Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Apr;43(2):149-155. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.149.
Comparison of Dysphagia Between Infratentorial and Supratentorial Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea. uraneky@gmail.com
- KMID: 2448997
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.149
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare dysphagia between infratentorial stroke patients and supratentorial stroke patients.
METHODS
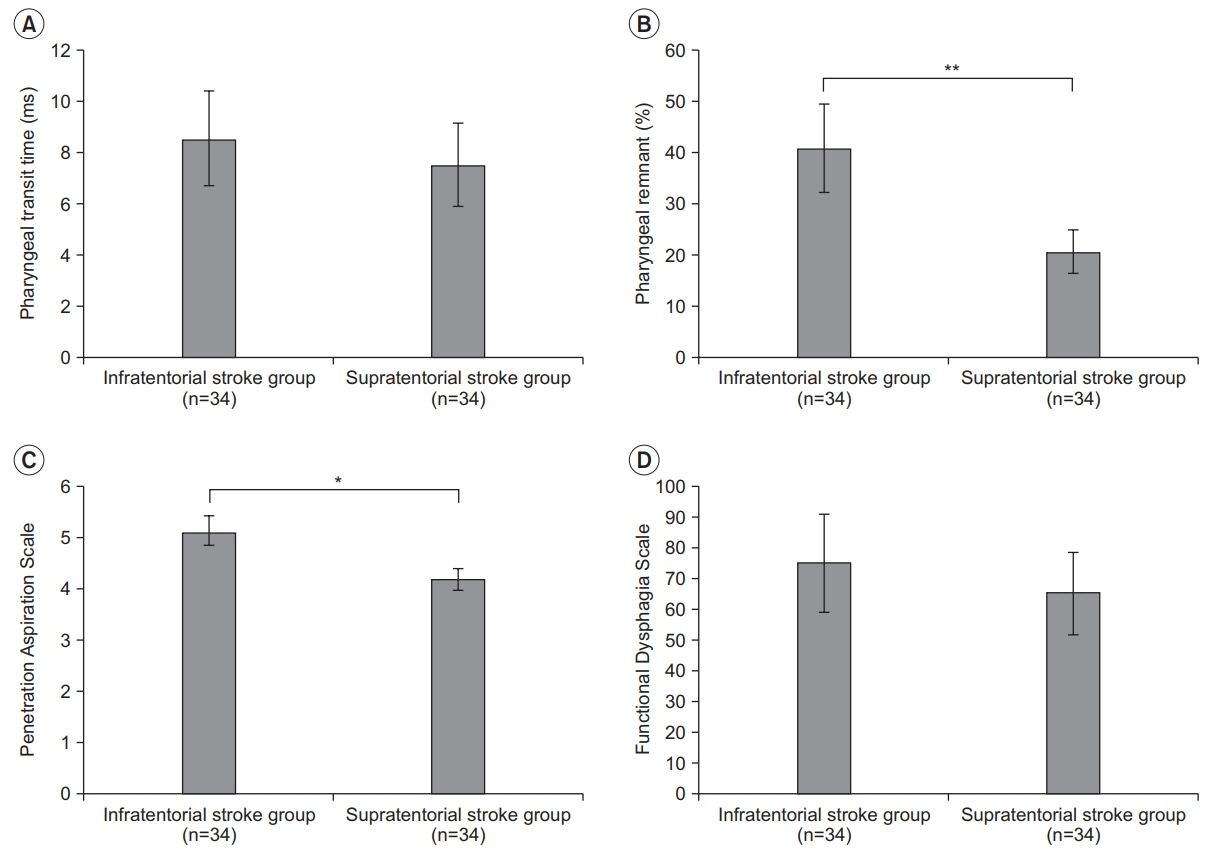
Subjects of this study were patients with post-stroke dysphagia (PSD) who were admitted to our medical institution between May 2014 and June 2017. We evaluated a total of 64 patients with PSD. A videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) was performed to determine dysphagia severity. We measured the following parameters: pharyngeal transit time (PTT), post-swallow pharyngeal remnant, Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) scores, and Functional Dysphagia Scale (FDS). We analyzed patient's results from VFSS performed at admission. All VFSS images were recorded using a camcorder running at 30 frames per second. An AutoCAD 2D screen was used to measure post-swallow pharyngeal remnant.
RESULTS
In this study, PTT and FDS were similar (p>0.05) between infratentorial stroke patients and supratentorial stroke patients. However, there were significant differences in pharyngeal remnant and PAS scores between the two groups (p<0.01 and p<0.05, respectively).
CONCLUSION
Both pharyngeal remnant and PAS score registered higher levels from VFSS test for infratentorial stroke patients than those for supratentorial stroke patients. This suggests greater chances of problems occurring with swallowing, the major functions of pons. Thus, clinicians should pay particular attention to active dysphagia evaluation and treatment in PSD of infratentorial stroke patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arnold M, Liesirova K, Broeg-Morvay A, Meisterernst J, Schlager M, Mono ML, et al. Dysphagia in acute stroke: incidence, burden and impact on clinical outcome. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0148424.
Article2. Gonzalez-Fernandez M, Ottenstein L, Atanelov L, Christian AB. Dysphagia after stroke: an overview. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2013; 1:187–96.
Article3. Kim BR, Moon WJ, Kim H, Jung E, Lee J. Association of dysphagia with supratentorial lesions in patients with middle cerebral artery stroke. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016; 40:637–46.
Article4. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. Quantifying swallowing function after stroke: a functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:677–82.
Article5. Kameda W, Kawanami T, Kurita K, Daimon M, Kayama T, Hosoya T, et al. Lateral and medial medullary infarction: a comparative analysis of 214 patients. Stroke. 2004; 35:694–9.6. Marik PE, Kaplan D. Aspiration pneumonia and dysphagia in the elderly. Chest. 2003; 124:328–36.
Article7. Sharma JC, Fletcher S, Vassallo M, Ross I. What influences outcome of stroke: pyrexia or dysphagia? Int J Clin Pract. 2001; 55:17–20.8. Suntrup S, Kemmling A, Warnecke T, Hamacher C, Oelenberg S, Niederstadt T, et al. The impact of lesion location on dysphagia incidence, pattern and complications in acute stroke. Part 1: dysphagia incidence, severity and aspiration. Eur J Neurol. 2015; 22:832–8.
Article9. Meng NH, Wang TG, Lien IN. Dysphagia in patients with brainstem stroke: incidence and outcome. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2000; 79:170–5.10. Horner J, Buoyer FG, Alberts MJ, Helms MJ. Dysphagia following brain-stem stroke: clinical correlates and outcome. Arch Neurol. 1991; 48:1170–3.11. Kim YK, Choi SS, Choi JH, Yoon JG. Effectiveness of rehabilitative balloon swallowing treatment on upper esophageal sphincter relaxation and pharyngeal motility for neurogenic dysphagia. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015; 39:524–34.
Article12. Kim JC, Kim JS, Jung JH, Kim YK. The effect of balloon dilatation through video-fluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) in stroke patients with cricopharyngeal dysfunction. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:23–6.13. McHorney CA, Robbins J, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, et al. The SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcomes tool for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults. III. Documentation of reliability and validity. Dysphagia. 2002; 17:97–114.
Article14. Martin-Harris B, Brodsky MB, Michel Y, Ford CL, Walters B, Heffner J. Breathing and swallowing dynamics across the adult lifespan. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005; 131:762–70.
Article15. Singh S, Hamdy S. Dysphagia in stroke patients. Postgrad Med J. 2006; 82:383–91.
Article16. Sue Eisenstadt E. Dysphagia and aspiration pneumonia in older adults. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2010; 22:17–22.
Article17. Paik NJ, Kim IS, Kim JH, Oh BM, Han TR. Clinical validity of the functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005; 29:43–9.18. Park CH, Kim DK, Lee YT, Yi Y, Lee JS, Kim K, et al. Quantitative analysis of swallowing function between dysphagia patients and healthy subjects using highresolution manometry. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017; 41:776–85.
Article19. Kim Y, Park T, Oommen E, McCullough G. Upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallow in stroke survivors. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015; 94:734–9.
Article20. Lee H, Chung H, Lee TH, Hong KS, Youn YH, et al. Therapeutic outcome of achalasia based on high-resolution manometry: a Korean multicenter study. Am J Ther. 2017; Sep. 11. [Epub]. http://doi.org/10.1097/MJT.0000000000000677 .
Article21. Daniels SK, Pathak S, Mukhi SV, Stach CB, Morgan RO, Anderson JA. The relationship between lesion localization and dysphagia in acute stroke. Dysphagia. 2017; 32:777–84.
Article22. Yuan MZ, Li F, Fang Q, Wang W, Peng JJ, Qin DY, et al. Research on the cause of death for severe stroke patients. J Clin Nurs. 2018; 27:450–60.
Article23. Steele CM, Grace-Martin K. Reflections on clinical and statistical use of the penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 2017; 32:601–16.
Article24. Kiyokawa J, Yamaguchi K, Okada R, Maehara T, Akita K. Origin, course and distribution of the nerves to the posterosuperior wall of the external acoustic meatus. Anat Sci Int. 2014; 89:238–45.
Article25. Perie S, Coiffier L, Laccourreye L, Hazebroucq V, Chaussade S, St Guily JL. Swallowing disorders in paralysis of the lower cranial nerves: a functional analysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999; 108:606–11.
Article26. Malandraki GA, Sutton BP, Perlman AL, Karampinos DC, Conway C. Neural activation of swallowing and swallowing-related tasks in healthy young adults: an attempt to separate the components of deglutition. Hum Brain Mapp. 2009; 30:3209–26.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Swallowing Functions Between Brain Tumor and Stroke Patients
- Epidemiology, Natural Recovery, Long-term Outcome of Post Stroke Dysphagia
- Lesion Characteristics of Chronic Dysphagia in Patients With Supratentorial Stroke
- Characteristics of Dizziness in Supratentorial Infarctions
- Relationship Between Cognitive Function and Dysphagia After Stroke