connexins: from cell to bedside. Heart Rhythm. 2006; 3:102–107.18. King JH, Huang CL, Fraser JA. Determinants of myocardial conduction velocity: implications for arrhythmogenesis. Front Physiol. 2013; 4:154.19. Munuswamy K, Alpert MA, Martin RH, Whiting RB, Mechlin NJ. Sensitivity and specificity of commonly used electrocardiographic criteria for left atrial enlargement determined by M-mode echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 1984; 53:829–832.20. Nichols CG, Makhina EN, Pearson WL, Sha Q, Lopatin AN. Inward rectification and implications for cardiac excitability. Circ Res. 1996; 78:1–7.21. Stables CL, Musa H, Mitra A, Bhushal S, Deo M, Guerrero-Serna G, Mironov S, Zarzoso M, Vikstrom KL, Cawthorn W, et al. Reduced Na(+) current density underlies impaired propagation in the diabetic rabbit ventricle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014; 69:24–31.22. Wiegerinck RF, Verkerk AO, Belterman CN, van Veen TA, Baartscheer A, Opthof T, Wilders R, de Bakker JM, Coronel R. Larger cell size in rabbits with heart failure increases myocardial conduction velocity and QRS duration. Circulation. 2006; 113:806–813.23. Spach MS, Heidlage JF, Barr RC, Dolber PC. Cell size and communication: role in structural and electrical development and remodeling of the heart. Heart Rhythm. 2004; 1:500–515.24. Nygren A, Olson ML, Chen KY, Emmett T, Kargacin G, Shimoni Y. Propagation of the cardiac impulse in the diabetic rat heart: reduced conduction reserve. J Physiol. 2007; 580:543–560.25. Gros D, Jarry-Guichard T, Ten Velde I, de Maziere A, van Kempen MJ, Davoust J, Briand JP, Moorman AF, Jongsma HJ. Restricted distribution of connexin40, a gap junctional protein, in mammalian heart. Circ Res. 1994; 74:839–851.26. Gourdie RG, Green CR, Severs NJ, Anderson RH, Thompson RP. Evidence for a distinct gap-junctional phenotype in ventricular conduction tissues of the developing and mature avian heart. Circ Res. 1993; 72:278–289.27. Delorme B, Dahl E, Jarry-Guichard T, Marics I, Briand JP, Willecke K, Gros D, Théveniau-Ruissy M. Developmental regulation of connexin 40 gene expression in mouse heart correlates with the differentiation of the conduction system. Dev Dyn. 1995; 204:358–371.28. Bagwe S, Berenfeld O, Vaidya D, Morley GE, Jalife J. Altered right atrial excitation and propagation in connexin40 knockout mice. Circulation. 2005; 112:2245–2253.29. Huo Y, Mitrofanova L, Orshanskaya V, Holmberg P, Holmqvist F, Platonov PG. P-wave characteristics and histological atrial abnormality. J Electrocardiol. 2014; 47:275–280.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Left Atrial Enlargement: Echocardiographic Assessment of Electrocardiographic Criteria
- Atrial Fibrillation in a Patient with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy after Induction of General Anesthesia: A case report
- Plain chest PA evaluation of left atrial thrombosis in mitral valvular disease
- Atrial Rhythms in Patients with Left Atrial Isomerism
- Comparison of Prolonged Atrial Electromechanical Delays with Different Definitions in the Discrimination of Patients with Non-Valvular Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation