J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Feb;31(2):183-189. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.183.
Clinical Evaluation of Rapid Diagnostic Test Kit Using the Polysaccharide as a Genus-Specific Diagnostic Antigen for Leptospirosis in Korea, Bulgaria, and Argentina
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. ywkim@hallym.ac.kr
- 2National Reference Vector-borne Infections Laboratory, National Center of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases, Bulgaria.
- 3Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias, Santa Fe, Argentina.
- KMID: 2360040
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.183
Abstract
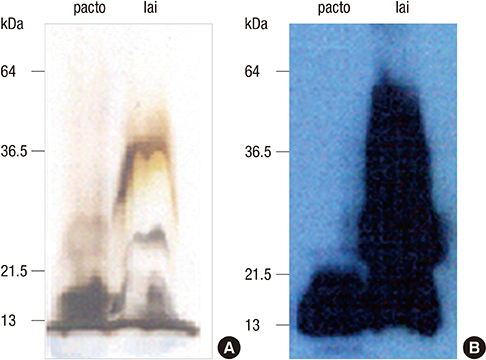
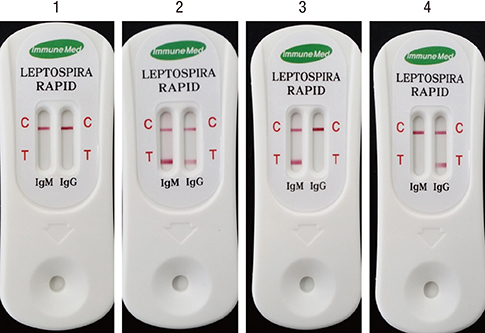
- Leptospirosis, a zoonotic disease that is caused by many serovars which are more than 200 in the world, is an emerging worldwide disease. Accurate and rapid diagnostic tests for leptospirosis are a critical step to diagnose the disease. There are some commercial kits available for diagnosis of leptospirosis, but the obscurity of a species- or genus-specific antigen of pathogenic Leptospira interrogans causes the reduced sensitivity and specificity. In this study, the polysaccharide derived from lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of nonpathogenic Leptospira biflexa serovar patoc was prepared, and the antigenicity was confirmed by immunoblot and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The performance of the rapid diagnostic test (RDT) kit using the polysaccharide as a diagnostic antigen was evaluated in Korea, Bulgaria and Argentina. The sensitivity was 93.9%, 100%, and 81.0% and the specificity was 97.9%, 100%, and 95.4% in Korea (which is a rare region occurring with 2 serovars mostly), Bulgaria (epidemic region with 3 serovars chiefly) and Argentina (endemic region with 19 serovars mainly) respectively. These results indicate that this RDT is applicable for global diagnosis of leptospirosis. This rapid and effective diagnosis will be helpful for diagnosis and manage of leptospirosis to use and the polysaccharide of Leptospira may be called as genus specific antigen for diagnosis.
MeSH Terms
-
Antigens, Bacterial/*immunology
Argentina
Bulgaria
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Female
Humans
Leptospira/isolation & purification/metabolism
Leptospira interrogans/isolation & purification/metabolism
Leptospirosis/*diagnosis/microbiology
Male
Polysaccharides/*immunology
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic/*standards
Republic of Korea
Sensitivity and Specificity
Antigens, Bacterial
Polysaccharides
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, Levett PN, Gilman RH, Willig MR, Gotuzzo E, et al. Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003; 3:757–771.2. Barnett JK, Barnett D, Bolin CA, Summers TA, Wagar EA, Cheville NF, Hartskeerl RA, Haake DA. Expression and distribution of leptospiral outer membrane components during renal infection of hamsters. Infect Immun. 1999; 67:853–861.3. Dey S, Mohan CM, Ramadass P, Nachimuthu K. Diagnosis of leptospirosis by recombinant antigen based single serum dilution ELISA. Indian J Med Res. 2008; 128:172–177.4. Chaudhry R, Das A, Premlatha MM, Choudhary A, Chourasia BK, Chandel DS, Dey AB. Serological & molecular approaches for diagnosis of leptospirosis in a tertiary care hospital in north India: a 10-year study. Indian J Med Res. 2013; 137:785–790.5. Cinco M. New insights into the pathogenicity of leptospires: evasion of host defences. New Microbiol. 2010; 33:283–292.6. Levett PN. Leptospirosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001; 14:296–326.7. Laras K, Cao BV, Bounlu K, Nguyen TK, Olson JG, Thongchanh S, Tran NV, Hoang KL, Punjabi N, Ha BK, et al. The importance of leptospirosis in Southeast Asia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002; 67:278–286.8. World Health Organization. International Leptospirosis Society. Human leptospirosis: guidance for diagnosis, surveillance and control. Geneva: World Health Organization;2003.9. Dias JP, Teixeira MG, Costa MC, Mendes CM, Guimarães P, Reis MG, Ko A, Barreto ML. Factors associated with Leptospira sp infection in a large urban center in northeastern Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2007; 40:499–504.10. Victoriano AF, Smythe LD, Gloriani-Barzaga N, Cavinta LL, Kasai T, Limpakarnjanarat K, Ong BL, Gongal G, Hall J, Coulombe CA, et al. Leptospirosis in the Asia Pacific region. BMC Infect Dis. 2009; 9:147.11. Tappero JW, Ashford DA, Perkins BA. Leptospira species (leptospirosis). In : Mendell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone;2000. p. 2495–2501.12. Cole JR Jr, Sulzer CR, Pursell AR. Improved microtechnique for the leptospiral microscopic agglutination test. Appl Microbiol. 1973; 25:976–980.13. Goris MG, Leeflang MM, Loden M, Wagenaar JF, Klatser PR, Hartskeerl RA, Boer KR. Prospective evaluation of three rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosis of human leptospirosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013; 7:e2290.14. Park KH, Choi YJ, Shin SH, Choi MK, Kim YW, Jang WJ. Identification of Leptospira species of Korean isolates using phylogenetic analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified 16S rDNA and LipL32 genes. J Bacteriol Virol. 2014; 44:59–66.15. McBride AJ, Santos BL, Queiroz A, Santos AC, Hartskeerl RA, Reis MG, Ko AI. Evaluation of four whole-cell Leptospira-based serological tests for diagnosis of urban leptospirosis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007; 14:1245–1248.16. Cho MK, Lee JH, Yoon CS, Kim YW, Min CH, Kim YS, Park KS, Oh HB. Serological analysis of Leptospira interrogans isolated in Korea using monoclonal antibodies and cross-agglutinin absorption test. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1989; 24:539–548.17. Christova I, Tasseva E, Manev H. Human leptospirosis in Bulgaria, 1989-2001: epidemiological, clinical, and serological features. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003; 35:869–872.18. Seijo A, Coto H, San Juan J, Videla J, Deodato B, Cernigoi B, Messina OG, Collia O, de Bassadoni D, Schtirbu R, et al. Lethal leptospiral pulmonary hemorrhage: an emerging disease in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002; 8:1004–1005.19. Liu D. Molecular detection of human bacterial pathogens. Boca Raton, FL: CRC press;2011.20. Byun YH, Chang IA, Cho MK, Chun JM, Kim IS, Kim WC, Kim YW, Kim YJ, Woo SD. Diagnostic formulation for tsutsugamushi disease. Korean Patent, WO 2008029981 A1. 2008. Mar. 13.21. Singh N, Mishra AK, Shukla MM, Chand SK, Bharti PK. Diagnostic and prognostic utility of an inexpensive rapid on site malaria diagnostic test (ParaHIT f) among ethnic tribal population in areas of high, low and no transmission in central India. BMC Infect Dis. 2005; 5:50.22. Matsuo K, Isogai E, Araki Y. Occurrence of [→3)-β-d-Manp-(1→4)-β-d-Manp-(1→]n units in the antigenic polysaccharides from Leptospira biflexa serovar patoc strain Patoc I. Carbohydr Res. 2000; 328:517–524.23. Yanagihara Y, Kamisango K, Takeda K, Mifuchi I, Azuma I. Identification of 4-O-methylmannose in cell wall polysaccharide of Leptospira. Microbiol Immunol. 1983; 27:711–715.24. Goris MG, Leeflang MM, Boer KR, Goeijenbier M, van Gorp EC, Wagenaar JF, Hartskeerl RA. Establishment of valid laboratory case definition for human leptospirosis. J Bacteriol Parasitol. 2012; 3:1000132.25. Zochowski WJ, Palmer MF, Coleman TJ. An evaluation of three commercial kits for use as screening methods for the detection of leptospiral antibodies in the UK. J Clin Pathol. 2001; 54:25–30.26. Caimi K, Varni V, Melendez Y, Koval A, Brihuega B, Ruybal P. A combined approach of VNTR and MLST analysis: improving molecular typing of Argentinean isolates of Leptospira interrogans. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012; 107:644–651.27. Goarant C, Bourhy P, D'Ortenzio E, Dartevelle S, Mauron C, Soupé-Gilbert ME, Bruyère-Ostells L, Gourinat AC, Picardeau M, Nato F, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of a new vertical flow rapid diagnostic test for the serodiagnosis of human leptospirosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013; 7:e2289.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of a Commercial Immuno-Chromatographic Assay Kit for Rapid Detection of IgM Antibodies against Leptospira Antigen in Human Serum
- Evaluation of COVID-19 Biokit IgG/IgM Clinical Effectiveness in COVID-19 Vaccinated Individuals
- Clinical evaluation of a rapid diagnostic test kit for detection of canine coronavirus
- Efficacy of the Troponin T Rapid Assay Kit in Early Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Response to positive patients with COVID-19 self-test visiting the emergency department