Association of Dysphagia With Supratentorial Lesions in Patients With Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine & Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. leej@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Konkuk University School of Medicine & Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2356649
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.4.637
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine the supratentorial area associated with poststroke dysphagia, we assessed the diffusion tensor images (DTI) in subacute stroke patients with supratentorial lesions.
METHODS
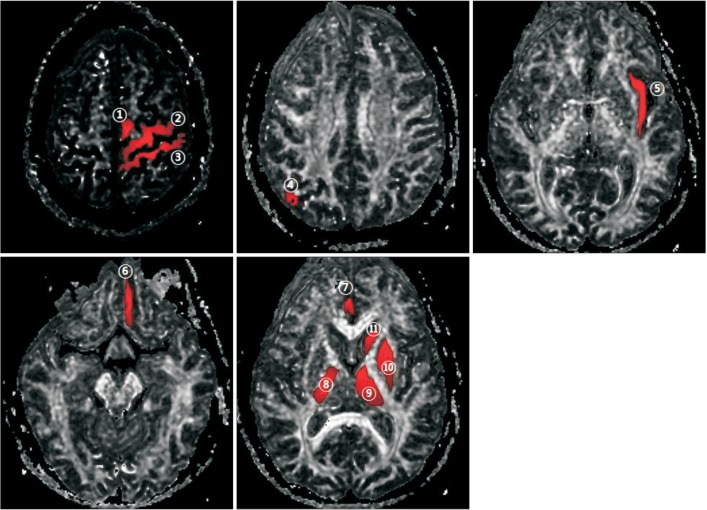
We included 31 patients with a first episode of infarction in the middle cerebral artery territory. Each subject underwent brain DTI as well as a videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) and patients divided were into the dysphagia and non-dysphagia groups. Clinical dysphagia scale (CDS) scores were compared between the two groups. The corticospinal tract volume (TV), fractional anisotropy (FA) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values were calculated for 11 regions of interest in the supratentorial area"”primary motor cortex, primary somatosensory cortex, supplementary motor cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, parieto-occipital cortex, insular cortex, posterior limb of the internal capsule, thalamus, and basal ganglia (putamen and caudate nucleus). DTI parameters were compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
Among the 31 subjects, 17 were diagnosed with dysphagia by VFSS. Mean TVs were similar across the two groups. Significant inter-group differences were observed in two DTI values: the FA value in the contra-lesional primary motor cortex and the ADC value in the bilateral posterior limbs of the internal capsule (all p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
The FA value in the primary motor cortex on the contra-lesional side and the ADC value in the bilateral PLIC can be associated with dysphagia in middle cerebral artery stroke.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Association of Brain Lesions and Videofluoroscopic Dysphagia Scale Parameters on Patients With Acute Cerebral Infarctions
Sang Jun Mo, Ho Joong Jeong, Yong Hyun Han, Kihun Hwang, Jong Kyoung Choi
Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(4):560-568. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.560.Comparison of Dysphagia Between Infratentorial and Supratentorial Stroke Patients
Yong Kyun Kim, Jung Hyun Cha, Kyun Yeon Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2019;43(2):149-155. doi: 10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.149.Association Between Duration of Dysphagia Recovery and Lesion Location on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients With Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction
Jae Ho Kim, Se Hyun Oh, Ho Joong Jeong, Young Joo Sim, Dung Gyu Kim, Ghi Chan Kim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2019;43(2):142-148. doi: 10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.142.
Reference
-
1. Alberts MJ, Horner-Catt J. Dysphagia and aspiration syndromes. In : Bogousslavsky J, Caplan L, editors. Stroke syndrome. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press;1995. p. 213–222.2. Gordon C, Hewer RL, Wade DT. Dysphagia in acute stroke. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987; 295:411–414.
Article3. Mann G, Hankey GJ, Cameron D. Swallowing function after stroke: prognosis and prognostic factors at 6 months. Stroke. 1999; 30:744–748. PMID: 10187872.4. Gonzalez-Fernandez M, Kleinman JT, Ky PK, Palmer JB, Hillis AE. Supratentorial regions of acute ischemia associated with clinically important swallowing disorders: a pilot study. Stroke. 2008; 39:3022–3028. PMID: 18688014.5. Mori S, Wakana S, Nagae-Poetscher LM, Van Zijl PC. MRI atlas of human white matter. Amsterdam: Elsevier;2005. p. 1–31.6. Basser PJ, Jones DK. Diffusion-tensor MRI: theory, experimental design and data analysis: a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002; 15:456–467. PMID: 12489095.7. Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR Biomed. 1995; 8:333–344. PMID: 8739270.
Article8. Mori S, Zhang J. Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its applications to basic neuroscience research. Neuron. 2006; 51:527–539. PMID: 16950152.
Article9. Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, Di Chiro G. Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology. 1996; 201:637–648. PMID: 8939209.
Article10. Beaulieu C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system: a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002; 15:435–455. PMID: 12489094.11. Granziera C, D'Arceuil H, Zai L, Magistretti PJ, Sorensen AG, de Crespigny AJ. Long-term monitoring of post-stroke plasticity after transient cerebral ischemia in mice using in vivo and ex vivo diffusion tensor MRI. Open Neuroimag J. 2007; 1:10–17. PMID: 19018310.
Article12. van der Steen JT, Ooms ME, Mehr DR, van der Wal G, Ribbe MW. Severe dementia and adverse outcomes of nursing home-acquired pneumonia: evidence for mediation by functional and pathophysiological decline. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50:439–448. PMID: 11943038.
Article13. Buchholz D. Neurologic causes of dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1987; 1:152–156.
Article14. Robbins JA, Logemann JA, Kirshner HS. Swallowing and speech production in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1986; 19:283–287. PMID: 3963773.
Article15. Kim H, Na DL. Normative data on the Korean version of the Western Aphasia Battery. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2004; 26:1011–1020. PMID: 15590457.
Article16. Schenkenberg T, Bradford DC, Ajax ET. Line bisection and unilateral visual neglect in patients with neurologic impairment. Neurology. 1980; 30:509–517. PMID: 7189256.
Article18. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW, Lee EK, Park MS. Standardization of dysphagia diet. Korean J Stroke. 2000; 2:191–195.19. Jung SH, Lee KJ, Hong JB, Han TR. Validation of clinical dysphagia scale: based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005; 29:343–350.20. Lee JS, Han MK, Kim SH, Kwon OK, Kim JH. Fiber tracking by diffusion tensor imaging in corticospinal tract stroke: topographical correlation with clinical symptoms. Neuroimage. 2005; 26:771–776. PMID: 15955486.
Article21. Jang SH. Somatotopic arrangement and location of the corticospinal tract in the brainstem of the human brain. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:553–557. PMID: 21623594.
Article22. Broadley S, Croser D, Cottrell J, Creevy M, Teo E, Yiu D, et al. Predictors of prolonged dysphagia following acute stroke. J Clin Neurosci. 2003; 10:300–305. PMID: 12763332.
Article23. Carnaby G, Hankey GJ, Pizzi J. Behavioural intervention for dysphagia in acute stroke: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:31–37. PMID: 16361020.
Article24. Horner J, Massey EW, Riski JE, Lathrop DL, Chase KN. Aspiration following stroke: clinical correlates and outcome. Neurology. 1988; 38:1359–1362. PMID: 3412582.
Article25. Kern MK, Jaradeh S, Arndorfer RC, Shaker R. Cerebral cortical representation of reflexive and volitional swallowing in humans. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001; 280:G354–G360. PMID: 11171617.
Article26. Hamdy S, Aziz Q, Rothwell JC, Singh KD, Barlow J, Hughes DG, et al. The cortical topography of human swallowing musculature in health and disease. Nat Med. 1996; 2:1217–1224. PMID: 8898748.
Article27. Mosier KM, Liu WC, Maldjian JA, Shah R, Modi B. Lateralization of cortical function in swallowing: a functional MR imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:1520–1526. PMID: 10512240.28. Daniels SK, Foundas AL. The role of the insular cortex in dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1997; 12:146–156. PMID: 9190100.
Article29. Meguro K, Constans JM, Courtheoux P, Theron J, Viader F, Yamadori A. Atrophy of the corpus callosum correlates with white matter lesions in patients with cerebral ischaemia. Neuroradiology. 2000; 42:413–419. PMID: 10929300.
Article30. Buchkremer-Ratzmann I, August M, Hagemann G, Witte OW. Electrophysiological transcortical diaschisis after cortical photothrombosis in rat brain. Stroke. 1996; 27:1105–1111. PMID: 8650722.
Article31. Witte OW, Stoll G. Delayed and remote effects of focal cortical infarctions: secondary damage and reactive plasticity. Adv Neurol. 1997; 73:207–227. PMID: 8959216.32. Andrews RJ. Transhemispheric diaschisis: a review and comment. Stroke. 1991; 22:943–949. PMID: 1853416.
Article33. Dobkin JA, Levine RL, Lagreze HL, Dulli DA, Nickles RJ, Rowe BR. Evidence for transhemispheric diaschisis in unilateral stroke. Arch Neurol. 1989; 46:1333–1336. PMID: 2590018.
Article34. Buffon F, Molko N, Herve D, Porcher R, Denghien I, Pappata S, et al. Longitudinal diffusion changes in cerebral hemispheres after MCA infarcts. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005; 25:641–650. PMID: 15689956.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lesion Characteristics of Chronic Dysphagia in Patients With Supratentorial Stroke
- Comparison of Dysphagia Between Infratentorial and Supratentorial Stroke Patients
- A Case Report Hemiparesis Caused by Ipsilateral Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction
- Intracranial Cerebrovascular Revascularization(Extracranial-Intracranial Arterial Bypass, EIAB)
- A Case of Right Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction with Quadriparesis