Clin Nutr Res.
2016 Oct;5(4):237-248. 10.7762/cnr.2016.5.4.237.
Effects of Activity-Based Personalized Nutrition Education on Dietary Behaviors and Blood Parameters in Middle-Aged and Older Type 2 Diabetes Korean Outpatients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Program of Clinical Nutrition, Graduate School of Human Environmental Sciences, Yonsei University, Seoul 03722, Korea. leeseungmin@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Severance Institute for Vascular and Metabolic Research, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul 03722, Korea.
- 3Department of Food and Nutrition, College of Human Ecology, Yonsei University, Seoul 03722, Korea.
- KMID: 2355296
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2016.5.4.237
Abstract
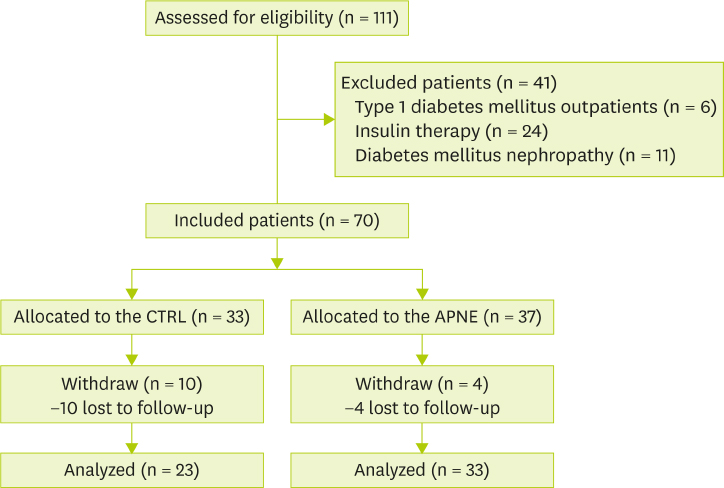
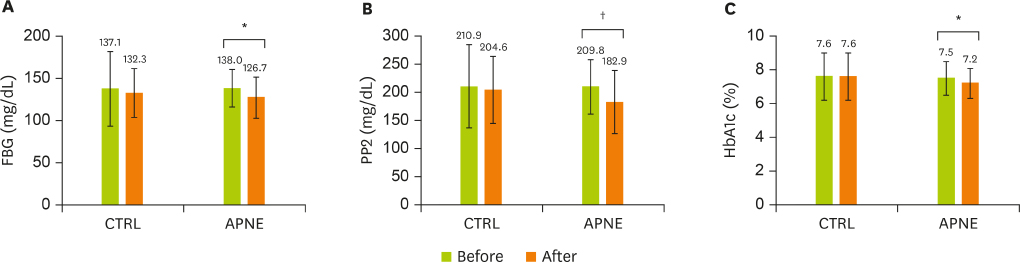
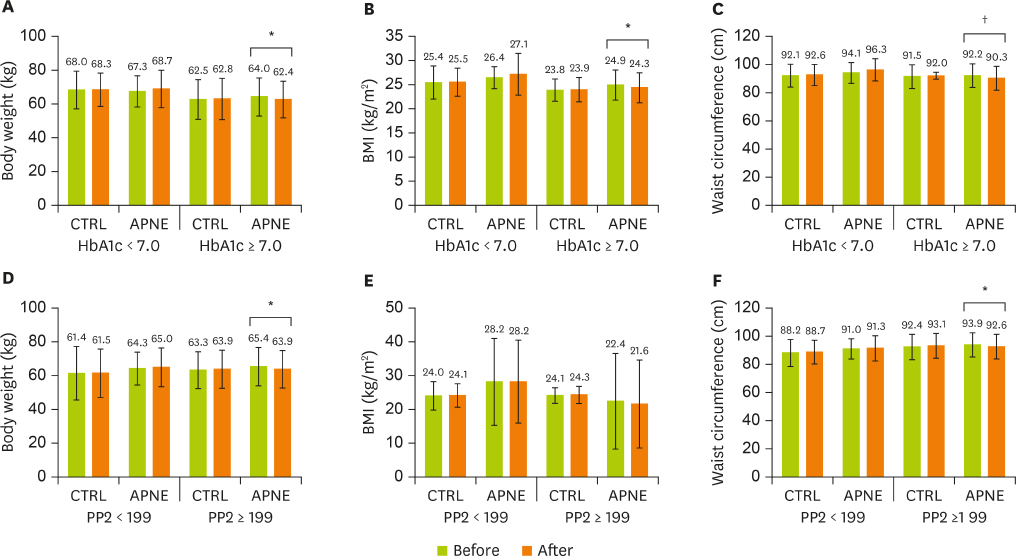
- This study aimed to compare the effects of activity-based personalized nutrition education (APNE) with a general instruction for diabetes (control, CTRL) in middle-aged and older Korean outpatients with type 2 diabetes. After an initial screening, 70 subjects were randomly assigned to APNE (n = 37) or CTRL (n = 33) group. APNE considered each patient's anthropometry, blood chemistry data, and dietary habits in addition to planning meal choices with the aid of registered dietitians. After 3 months, dietary behavior, food intake, and anthropometric and blood measurement results were evaluated. Fasting blood glucose, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, and glycated hemoglobin levels decreased in the APNE group (n = 33) but not in the CTRL group (n = 23). In the APNE group, the meal intervals and number of days of consuming high-fat food were decreased, while the number of days following a meal plan and balanced diet that entailed consuming fruits, vegetables, and healthy food was increased. A lower consumption of carbohydrates, saccharides, grains, and tuber crops and a higher protein, pulses, and fat-derived calorie intake compared with the initial values were observed in the APNE group. In contrast, only the number of days following the meal plan and balanced diet was increased in the CRTL group, without significantly changing the individual macronutrient-derived calorie intake. The APNE approach appeared to effectively educate outpatients with type 2 diabetes about changing their dietary behavior and food intake and improving the clinical parameters related to diabetic conditions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Status and Effects of Dining with Diabetes in Korea and Abroad
Seung Hye Yang
J Korean Diabetes. 2017;18(2):117-120. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2017.18.2.117.
Reference
-
1. Puavilai G, Chanprasertyotin S, Sriphrapradaeng A. Diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance: 1997 criteria by the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (ADA), 1998 WHO consultation criteria, and 1985 WHO criteria. World Health Organization. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1999; 44:21–26.
Article2. DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care. 1992; 15:318–368.
Article3. Toyama K, Neriishi S, Kawamoto S, Kato H, Miyake S, Nagataki S. Risk factors of cerebro-cardiovascular disorders in mild diabetes. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1983; 141:Suppl. 535–540.
Article4. King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:1414–1431.
Article5. Kim CS, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim NH, Kim JH, Lim S, Choi SH, Song KH, Won JC, Kim DJ, Cha BY; Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Prevalence, awareness, and management of obesity in Korea: data from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (1998-2011). Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:35–43.
Article6. Swanson CM, Bersoux S, Larson MH, Aponte-Furlow RT, Flatten SS, Olsen CL, LaRosa C, Verona PM, Jameson KA, Cook CB. An outpatient-based clinical program for diabetes prevention: an update. Endocr Pract. 2012; 18:200–208.
Article7. Ratner RE; Diabetes Prevention Program Research. An update on the diabetes prevention program. Endocr Pract. 2006; 12:Suppl 1. 20–24.
Article8. Norris SL, Lau J, Smith SJ, Schmid CH, Engelgau MM. Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of the effect on glycemic control. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1159–1171.9. Chodosh J, Morton SC, Mojica W, Maglione M, Suttorp MJ, Hilton L, Rhodes S, Shekelle P. Meta-analysis: chronic disease self-management programs for older adults. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 143:427–438.
Article10. Kargar Jahromi M, Ramezanli S, Taheri L. Effectiveness of diabetes self-management education on quality of life in diabetic elderly females. Glob J Health Sci. 2014; 7:10–15.
Article11. Ricci-Cabello I, Ruiz-Pérez I, Rojas-García A, Pastor G, Rodríguez-Barranco M, Gonçalves DC. Characteristics and effectiveness of diabetes self-management educational programs targeted to racial/ethnic minority groups: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. BMC Endocr Disord. 2014; 14:60.
Article12. Haas L, Maryniuk M, Beck J, Cox CE, Duker P, Edwards L, Fisher EB, Hanson L, Kent D, Kolb L, McLaughlin S, Orzeck E, Piette JD, Rhinehart AS, Rothman R, Sklaroff S, Tomky D, Youssef G. 2012 Standards Revision Task Force. National standards for diabetes self-management education and support. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:Suppl 1. S144–53.13. Funnell MM, Brown TL, Childs BP, Haas LB, Hosey GM, Jensen B, Maryniuk M, Peyrot M, Piette JD, Reader D, Siminerio LM, Weinger K, Weiss MA. National standards for diabetes self-management education. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:Suppl 1. S101–8.
Article14. Lemon CC, Lacey K, Lohse B, Hubacher DO, Klawitter B, Palta M. Outcomes monitoring of health, behavior, and quality of life after nutrition intervention in adults with type 2 diabetes. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004; 104:1805–1815.
Article15. Franz MJ, Monk A, Barry B, McClain K, Weaver T, Cooper N, Upham P, Bergenstal R, Mazze RS. Effectiveness of medical nutrition therapy provided by dietitians in the management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995; 95:1009–1017.
Article16. Brown SA. Interventions to promote diabetes self-management: state of the science. Diabetes Educ. 1999; 25:52–61.
Article17. Woo YJ, Lee HS, Kim WY. Individual diabetes nutrition education can help management for type II diabetes. Korean J Nutr. 2006; 39:641–648.18. Kim HS, Shim KH. Effect of a diabetic camp program on the fasting blood sugar level in type 2 diabetic patients. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 1999; 11:477–483.19. Lee HY. The effect of a diabetic group teaching program. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1993; 23:170–186.
Article20. Miller NH. Compliance with treatment regimens in chronic asymptomatic diseases. Am J Med. 1997; 102:43–49.
Article21. Song O, Park HY, Yoo HJ, Yoon YG. Analysis of group diabetes education in Korea. J Korean Diet Assoc. 1988; 12:201–206.22. Kim TK, Kang YE, Kim JM, Hong WJ, Kim KS, Kim HJ, Kim YK, Ku BJ. Effects of diabetic camp in type 2 diabetic patients. Korean J Med. 2012; 83:210–215.
Article23. American Association of Diabetes Educators. AADE position statement. Individualization of diabetes self-management education. Diabetes Educ. 2007; 33:45–49.24. Toobert DJ, Hampson SE, Glasgow RE. The summary of diabetes self-care activities measure: results from 7 studies and a revised scale. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:943–950.
Article25. Choi EJ, Nam M, Kim SH, Park CG, Toobert DJ, Yoo JS, Chu SH. Psychometric properties of a Korean version of the summary of diabetes self-care activities measure. Int J Nurs Stud. 2011; 48:333–337.
Article26. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care for patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:Suppl 1. S33–50.27. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim J, Kim DJ. Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998-2005. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:2016–2020.28. Koro CE, Bowlin SJ, Bourgeois N, Fedder DO. Glycemic control from 1988 to 2000 among U.S. adults diagnosed with type 2 diabetes: a preliminary report. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:17–20.
Article29. Kim SH, Lee SJ, Kang ES, Kang S, Hur KY, Lee HJ, Ahn CW, Cha BS, Yoo JS, Lee HC. Effects of lifestyle modification on metabolic parameters and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2006; 55:1053–1059.
Article30. Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hämäläinen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, Salminen V, Uusitupa M; Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1343–1350.
Article31. Chuang LM, Tsai ST, Huang BY, Tai TY; Diabcare-Asia 1998 Study Group. The status of diabetes control in Asia--a cross-sectional survey of 24 317 patients with diabetes mellitus in 1998. Diabet Med. 2002; 19:978–985.
Article32. Anderson JW, Kendall CW, Jenkins DJ. Importance of weight management in type 2 diabetes: review with meta-analysis of clinical studies. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003; 22:331–339.
Article33. Klein S, Sheard NF, Pi-Sunyer X, Daly A, Wylie-Rosett J, Kulkarni K, Clark NG; American Diabetes Association. North American Association for the Study of Obesity; American Society for Clinical Nutrition. Weight management through lifestyle modification for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: rationale and strategies: a statement of the American Diabetes Association, the North American Association for the Study of Obesity, and the American Society for Clinical Nutrition. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:2067–2073.
Article34. Yoshida Y, Hashimoto N, Tokuyama Y, Kitagawa H, Takahashi K, Yagui K, Kanatsuka A, Bujo H, Higurashi M, Miyazawa S, Yoshida S, Saito Y. Effects of weight loss in obese subjects with normal fasting plasma glucose or impaired glucose tolerance on insulin release and insulin resistance according to a minimal model analysis. Metabolism. 2004; 53:1095–1100.
Article35. Williams KV, Mullen ML, Kelley DE, Wing RR. The effect of short periods of caloric restriction on weight loss and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:2–8.
Article36. Wing RR. Behavioral treatment of obesity. Its application to type II diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1993; 16:193–199.
Article37. Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, Nathan DM; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:393–403.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Nutrition Education for Diabetes Mellitus Management of Older Adults
- A Factor Analysis Study on Blood Glucose Control in Diabetics Mellitus Patients(1):Focus on Blood Glucose Control and Lifestyle Factors
- A Study on Dietary Habits, Dietary Behaviors and Body Image Recognition of Nutrition Knowledge after Nutrition Education for Obese Children in Seoul
- Effects of Nutrition Education on Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitudes, and Food Behavior of College Students
- Coaching for Self-Management of Diabetes in Medical Nutrition Therapy