Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Jun;8(2):123-128. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.2.123.
Increase in the Level of Proinflammatory Cytokine HMGB1 in Nasal Fluids of Patients With Rhinitis and its Sequestration by Glycyrrhizin Induces Eosinophil Cell Death
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Sciences, Section of Clinical Pharmacology and Oncology, University of Florence, Firenze, Italy. leonardo.cavone@unifi.it
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Unit of Genetic and Immunology, University of Messina, Messina, Italy.
- KMID: 2360782
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.2.123
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The nuclear protein high mobility group protein box 1 (HMGB1) is a proinflammatory mediator that belongs to the alarmin family of proinflammatory mediators, and it has recently emerged as a key player in different acute and chronic immune disorders. Several lines of evidence demonstrate that HMGB1 is actively released extracellularly from immune cells or passively released from necrotic cells. Because of the ability of HMGB1 to sustain chronic inflammation, we investigated whether the protein is present in nasal fluids of patients with different forms of rhinitis.
METHODS
HMGB1 levels were evaluated in nasal fluids of healthy subjects or rhinitis patients who were treated or not treated with different treatments.
RESULTS
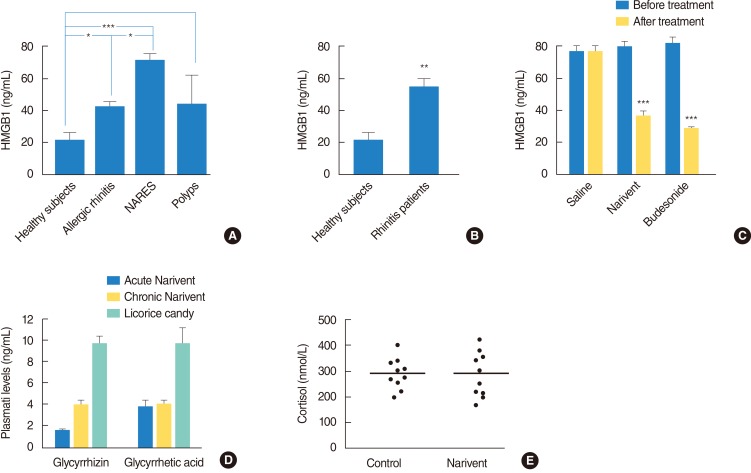
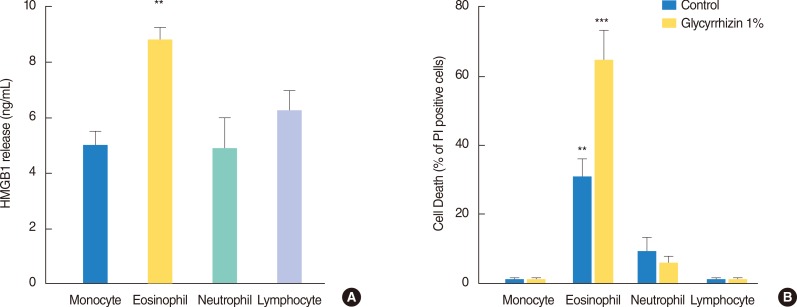
We report that the level of HMGB1 was significantly increased in nasal fluids of patients with allergic rhinitis, patients with NARES (nonallergic rhinitis with eosinophiliac syndrome), as well as patients with polyps. We also found that a formulation containing the HMGB1-binding compound glycyrrhizin (GLT) reduced the HMGB1 content in nasal fluids of rhinitis patients to an extent similar to that with nasal budesonide treatment. We also found that among the cultured human leukocyte populations, eosinophils released higher amounts of HMGB1. Based on the ability of HMGB1 to sustain eosinophil survival and the ability of GLT to inactivate HMGB1, we report that GLT selectively killed cultured eosinophils and had no effect on neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes.
CONCLUSION
Collectively, these data underscore the role of HMGB1 in rhinitis pathogenesis and the therapeutic potential of GLT formulations in treatment of chronic inflammatory disorders of the nasal mucosa.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pallier C, Scaffidi P, Chopineau-Proust S, Agresti A, Nordmann P, Bianchi ME, et al. Association of chromatin proteins high mobility group box (HMGB) 1 and HMGB2 with mitotic chromosomes. Mol Biol Cell. 2003; 8. 14(8):3414–3426. PMID: 12925773.
Article2. Ulloa L, Messmer D. High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein: friend and foe. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006; 6. 17(3):189–201. PMID: 16513409.
Article3. Yang H, Wang H, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ. HMGB1 as a cytokine and therapeutic target. J Endotoxin Res. 2002; 8(6):469–472. PMID: 12697092.
Article4. Rouhiainen A, Tumova S, Valmu L, Kalkkinen N, Rauvala H. Pivotal advance: analysis of proinflammatory activity of highly purified eukaryotic recombinant HMGB1 (amphoterin). J Leukoc Biol. 2007; 1. 81(1):49–58. PMID: 16980512.5. Cavone L, Muzzi M, Mencucci R, Sparatore B, Pedrazzi M, Moroni F, et al. 18β-glycyrrhetic acid inhibits immune activation triggered by HMGB1, a pro-inflammatory protein found in the tear fluid during conjunctivitis and blepharitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2011; 6. 19(3):180–185. PMID: 21426233.
Article6. Dumitriu IE, Baruah P, Manfredi AA, Bianchi ME, Rovere-Querini P. HMGB1: guiding immunity from within. Trends Immunol. 2005; 7. 26(7):381–387. PMID: 15978523.
Article7. Bianchi ME, Manfredi AA. Immunology: dangers in and out. Science. 2009; 3. 323(5922):1683–1684. PMID: 19325105.8. Lotze MT, Tracey KJ. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005; 4. 5(4):331–342. PMID: 15803152.
Article9. Agnello D, Wang H, Yang H, Tracey KJ, Ghezzi P. HMGB-1, a DNA-binding protein with cytokine activity, induces brain TNF and IL-6 production, and mediates anorexia and taste aversion. Cytokine. 2002; 5. 18(4):231–236. PMID: 12126646.
Article10. Mollica L, De Marchis F, Spitaleri A, Dallacosta C, Pennacchini D, Zamai M, et al. Glycyrrhizin binds to high-mobility group box 1 protein and inhibits its cytokine activities. Chem Biol. 2007; 4. 14(4):431–441. PMID: 17462578.
Article11. Fulkerson PC, Rothenberg ME. Targeting eosinophils in allergy, inflammation and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013; 2. 12(2):117–129. PMID: 23334207.
Article12. Salpietro C, Cuppari C, Grasso L, Tosca MA, Miraglia Del Giudice M, La Rosa M, et al. Nasal high-mobility group box-1 protein in children with allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013; 161(2):116–121. PMID: 23343652.
Article13. Pittelli M, Felici R, Pitozzi V, Giovannelli L, Bigagli E, Cialdai F, et al. Pharmacological effects of exogenous NAD on mitochondrial bioenergetics, DNA repair, and apoptosis. Mol Pharmacol. 2011; 12. 80(6):1136–1146. PMID: 21917911.
Article14. Lapucci A, Pittelli M, Rapizzi E, Felici R, Moroni F, Chiarugi A. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 is a nuclear epigenetic regulator of mitochondrial DNA repair and transcription. Mol Pharmacol. 2011; 6. 79(6):932–940. PMID: 21441600.15. Damiani V, Camaioni A, Viti C, Scire AS, Morpurgo G, Gregori D. A single-centre, before-after study of the short- and long-term efficacy of Narivent(®) in the treatment of nasal congestion. J Int Med Res. 2012; 40(5):1931–1941. PMID: 23206477.
Article16. Olukoga A, Donaldson D. Liquorice and its health implications. J R Soc Promot Health. 2000; 6. 120(2):83–89. PMID: 10944880.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extracellular HMGB1 Released after Zinc-treatment Induces Neuronal Death in Primary Cortical Cultures
- Clinical Value of Eosinophil Cationic Protein Level in Nasal Secretion of Allergic Rhinitis Patients
- The diagnostic usefulness and correlation of nasal eosinophil count and percentage in children with rhinitis
- Diagnostic Value of Eosinophil Cationic Protein (ECP) in Nasal Secretion of Allergic Rhinitis
- Nasal eosinophilia and eosinophil peroxidase in children and adolescents with rhinitis