Ann Surg Treat Res.
2016 Dec;91(6):273-277. 10.4174/astr.2016.91.6.273.
Silencing the livin gene enhances the cytotoxic effects of anticancer drugs on colon cancer cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ralee@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2360386
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.91.6.273
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Livin is associated with drug response in several cancers. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of silencing the livin gene expression on anticancer drug response in colorectal cancer.
METHODS
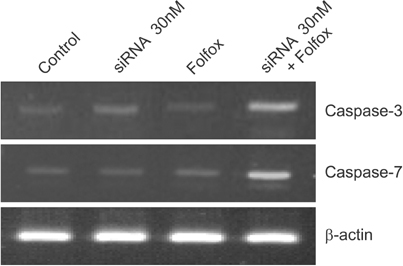
siRNA was transfected at different concentrations (0, 10, and 30nM) into HCT116 cells, then cells were treated with either 5-fluorouracil (FU)/leucovorin (LV) or oxaliplatin (L-OHP)/5-FU/LV. Cellular viability and apoptosis were evaluated following silencing of livin gene expression combined with treatment with anticancer drugs.
RESULTS
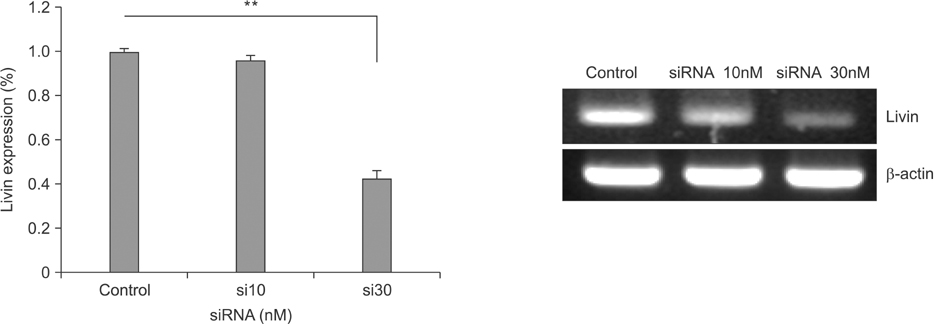
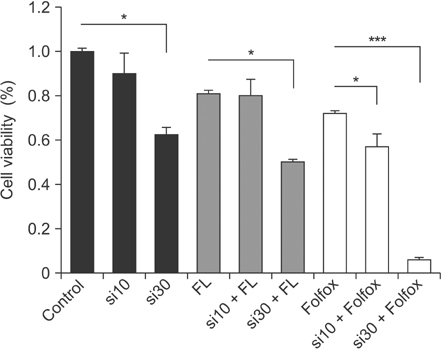
Livin gene expression was effectively suppressed by 30nM siRNA compared with control and 10nM siRNA. The 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay showed that proliferation was effectively inhibited in cells treated with a combination of both siRNA and an anticancer drug, compared to cells treated with siRNA-Livin or anticancer drug alone. In particular, the combination of 30nM siRNA and L-OHP/5-FU/LV resulted in a 93.8% and 91.4% decrease, compared to untreated control or L-OHP/5-FU/LV alone, respectively. Cellular proliferation was most effectively suppressed by a combination of 30nM of siRNA and L-OHP/5-FU/LV compared to other combinations.
CONCLUSION
siRNA-mediated down-regulation of livin gene expression could significantly suppress colon cancer growth and enhance the cytotoxic effects of anticancer drugs such as 5-FU and L-OHP. The results of this study suggest that silencing livin gene expression in combination with treatment with anticancer drugs might be a novel cancer therapy for colorectal cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. de Castro-Carpeno J, Belda-Iniesta C, Casado Saenz E, Hernandez Agudo E, Feliu Batlle J, Gonzalez Baron M. EGFR and colon cancer: a clinical view. Clin Transl Oncol. 2008; 10:6–13.2. Oh SY, Kim DY, Suh KW. Oncologic outcomes following metastasectomy in colorectal cancer patients developing distant metastases after initial treatment. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015; 88:253–259.3. Bremer E, van Dam G, Kroesen BJ, de Leij L, Helfrich W. Targeted induction of apoptosis for cancer therapy: current progress and prospects. Trends Mol Med. 2006; 12:382–393.4. Schimmer AD. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: translating basic knowledge into clinical practice. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:7183–7190.5. Chang H, Schimmer AD. Livin/melanoma inhibitor of apoptosis protein as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of malignancy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007; 6:24–30.6. Oh BY, Lee RA, Kim KH. siRNA targeting Livin decreases tumor in a xenograft model for colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:2563–2571.7. Zhao X, Yuan Y, Zhang Z, Feng X, Zhang J, Yuan X, et al. Effects of shRNA-silenced livin and survivin on lung cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. J BUON. 2014; 19:757–762.8. Wang SL, Deng WT, Wen GF, Li CW, Zeng YJ. Construction of a Hep-2 cell line stably transfected with Livin shRNA. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2016; 117:272–275.9. Liu P, Wang TS, You SH, Ge HM. Expression of livin in gastric cancer and effect of silencing of the livin gene on apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2007; 29:570–574.10. Wang TS, Ding QQ, Guo RH, Shen H, Sun J, Lu KH, et al. Expression of livin in gastric cancer and induction of apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells by shRNA-mediated silencing of livin gene. Biomed Pharmacother. 2010; 64:333–338.11. Wang X, Xu J, Ju S, Ni H, Zhu J, Wang H. Livin gene plays a role in drug resistance of colon cancer cells. Clin Biochem. 2010; 43:655–660.12. Liu Y, Guo Q, Zhang H, Li GH, Feng S, Yu XZ, et al. Effect of siRNA-Livin on drug resistance to chemotherapy in glioma U251 cells and CD133+ stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2015; 10:1317–1323.13. Lazar I, Yaacov B, Shiloach T, Eliahoo E, Kadouri L, Lotem M, et al. The oncolytic activity of Newcastle disease virus NDV-HUJ on chemoresistant primary melanoma cells is dependent on the proapoptotic activity of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein Livin. J Virol. 2010; 84:639–646.14. Sun JG, Liao RX, Zhang SX, Duan YZ, Zhuo WL, Wang XX, et al. Role of inhibitor of apoptosis protein Livin in radiation resistance in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2011; 26:585–592.15. Yu L, Wang Z. Effects of Livin gene RNA interference on apoptosis of cervical cancer HeLa cells and enhanced sensitivity to cisplatin. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2009; 29:625–630.16. Wang R, Lin F, Wang X, Gao P, Dong K, Zou AM, et al. Silencing Livin gene expression to inhibit proliferation and enhance chemosensitivity in tumor cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2008; 15:402–412.17. Crnkovic-Mertens I, Wagener N, Semzow J, Grone EF, Haferkamp A, Hohenfellner M, et al. Targeted inhibition of Livin resensitizes renal cancer cells towards apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007; 64:1137–1144.18. Bavykin AS, Korotaeva AA, Poyarkov SV, Syrtsev AV, Tjulandin SA, Karpukhin AV. Double siRNA-targeting of cIAP2 and LIVIN results in synergetic sensitization of HCT-116 cells to oxaliplatin treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 2013; 6:1333–1340.19. Liu F, Chang H, Xu W, Zhai Y. The effects of Livin shRNA on the response to cisplatin in HepG2 cells. Oncol Lett. 2015; 10:2957–2961.20. Kasof GM, Gomes BC. Livin, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis protein family member. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:3238–3246.21. Wang L, Zhang Q, Liu B, Han M, Shan B. Challenge and promise: roles for Livin in progression and therapy of cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008; 7:3661–3669.22. Ryther RC, Flynt AS, Phillips JA 3rd, Patton JG. siRNA therapeutics: big potential from small RNAs. Gene Ther. 2005; 12:5–11.23. Park DG. Antichemosensitizing effect of resveratrol in cotreatment with oxaliplatin in HCT116 colon cancer cell. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2014; 86:68–75.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of p53 and p38 MAPK on Doxorubicin and Lovastatin-induced Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells
- Enhancement of Cytotoxicity by the Combination of Anticancer Drugs in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Line (PC-14)
- Epigenetic Silencing of MORT Is an Early Event in Cancer and Is Associated with Luminal, Receptor Positive Breast Tumor Subtypes
- Differential cytotoxic effects of fenbendazole on mouse lymphoma EL-4 cells and spleen cells
- Gene Expression Changes of Drug-resistant Saos-2 Cells Induced by Anticancer Drug